
Ever hit that frustrating buffering icon while streaming your favorite show? Or experienced lag during a crucial video call? The culprit often isn't the vast internet backbone but the final, critical link in the chain: the access network.
Often called the "last mile" (even though its length can vary), the access network is the bridge between you, the end-user, and your Internet Service Provider's (ISP) core network. It's the digital driveway that connects your home or business to the information superhighway.
In this article, we'll demystify what an access network is, explore its different types, and highlight the key technologies—including cutting-edge optical modules—that keep you connected at high speeds.
📝 What Exactly is an Access Network?
An access network is the portion of a telecommunications network that connects subscribers to their immediate service provider. It is the most visible part of the network ecosystem for consumers. Its primary job is to aggregate data from multiple end-users and funnel it into the core network, and vice-versa.
Think of it this way:
Core Network: The massive interstate highway system for data.
Metro Network: The major city ring roads and arteries.
Access Network: Your local street and, finally, your own driveway.
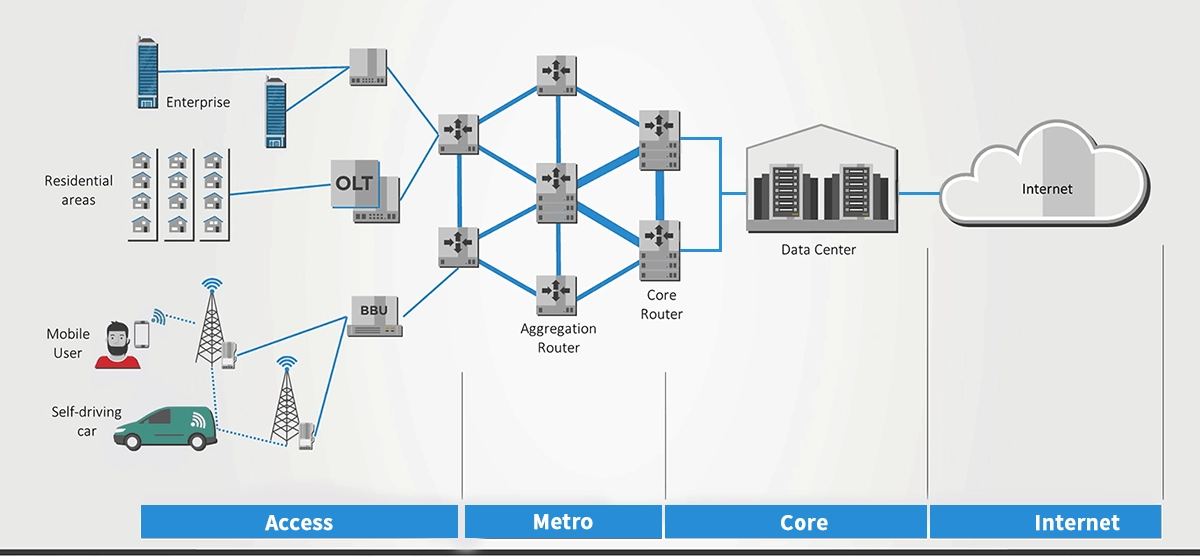
📝 Types of Access Networks: From Copper to Light
Access technologies have evolved dramatically. Here’s a breakdown of the most common types:
Technology | Medium | Max Speed (Theoretical) | Key Advantage | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) | Copper Telephone Lines | ~100Mbps | Uses existing infrastructure | Speed drops severely with distance |
Cable Internet | Coaxial Cable (TV Lines) | ~1Gbps | High speeds widely available | Bandwidth is shared with neighbors |
Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) | Glass Fiber Optics | 1-10Gbps+ | Extremely high speed, reliable | Higher deployment cost |
5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) | Radio Waves | ~1Gbps | Rapid deployment, no cables | Signal can be affected by obstructions |
Satellite Internet | Radio Waves (to Satellite) | ~100-500Mbps | Available in remote areas | High latency, weather sensitive |
As the table shows, Fiber Optic access—specifically GPON (Gigabit Passive Optical Network) and XGS-PON—is the gold standard for future-proofing our digital lives, offering symmetrical speeds (same upload and download) that are essential for cloud computing, gaming, and HD content creation.
📝 The Role of Optical Modules in Modern Access Networks
This is where the magic happens. To push massive amounts of data over fiber, ISPs need sophisticated equipment at both ends: in your home (ONT - Optical Network Terminal) and in their central office (OLT - Optical Line Terminal).
The heart of this equipment is the optical transceiver module. These small, powerful devices are responsible for:
Converting electrical signals from switches/routers into light signals for transmission over fiber.
Converting incoming light signals back into electrical data for your devices.
The performance and reliability of these modules directly impact your internet speed and stability. For ISPs building robust fiber optic access networks, choosing high-quality, compatible, and durable modules is non-negotiable.
This is where a brand like LINK-PP excels. Their optical modules are engineered for the demanding environments of service provider networks. For instance, deploying a LINK-PP SFP28-25G-LR module in an OLT line card enables ISPs to deliver multi-gigabit services to businesses and power users, ensuring they stay ahead of bandwidth demands.
When planning your PON network design, considering the quality of components like optical transceivers is a critical step for long-term success.
📝 Why Your Access Network Choice Matters Today
We're no longer just browsing the web. Our demands have skyrocketed with:
Widespread 4K/8K streaming
The Internet of Things (IoT) (dozens of connected devices per home)
Cloud-based everything (from storage to gaming)
Remote work and teleconferencing
A robust, fiber-based access network is no longer a luxury; it's a necessity for participating in the modern digital economy. Upgrading this "last mile" is the single most important step for communities and countries to ensure digital equity and economic growth.
📝 Future-Proofing Connectivity: What's Next?
The evolution never stops. Technologies like NG-PON2 (Next-Generation PON 2), which allows for wavelength division multiplexing, will push fiber capacities even further. The integration of 10G PON technology is already underway, setting the stage for the next decade of hyper-fast connectivity.
For network architects, this means investing in flexible and upgradeable infrastructure. Choosing vendor-agnostic, high-performance components is key. LINK-PP's PON Module offers a perfect blend of performance and compatibility, allowing for a smooth transition to higher-speed tiers without overhauling the entire network.
📝 Conclusion: Don't Underestimate the Last Mile
The access network is the unsung hero of your online experience. Understanding its types and the technology behind it empowers you to make better choices for your home or business internet service.
As we embrace a more connected future, the innovation in this space, driven by companies providing reliable components like LINK-PP, will continue to shrink the digital divide, one connection at a time.
Ready to Dive Deeper into Network Infrastructure?
Are you a network engineer, ISP planner, or a tech enthusiast looking to source reliable, high-performance components for your projects? Explore LINK-PP's full range of compatible optical transceivers and discover how they can enhance your access network's reliability and speed. [Contact our team today for a custom solution!]




