In today’s data-driven world, the demand for faster, more efficient network connectivity continues to skyrocket. At the heart of this revolution lies optical transceiver module technology, a critical component enabling high-speed data transmission. Among its advanced implementations, Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) stands out as a game-changer. In this blog, we’ll explore how WDM technology works, its benefits, and why it’s indispensable for modern optical communication systems.
What is WDM Technology?
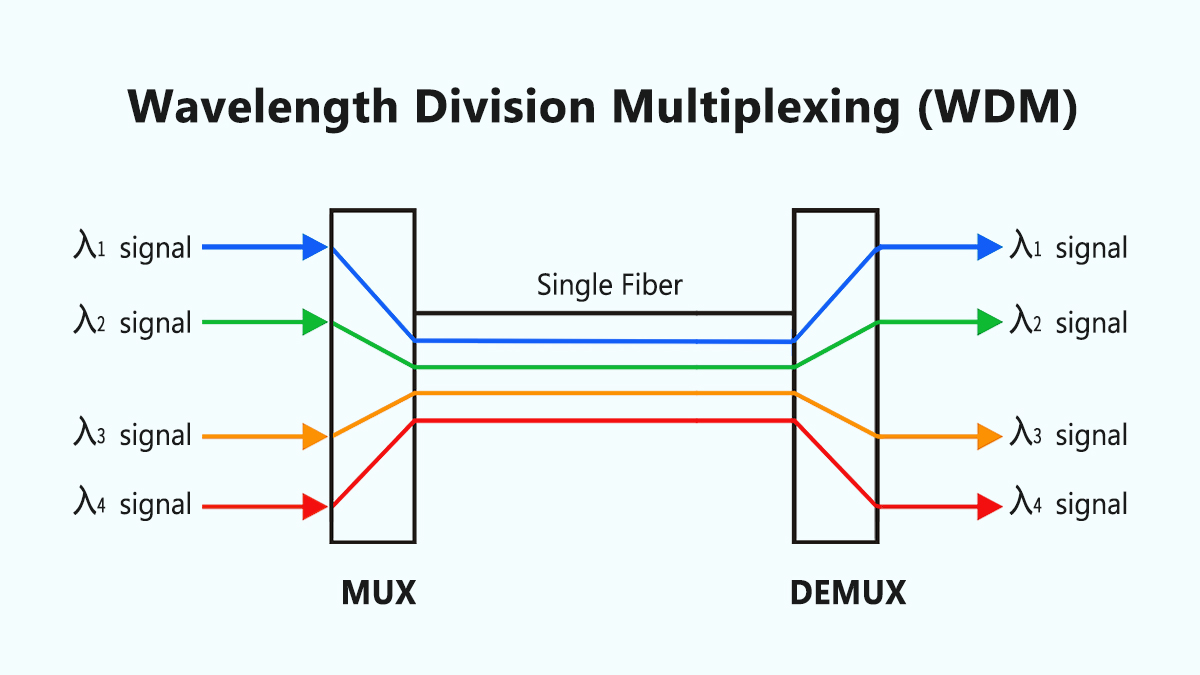
Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) is a method that combines multiple optical carrier signals onto a single optical fiber by using different wavelengths (or colors) of laser light. This technique dramatically increases the bandwidth capacity of fiber-optic networks without requiring additional physical infrastructure. Two primary variants dominate the market:
Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing (CWDM)
Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM)
Both technologies rely on specialized WDM optical transceiver modules to transmit and receive data across distinct wavelengths, enabling simultaneous bidirectional communication.
How Do WDM Optical Transceiver Modules Work?
An optical transceiver module equipped with WDM technology integrates lasers, photodiodes, and multiplexers/demultiplexers to handle multiple wavelengths. Here’s a simplified breakdown:
Transmission Side: The module’s laser diodes emit light at specific wavelengths (e.g., 1310nm, 1550nm).
Multiplexing: A WDM multiplexer combines these wavelengths into a single fiber strand.
Reception Side: At the destination, a demultiplexer separates the wavelengths, which are then converted back to electrical signals by photodiodes.
This process allows a single fiber to carry terabytes of data per second, making WDM-enabled optical transceivers ideal for high-density networks like data centers, telecom backbones, and 5G infrastructure.
Key Advantages of WDM in Optical Transceiver Modules
Maximized Fiber Utilization
By transmitting multiple data channels over one fiber, WDM reduces the need for additional cabling—a cost-effective solution for congested network environments.Scalability
Adding new wavelengths (or channels) is simpler than deploying new fibers. This flexibility makes DWDM optical transceiver modules particularly valuable for long-haul networks.Low Latency & High Speed
WDM technology supports ultra-high-speed data rates (up to 400G and beyond) with minimal signal degradation, meeting the demands of cloud computing and real-time applications.Future-Proofing Networks
As bandwidth needs grow, upgrading WDM systems often requires only software adjustments or new plug-and-play optical transceivers, avoiding costly infrastructure overhauls.
Applications of WDM Optical Transceivers
Data Center Interconnects: Enables high-capacity links between servers and storage systems.
Telecom Networks: Powers backbone networks for 5G, FTTH (Fiber-to-the-Home), and undersea cables.
Enterprise Networks: Supports campus-wide connectivity with minimal fiber deployment.
Choosing the Right WDM Optical Transceiver Module
When selecting a WDM transceiver, think about capacity, distance, and cost. CWDM is cheaper and simpler but works for shorter distances and fewer channels. DWDM costs more but offers higher capacity and works over longer distances.
Metric | CWDM | DWDM |
|---|---|---|
Channel Spacing | 20nm apart for up to 18 channels | ~0.4/0.8nm for 40, 80, or 160 channels |
Transmission Distance | Shorter reach due to high losses | Long distances with amplification |
Power Requirements | Uses uncooled lasers, less power needed | Uses cooled lasers, consumes more power |
Costs | Generally less expensive | Higher costs due to precision and cooling |
The Future of WDM Technology
Emerging trends like L-band expansion (extending wavelength ranges) and coherent optics (enhancing signal integrity) promise even greater efficiencies. Additionally, advancements in silicon photonics are driving down the cost of WDM-enabled optical transceiver modules, making them accessible to smaller enterprises.
Conclusion
WDM technology has redefined the capabilities of optical transceiver modules, offering unparalleled bandwidth scalability and cost savings. Whether you’re upgrading a data center or deploying a 5G network, integrating WDM solutions ensures your infrastructure stays ahead of the curve.
By leveraging WDM optical transceivers, businesses can future-proof their networks while meeting the explosive demand for faster, more reliable connectivity. Ready to harness the power of WDM? Partner with a trusted supplier to explore the best modules for your needs.
See Also
The Importance of Digital Monitoring in Optical Transceivers


