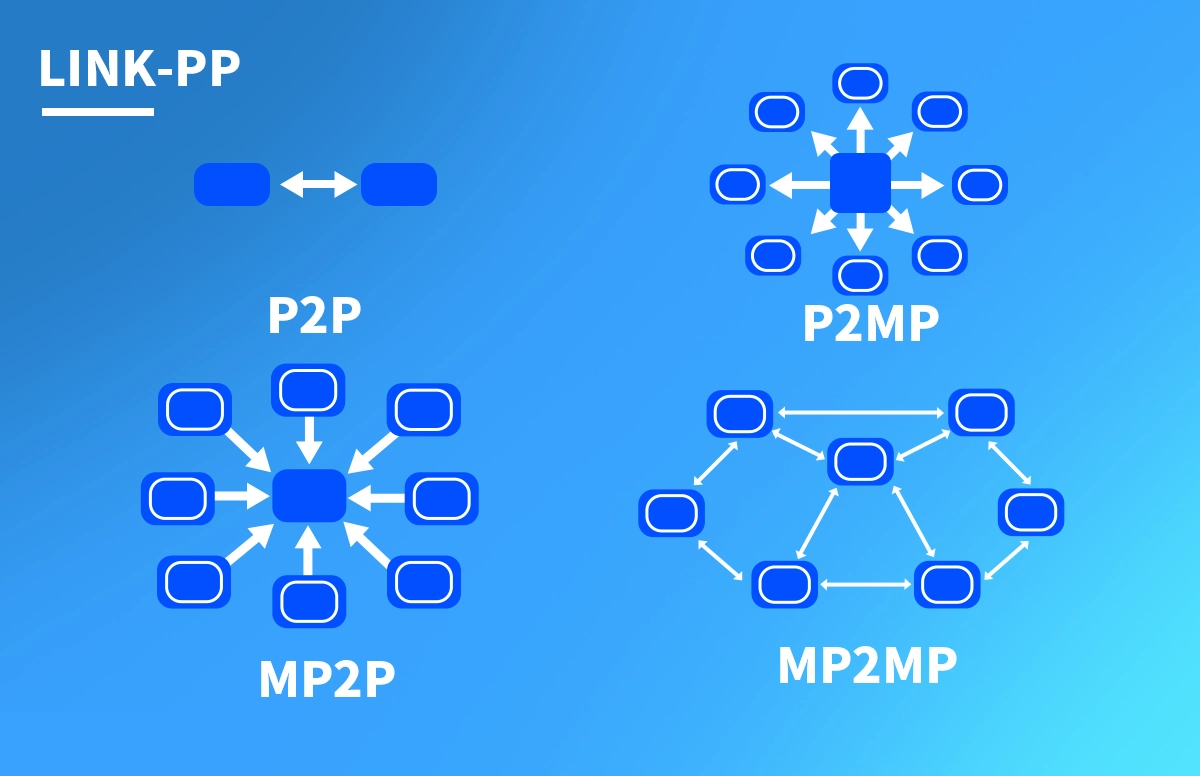
✅ Overview of Main Network Communication Architectures
In modern communication systems, the choice of network architecture defines how devices exchange data, how efficiently bandwidth is used, and how the network scales. The four core architectures—Point-to-Point (P2P), Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP), Multipoint-to-Point (MP2P), and Multipoint-to-Multipoint (MP2MP)—form the foundation of today’s wired and optical communication networks.
This article explores each architecture in detail and discusses how LINK-PP optical transceivers support high-performance network connectivity across these models.
✅ Point-to-Point (P2P) — Direct, High-Performance Links

A Point-to-Point network establishes a dedicated connection between two nodes, such as a switch and a server, or two optical devices. This structure provides:
Exclusive bandwidth between endpoints
Minimal latency and interference
High security due to direct transmission
P2P architecture is commonly used in data center interconnects (DCI), .
🔗 Recommended LINK-PP solution:
LINK-PP SFP and SFP+ Optical Transceivers — ideal for 1G/10G/25G point-to-point optical links between switches or routers.
