Introduction: Why Laser Types Matter in Optical Modules
Laser diodes are the heart of optical modules—they convert electrical signals into light for fast and efficient fiber-optic communication. Optical transceivers rely on integrated lasers to deliver precise, reliable, and high-bandwidth signal transmission. This article compares the four main types—VCSEL, FP, DFB, and EML—highlighting their strengths, limitations, and how LINK‑PP includes them in its optical transceivers product line.
Overview of Common Lasers in Optical Modules
♦ VCSEL (Vertical-Cavity Surface-Emitting Laser)
Emits light perpendicular to the chip surface.
Affordable, reliable, and easy to produce at scale.
Ideal for short-range links like data center connections.
Common wavelength: 850 nm for multimode fiber.
Typical range: ~300 m at 10 Gbps; up to 2 km at lower speeds (e.g., 155 Mbps).
♦ FP (Fabry‑Pérot) Laser
Emits multiple wavelengths in a horizontal cavity structure.
Simple and economical design.
Best suited for short to medium distances.
Common wavelength: 1310 nm or 1550 nm.
Typical distance: Up to ~20 km at 1.25 Gbps.
♦ DFB (Distributed Feedback) Laser
Features an internal grating for single-mode, stable emission.
Narrow spectral width and high wavelength precision.
Common wavelength: 1310 nm and 1550 nm.
Typical distance: 40 km+ at high speeds; up to 150 km at lower speeds (e.g., 155 Mbps) depending on application (e.g., CWDM/DWDM).
♦ EML (Electro‑Absorption Modulated Laser)
Combines a laser diode with an integrated modulator on the same chip.
Provides clean, high-speed signal modulation.
Common wavelength range: 1470–1610 nm (typically in the C-band around 1550 nm).
Typical distance: Up to 80 km at 10 Gbps.
Side-by-Side Technical Comparison Table
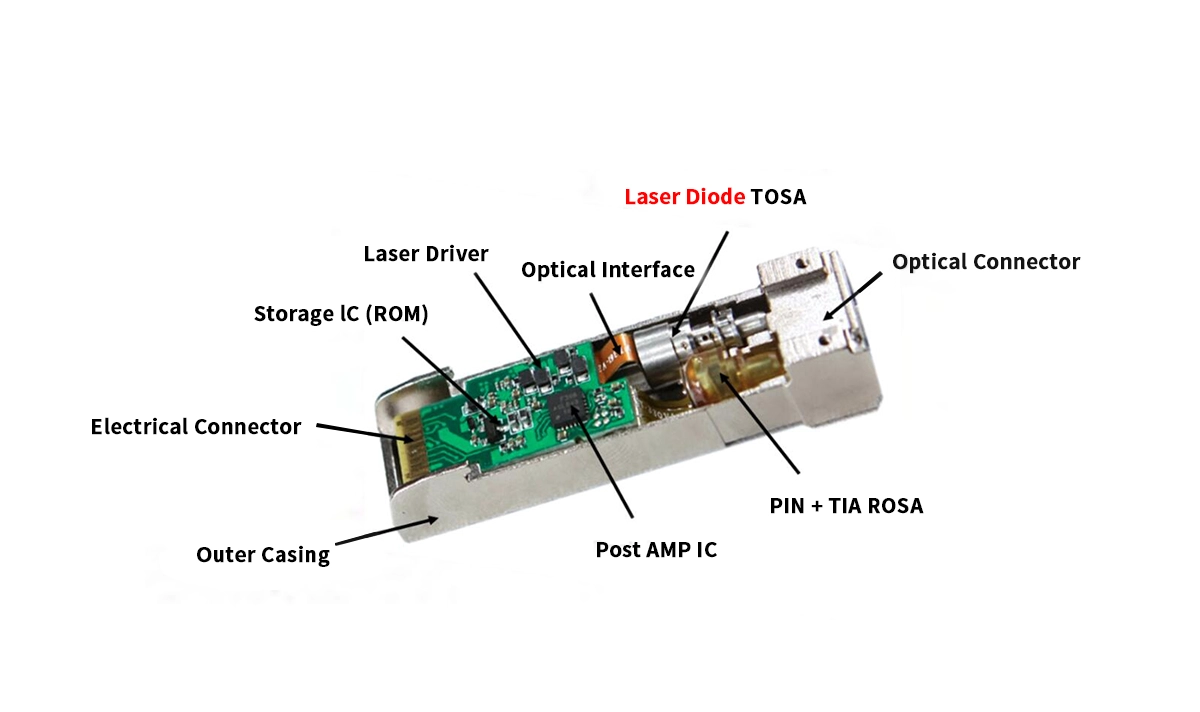
Attribute | VCSEL | FP | DFB | EML |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Emission Direction | Surface-emitting | Edge-emitting | Edge w/ grating | Integrated modulator |
Wavelengths | 850 nm | 1310 nm, 1550 nm | 1310 nm, 1550 nm | 1470–1610 nm |
Best Use Case | Short-range (meters to ~2 km) | Up to ~20 km | Long-haul (40 km+, up to 150 km) | High-speed long-distance (up to 80 km) |
Cost | Low | Low | Moderate | High |
Key Advantage | Cheap, low power, easy to test | Simple and cost-efficient | High spectral purity, stable output | Superior modulation quality |
Typical Application Scenarios and Deployment Mapping
VCSEL: High-density data center links, server interconnects, short-haul parallel fiber links.
FP: Access and enterprise networks, cost-sensitive telco and PON scenarios.
DFB: Metro/long-haul networks, DWDM, 5G backbone, enterprise campus distribution.
Why Laser Choice Matters
Distance Needs: VCSEL and FP are suited for shorter links, whereas DFB and EML handle longer distances.
Speed & Clarity: EML offers the cleanest high-speed modulation; DFB shines in stable long-distance transmission.
Budget Considerations: FP and VCSEL are more economical; DFB and EML bring higher performance at higher cost.
How LINK‑PP Integrates These Lasers
LINK‑PP’s official store provides a wide range of transceiver modules with different laser types to meet diverse needs. From cost-effective VCSEL or FP-based SFP modules for everyday networking to high-performance DFB and EML-based units for demanding, long-distance deployments, LINK‑PP supports both quality and flexibility by matching laser technology to performance needs.
Final Thoughts
Understanding these laser types helps in choosing the right optical module for your network design—whether it's for short connections in a server room or long-haul links across cities. With updated performance and distance details, this guide reflects the latest technical ranges based on real-world deployments.
LINK‑PP gives practical, laser-technology-aware options across its product catalog, empowering networks with clarity, speed, and reliability.
References:




