
🌐 Introduction
EtherCAT (Ethernet for Control Automation Technology) is a high‑performance, real‑time Industrial Ethernet protocol widely adopted in automation, robotics, CNC machinery, and smart factory applications. With deterministic timing, ultra‑low communication latency, and sub‑microsecond synchronization, EtherCAT has become a foundational technology for modern motion control and high‑speed industrial systems.
This guide provides a professional, engineering‑level explanation of EtherCAT’s operating principles, synchronization mechanisms, topology options, safety standards, and physical‑layer considerations.
🌐 Limitations of Traditional Ethernet in Industrial Automation
Standard Ethernet was originally designed for office environments—not for synchronized, deterministic industrial control. Key limitations include:
Non‑deterministic communication caused by CSMA/CD arbitration
High protocol overhead due to multi‑layer processing
High jitter is unsuitable for motion control loops
Poor scalability when many devices are connected in a time‑critical system
Industrial applications such as robotics and multi‑axis servomotion often require cycle times under 100 µs and jitter measured in hundreds of nanoseconds or less. Traditional Ethernet cannot meet these constraints.
EtherCAT directly addresses these real‑time challenges with a hardware‑accelerated communication model designed specifically for high‑performance automation.

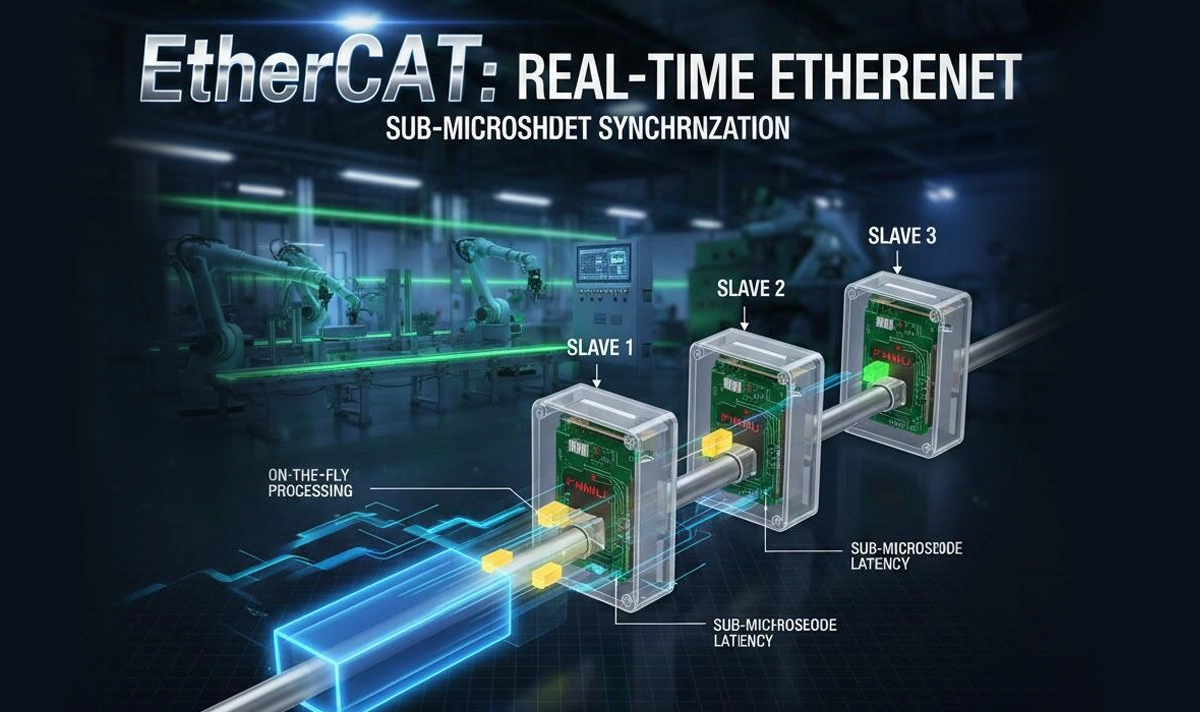
🌐 Core Principle: On‑the‑Fly Frame Processing (FMMU)
The fundamental concept that differentiates EtherCAT from other Industrial Ethernet systems is its method of processing Ethernet frames on the fly, enabled by a hardware unit known as the FMMU (Fieldbus Memory Management Unit).
● How EtherCAT Processes Data
Single Frame Transmission: The EtherCAT master sends one standard Ethernet frame containing datagrams for all slave devices.
On‑the‑Fly Hardware Processing: Each slave extracts its output data and inserts its input data directly into the frame as it passes by. Typical processing delay per slave is < 1 µs.
Frame Loopback: The modified frame returns to the master with consolidated input data from all slaves.
● Performance Characteristics
Deterministic latency independent of node count
Bandwidth utilization > 90%
Example performance:
1000 digital I/O points in ~30 µs
100 servo axes in ~100 µs
This efficiency makes EtherCAT one of the fastest industrial networks available today.
🌐 Distributed Clocks (DC): Sub‑Microsecond Synchronization
Precise synchronization is essential for coordinated robotics, CNC machining, and multi‑axis servomotion. EtherCAT achieves synchronization better than 100 ns using a decentralized, clock‑distribution mechanism.
▷ DC Operating Principle
Reference Clock Selection: The first DC‑capable slave acts as the reference clock.
Timestamp Capture: Each slave measures frame arrival and departure times to determine propagation delay.
Automatic Drift Compensation: The master computes offsets and distributes correction values to all slaves.
▷ Benefits of DC Synchronization
Nanosecond‑level phase alignment across hundreds of devices
Extremely stable motion profiles for robotics and positioning systems
Accurate simultaneous data acquisition
The DC system provides deterministic and precise network timing without requiring a centralized master clock.
🌐 Flexible Network Topology and Redundancy
EtherCAT supports a wide range of wiring topologies without requiring Ethernet switches.
1. Supported Topologies
Line (most common)
Tree / Branch / Drop Line
Star (using EtherCAT junctions)
Ring (full media redundancy)
2. Fault Tolerance
In a ring structure, if a cable breaks:
The frame automatically reverses direction
Communication with the remaining network continues uninterrupted
This ensures high availability in demanding industrial environments.
🌐 Functional Safety over EtherCAT (FSoE)
EtherCAT integrates functional safety within the same network using FSoE, a TÜV‑certified protocol supporting SIL 3 (IEC 61508).
Examples of safety functions:
Emergency stop
Safe Torque Off (STO)
Safe Speed Monitoring (SSM)
Safe limited position or direction monitoring
By embedding safety data inside standard EtherCAT frames, FSoE eliminates the need for a separate safety bus, reducing cost and wiring complexity.
🌐 Role of Physical Layer Components in EtherCAT Performance
While EtherCAT’s performance is protocol‑driven, its real‑time integrity relies heavily on physical‑layer hardware quality.
Key requirements include:
High signal integrity under heavy EMI conditions
Excellent common‑mode noise rejection
Reliable transformer‑based galvanic isolation
Industrial‑grade RJ45 integrated magnetic connectors
High‑quality magnetics and PHY components enable EtherCAT systems to maintain microsecond‑level timing and nanosecond‑level synchronization even in electrically noisy environments.
🌐 Global Adoption and Application Domains
EtherCAT is one of the fastest‑growing Industrial Ethernet technologies worldwide, supported by the EtherCAT Technology Group (ETG). Its high performance and open architecture drive widespread use in:
Semiconductor equipment
Robotics and automation systems
CNC machines and high‑precision machining
Packaging machinery
Wind turbines and renewable energy systems
Smart factory / Industry 4.0 infrastructure
Its scalability, low cost, and real‑time capability have made EtherCAT a global automation standard.
🌐 Summary of Technical Advantages
Feature | Technical Benefit | Impact on Control System |
|---|---|---|
On‑the‑Fly Processing | Eliminates protocol‑stack overhead | Deterministic, ultra‑low latency |
Distributed Clocks | <100‑ns synchronization | High‑precision multi‑axis control |
Flexible Topologies | Supports Line, Tree, Star, Ring | Simplified wiring, lower costs |
FSoE Integration | SIL3‑certified functional safety | Unified safety + control network |
🌐 Conclusion
EtherCAT delivers industry‑leading real‑time performance through deterministic communication, efficient bandwidth usage, and nanosecond‑level synchronization. Its flexible topology, integrated functional safety, and robust physical‑layer requirements make it a foundational technology for next‑generation industrial automation.
For engineers developing motion control, robotics, CNC, or high‑performance automation systems, EtherCAT offers an unparalleled balance of speed, reliability, and scalability.