✅ Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP) — One-to-Many Distribution
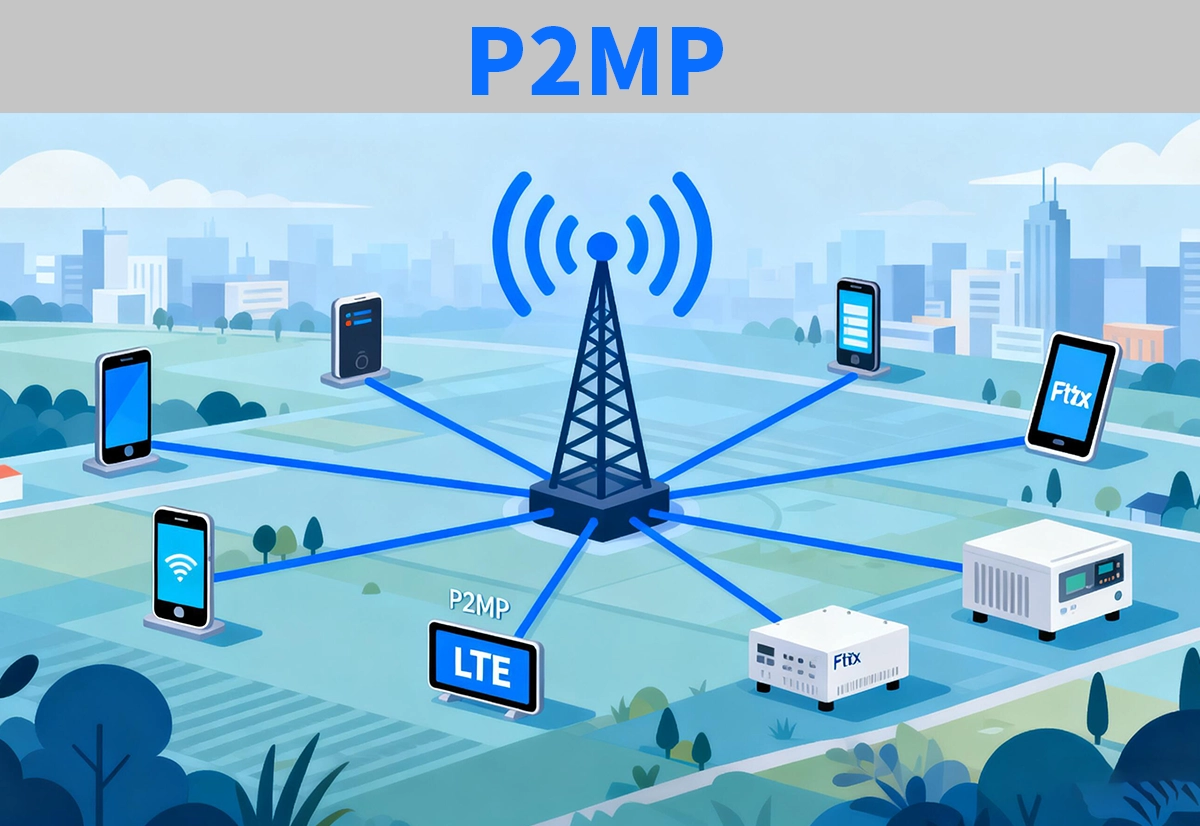

In a Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP) network, a single central node (such as a base station or an optical line terminal) connects to multiple remote endpoints. Data flows from one source to many receivers, enabling efficient broadcast or distribution.
This structure is often used in:
Wireless access systems (e.g., LTE, Wi-Fi)
Surveillance and IoT networks
P2MP allows centralized management but requires robust upstream capacity and synchronization.
🔗 Recommended LINK-PP solution:
LINK-PP GPON and EPON Optical Modules — optimized for multi-user downstream distribution in access networks.
✅ Multipoint-to-Point (MP2P) — Data Aggregation Model
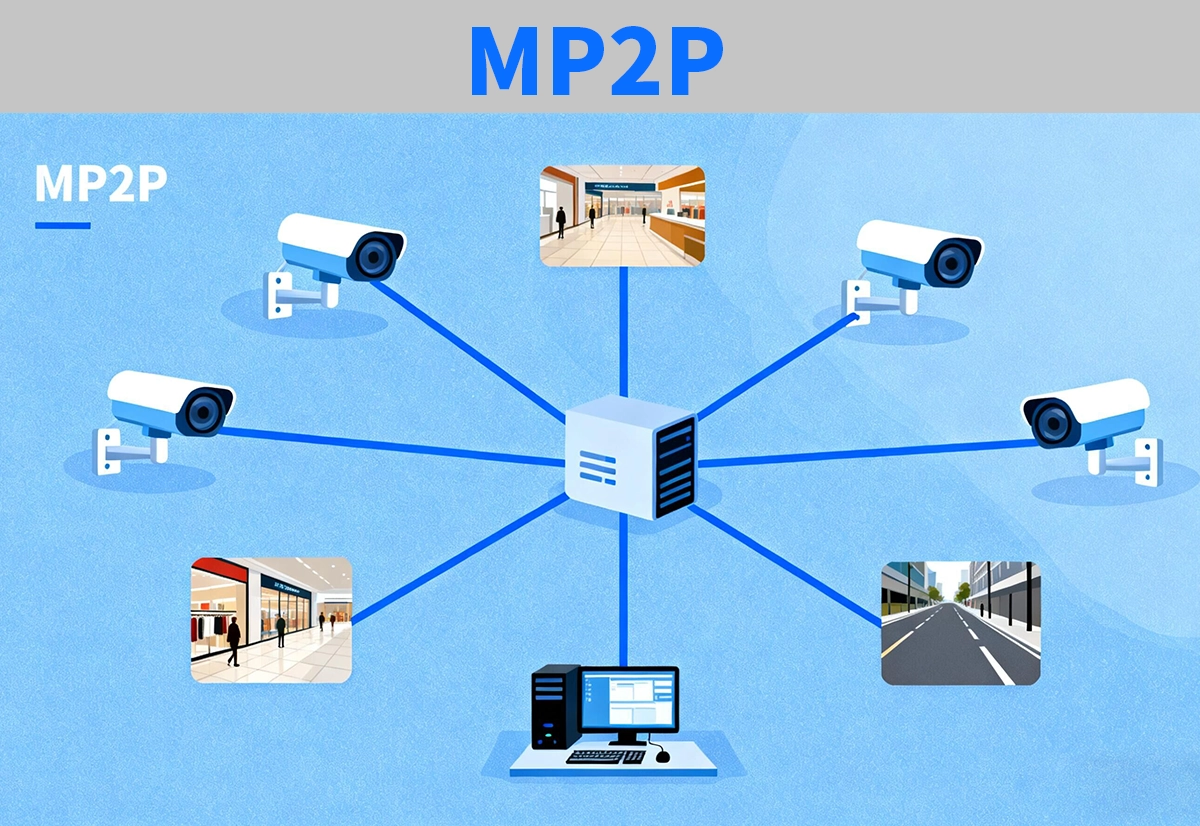
Multipoint-to-Point (MP2P) describes the reverse flow of P2MP—multiple nodes sending data to a single central node. This “many-to-one” topology is vital in data collection and monitoring systems such as:
IoT and industrial sensor networks
Video surveillance systems
Cloud-based data aggregation platforms
In MP2P systems, multiple sources transmit simultaneously or sequentially to a controller, requiring strong signal management and buffering.
🔗 Recommended LINK-PP solution:
LINK-PP Industrial-Grade SFP Transceivers — designed for reliable uplink transmission in harsh or high-traffic environments.
