In the digital age, data is the lifeblood of every organization. But how you store, access, and manage that data is critical to your business's performance and efficiency. Three major storage architectures often come into play: DAS, NAS, and SAN.
Choosing the wrong one can lead to bottlenecks, downtime, and wasted resources. This guide will demystify these technologies, compare them head-to-head, and help you make an informed decision for your infrastructure.
📝 Key Takeaways
DAS works best for one person who needs fast access. It connects right to a computer and is simple to use.
NAS lets many people share files using a network. It is flexible and can grow as you need more space. This makes it good for small businesses and families.
SAN gives fast speed and is very reliable for big companies. It links many servers to storage. This is good for data centers with lots of data.
Think about your budget and what you might need later when picking storage. DAS costs the least, NAS costs a bit more, and SAN costs the most but has more features.
Check how many people will use the storage and if speed is important. This helps you pick the best storage for your needs.
📝 DAS (Direct-Attached Storage) - The Solo Artist
What it is: DAS is storage that is directly connected to a single computer or server, without a network in between. Think of an external HDD/SSD plugged into your laptop or drives installed inside a server.
Pros: Simple to configure, high-speed access (low latency), low cost for small setups.
Cons: Not shareable over a network, difficult to scale, limited management features.
Best for: Single-user environments, local backups, small businesses with minimal data sharing needs.
📝 NAS (Network-Attached Storage) - The Collaborative Team Player
What it is: NAS is a dedicated storage device connected to a local area network (LAN), typically via Ethernet. It operates as a shared network node, making data accessible to multiple authorized users and clients.
Pros: Easy file sharing and collaboration, cost-effective for mid-sized teams, simple management via a web interface.
Cons: Performance can be impacted by network traffic (latency), not ideal for high-speed block-level data.
Best for: File sharing for departments, centralized document repositories, media streaming, and SMB backups.
📝 SAN (Storage Area Network) - The High-Performance Powerhouse
What it is: A SAN is a dedicated, high-speed network that interconnects and presents shared pools of storage devices to multiple servers. It uses a separate network infrastructure (like Fibre Channel) and makes storage appear as if it's locally attached to the operating system.
Pros: Extremely high performance and low latency, excellent scalability, enables advanced features like snapshots and replication.
Cons: High cost, complex to set up and manage, requires specialized hardware and knowledge.
Best for: Mission-critical databases, virtualized environments (VMware, Hyper-V), large-scale enterprise applications, and high-transaction environments.
📝 SAN vs NAS vs DAS: What is the differences?
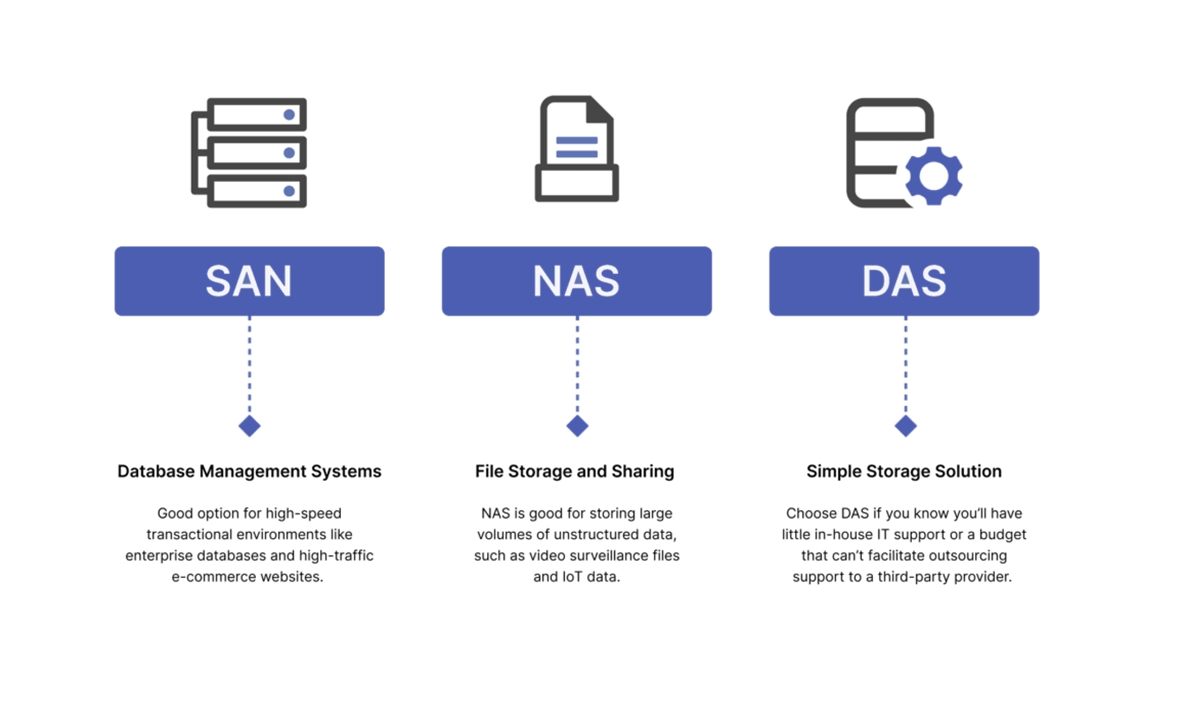
To make the differences crystal clear, here’s a quick comparison table:
Feature | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Connection | Direct (SATA, SAS, USB) | Ethernet (TCP/IP) | Fibre Channel, iSCSI, NVMe-oF |
Data Delivery | Block Level | File Level | Block Level |
Ease of Use | Very Easy | Easy | Complex |
Scalability | Limited | Good | Excellent |
Performance | High (Low Latency) | Moderate (Network Dependent) | Very High (Low Latency) |
Cost | Low | Medium | High |
Best Use Case | Single Server | File Sharing | Mission-Critical Apps |
So, Which One is Right for You?
Choose DAS for simple, low-cost, single-server storage.
Choose NAS for affordable, easy-to-manage file sharing across a team.
Choose SAN for high-performance, scalable, and reliable block storage for servers and databases.
Many modern data centers actually use a hybrid approach, leveraging the strengths of each architecture for different workloads.
📝 The Unsung Hero of SAN Performance: Optical Transceivers
The blazing speed of a Fibre Channel or Ethernet SAN is made possible by optical transceivers (like SFP+, QSFP28, SFP28). These small modules convert electrical signals to light, transmitting data over fiber optic cables at incredible speeds with high reliability and low latency.
For optimal performance and compatibility, it's crucial to use high-quality, certified modules from reputable manufacturers. This is where a brand like LINK-PP stands out. Using reliable components ensures your storage network runs at peak efficiency without unexpected drops or errors.
For instance, a high-performance LINK-PP SFP-10G-SR module is a perfect fit for a 10GbE iSCSI SAN, providing robust and stable connections for your critical data flows. When planning your high-speed data center storage or looking for low-latency Fibre Channel solutions, always consider the quality of your optical transceivers.
📝 Final Thoughts & Next Steps
Understanding the difference between DAS, NAS, and SAN is the first step in building an efficient and scalable IT infrastructure. The right choice depends entirely on your specific needs for performance, scalability, budget, and expertise.
📝 FAQ
What is the main difference between DAS, NAS, and SAN?
DAS connects straight to your computer. NAS uses your network to share files. SAN links servers and storage with a fast network. Each one gives you different speed and ways to get to your data.
How does accessibility change with each storage type?
DAS gives basic access since only one device connects. NAS lets many devices on your network reach files. SAN gives advanced access for lots of servers in data centers with a special network.
Can you use these storage solutions for backup solutions?
You can use DAS for simple backups. NAS makes it easy for many users to back up over your network. SAN helps big data centers do fast and safe backups with a high-speed network.
Which storage type is best for collaboration and shared storage?
NAS helps teams work together and share files on the network. SAN also lets big groups in data centers share and work on files using a special network.
Do you need special skills to set up a SAN?
You need expert skills to set up SAN. It uses a fast network and advanced tools. You manage complex systems in data centers. NAS and DAS are easier for most people to set up and use.