✅ Multipoint-to-Multipoint (MP2MP) — Full-Mesh Connectivity
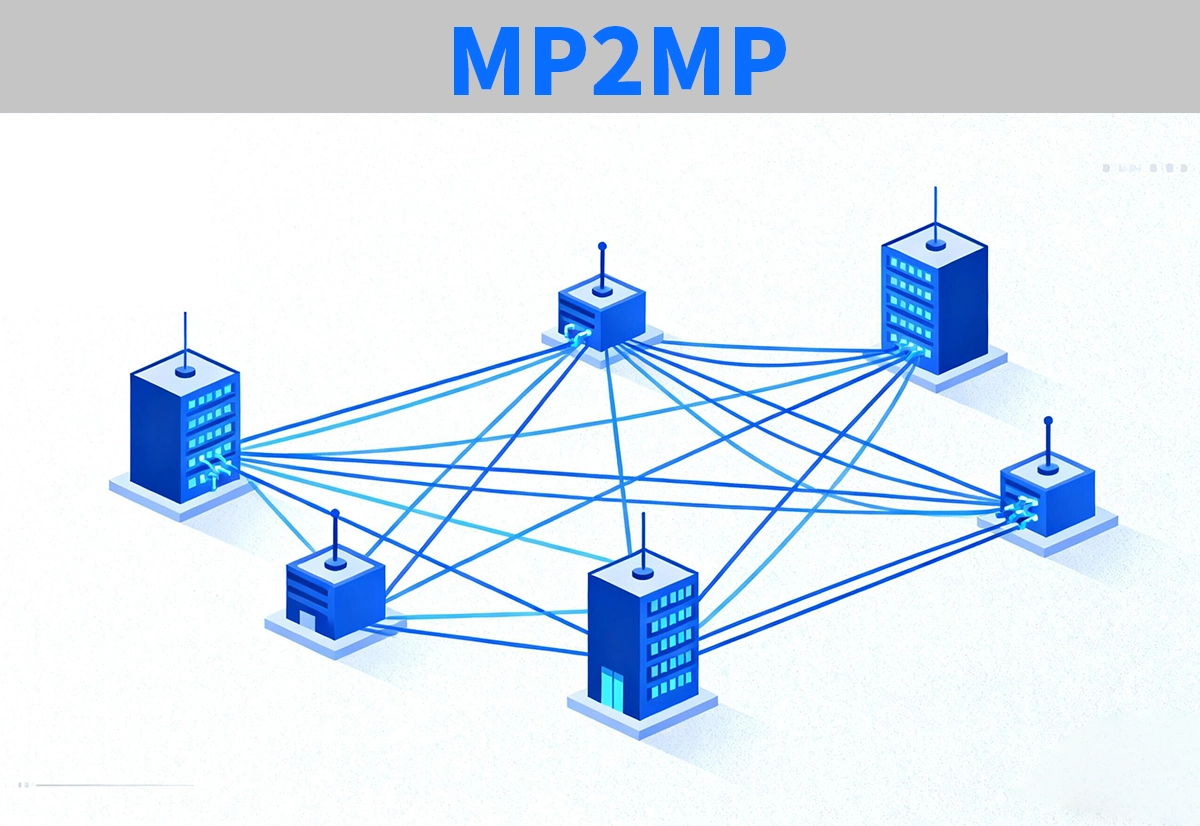
The Multipoint-to-Multipoint (MP2MP) network architecture enables all nodes to communicate with one another. This model underpins distributed and collaborative systems such as:
Internet backbones and SDN fabrics
Data center spine-leaf networks
Peer-to-peer and mesh communication frameworks
MP2MP architectures offer unmatched flexibility and redundancy, though they require high-capacity switching and routing to handle dynamic traffic patterns.
🔗 Recommended LINK-PP solution:
LINK-PP QSFP+ and QSFP28 Transceivers — enabling scalable 40G/100G/400G mesh interconnects between core and aggregation layers.
✅ Key Comparison of the Four Architectures

Architecture | Communication Type | Direction | Typical Use Case | LINK-PP Product Fit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
One-to-One | Bidirectional | Data center links | SFP / SFP+ Transceivers | |
One-to-Many | Downstream | Access & distribution | GPON / EPON Modules | |
Many-to-One | Upstream | IoT / sensor networks | Industrial SFP Modules | |
Many-to-Many | Full duplex | Core networks / SDN | QSFP+ / QSFP28 Modules |
✅ How LINK-PP Optical Transceivers Support Every Network
Whether you are designing a simple point-to-point fiber link or deploying a full mesh data center architecture, LINK-PP provides a comprehensive range of SFP, SFP+, QSFP, and QSFP28 optical transceivers that deliver:
High-speed transmission from 1G to 400G
Compatibility with Cisco, Intel, and HP systems
Long-distance connectivity up to 80 km
Low power consumption and industrial temperature range
✅ Conclusion
Each network communication architecture—P2P, P2MP, MP2P, and MP2MP—serves a unique role in modern connectivity. From direct links to large-scale mesh systems, these models define how data travels efficiently and securely across global networks.
LINK-PP optical transceivers bridge these architectures by providing flexible, high-speed, and reliable interfaces for every layer of communication—from edge devices to data center cores.
Empower your network with LINK-PP:
🌐 www.l-p.com — Professional Optical Connectivity Solutions for Global Communication.
✅ Also See
For deeper technical insights into each architecture and related optical network applications, explore these resources from the LINK-PP Knowledge Center:




