
In the high-stakes world of modern networking, agility and scalability are not just advantages—they are necessities. At the heart of this dynamic landscape lies a critical, yet often overlooked, technology: Pluggable Optics. These small, hot-swappable devices are the unsung heroes powering our data centers, telecom networks, and enterprise infrastructures.
This guide will demystify pluggable optics, explore their undeniable benefits, and highlight why they are fundamental to the future of high-speed data transmission. Whether you're a network engineer, a IT manager, or simply tech-curious, understanding this technology is key to navigating the future of connectivity.
✅ Key Takeaways
Pluggable optics make it easy to upgrade your network. You do not need to replace whole devices. This makes things faster and saves money.
These modules use less power than fixed optics. This helps lower your energy bills. It also helps keep your equipment cool.
Hot-swapping lets you change modules while the network is on. You do not need to turn it off. This means less downtime and smoother service.
Linear pluggable optics (LPO) give fast connections with low delay. They are great for data centers and AI work.
Keep learning about new standards for pluggable optics. This helps your network stay strong and ready for the future.
✅ What Exactly Are Pluggable Optics?
In simple terms, pluggable optics are modular transceivers that can be easily inserted into and removed from network equipment switches, routers, and servers. They act as the crucial interface, converting electrical signals from the device into optical signals for transmission over fiber optic cables, and vice-versa.
Think of them as the universal translators of the networking world, enabling communication across different media and over vast distances. Their "pluggable" nature is their superpower, offering unparalleled flexibility compared to fixed, soldered-on optical components.
The evolution of pluggable optics has been driven by the relentless demand for higher bandwidth and greater density. From the early GBIC to today's advanced QSFP-DD and OSFP form factors, each generation has packed more speed into the same or smaller physical space.
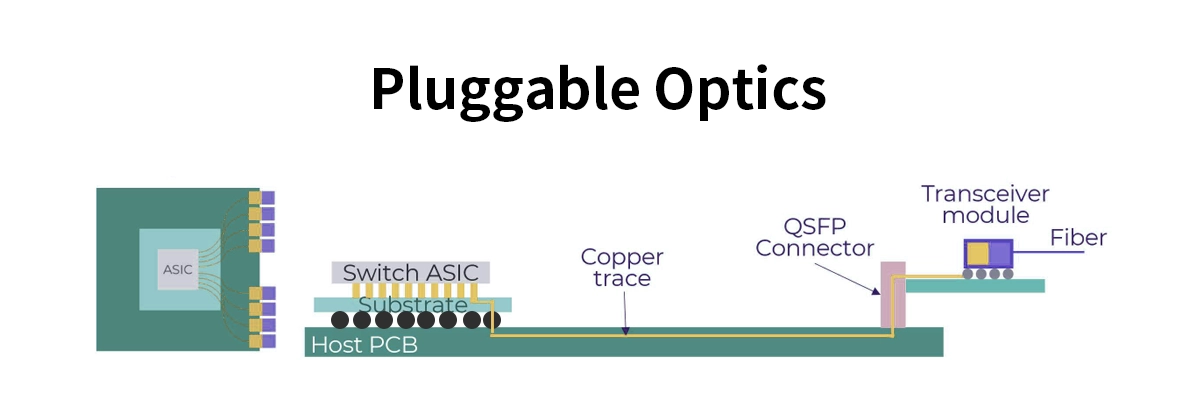
✅ Why Pluggable Optics? The Unbeatable Advantages
The shift towards pluggable optics is a strategic move for any organization looking to optimize its network. Here’s why they have become the industry standard:
✨ Unmatched Flexibility & Scalability: Need to upgrade a link from 10G to 100G? Simply swap the optic. This allows for seamless network upgrades and technology migrations without replacing entire systems, making it a cornerstone of scalable data center design.
💰 Significant Cost-Effectiveness: Pluggable optics decouple the lifecycle of the transceiver from the host system. You can purchase switches and optics from different vendors (where compatible) and only upgrade components as needed, leading to major cost savings in network infrastructure.
⚡ Simplified Maintenance & Inventory: Instead of stocking entire spare switches, network operators can maintain a small inventory of various pluggable optic types. Failed modules can be hot-swapped in minutes, drastically reducing downtime in high-availability networks.
🌍 Multi-Vendor Interoperability: While compatibility should always be verified, standards like MSA (Multi-Source Agreement) ensure that optics from different manufacturers can work with equipment from various vendors, preventing vendor lock-in.
The table below summarizes the key benefits for quick reference:
Advantage | Impact on Your Network |
|---|---|
Flexibility | Enables easy upgrades and technology adoption without hardware overhaul. |
Cost Savings | Reduces capital expenditure (CapEx) and operational expenditure (OpEx). |
Ease of Maintenance | Minimizes downtime through simple, hot-swappable replacements. |
Interoperability | Provides freedom to choose components from a competitive market. |
✅ A Landscape of Choices: Common Pluggable Optics Form Factors
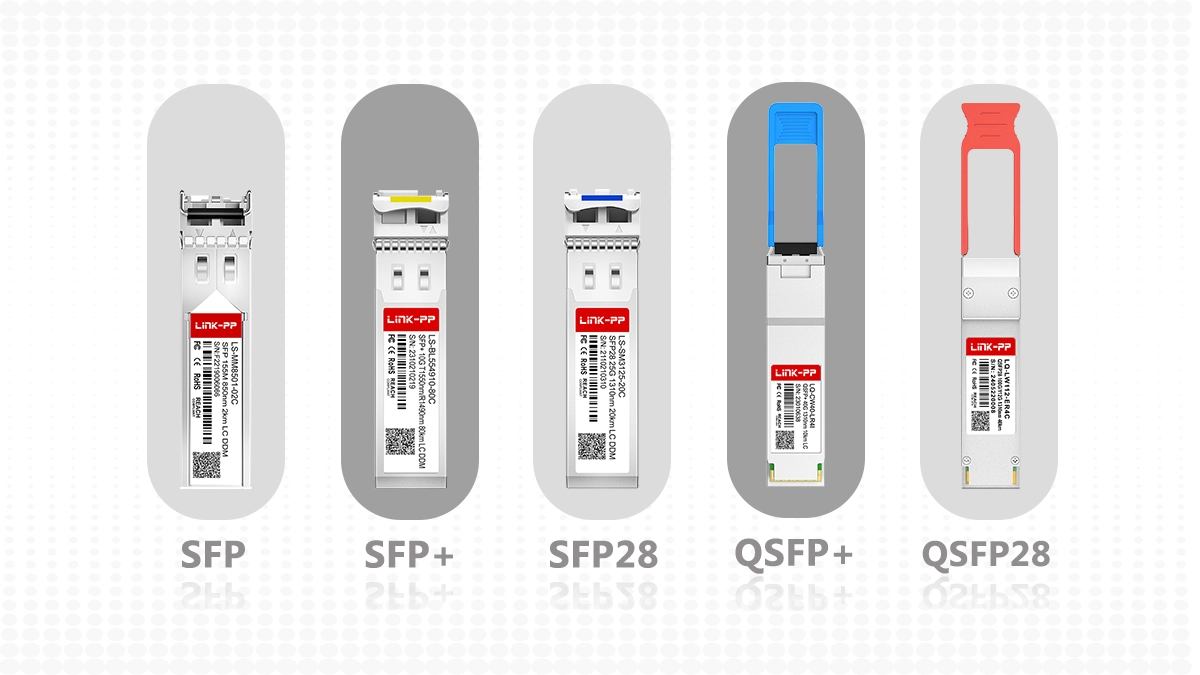
The world of pluggable optics is diverse, with different form factors designed for specific speed, reach, and power consumption requirements. Navigating this landscape is key to selecting the right component for your high-speed networking applications.
Here’s a brief overview of the most prevalent types:
SFP / SFP+ (Small Form-factor Pluggable): The workhorse for 1G/10G connectivity, widely used in enterprise and service provider networks.
QSFP / QSFP+ / QSFP28 / QSFP-DD (Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable): These are the powerhouses for high-density, high-speed applications. QSFP28 supports 100G, while QSFP-DD (Double Density) can handle 400G and even 800G, making it a future-proof solution for next-generation data center optics.
OSFP (Octal Small Form-factor Pluggable): Another contender for 400G/800G applications, designed with a slightly larger form factor to handle higher power requirements.
CFP (C Form-factor Pluggable): Typically used for highest-speed and longest-reach applications, such as 100G+ coherent optics in telecom transport networks.
Choosing the right form factor depends on a careful analysis of your bandwidth requirements for pluggable transceivers, power budget, and physical space constraints.
✅ Spotlight on Optical Transceivers: The Heart of the Matter
While "pluggable optics" is the broad term, the specific device you plug in is an optical transceiver. This component is a marvel of engineering, integrating a transmitter, a receiver, and sophisticated electronics into a tiny package.
Key specifications to consider when selecting a transceiver include:
Data Rate: The speed it supports (e.g., 10G, 25G, 100G, 400G).
Form Factor: The physical shape and size (e.g., SFP+, QSFP28).
Wavelength: The specific light wavelength used for transmission (e.g., 850nm for multi-mode, 1310nm/1550nm for single-mode).
Reach: The maximum transmission distance, which can range from a few meters (intra-data center) to over 100 kilometers (long-haul telecom).
Media Type: The type of fiber it works with—Multi-mode Fiber (MMF) for short distances or Single-mode Fiber (SMF) for long hauls.
For network architects looking for reliability and performance, choosing a trusted supplier is paramount. This is where brands like LINK-PP distinguish themselves. LINK-PP specializes in manufacturing high-quality, MSA-compliant optical transceivers that deliver robust performance for demanding environments. A great example of their engineering excellence is the LINK-PP QSFP28-100G-SR4 transceiver. This module is a perfect solution for cost-effective 100G connectivity over parallel multi-mode fiber, ideal for high-performance computing and data center spine-leaf architectures, ensuring low latency and high reliability.
✅ The Road Ahead: Future Trends in Pluggable Optics
The innovation in pluggable optics is far from over. As we push towards an AI-driven, hyper-connected world, the demands on network infrastructure will only intensify. The future points towards several key trends:
Higher Speeds in Smaller Packages: The race for 800G and 1.6T (Terabit) transceivers in form factors like QSFP-DD and OSFP is already underway. This continuous evolution is critical for supporting AI and machine learning workloads that consume massive amounts of data.
Coherent Technology Going Pluggable: Coherent optics, once the domain of large, fixed-line systems, are now available in pluggable form factors like QSFP-DD. This brings superior performance and reach for data center interconnects (DCI) directly into the data center switch.
Focus on Power Efficiency: As densities increase, power consumption per bit becomes a critical metric. Newer generations of optics are being designed to deliver more bandwidth while staying within strict power budgets, a crucial consideration for sustainable operations.
Intelligence and Monitoring: Enhanced Digital Diagnostics Monitoring (DDM or DOM) capabilities are becoming standard, providing real-time insights into transceiver health, temperature, and power levels, enabling proactive network management.
✅ Conclusion: Building Agile Networks with Pluggable Optics
Pluggable optics are more than just components; they are a strategic enabler for modern, agile, and cost-effective networks. Their ability to provide flexible and scalable network solutions has made them indispensable in everything from cloud data centers to 5G infrastructure.
By understanding the different form factors, their applications, and partnering with reliable manufacturers like LINK-PP, businesses can future-proof their investments and build networks that are ready for the challenges of tomorrow. Embracing this technology is not just an option—it's a prerequisite for success in the digital age.
✅ FAQ
What is a pluggable optic module?
A pluggable optic module is a small device. You put it into network equipment. It sends data using light signals. You can take it out and swap it. This helps you upgrade or fix your network.
What makes linear pluggable optics special?
Linear pluggable optics do not use a digital signal processor. They use less power and have less delay. These modules work best for short and fast connections. Data centers use them for quick links.
What types of devices use pluggable optics?
Pluggable optics are found in switches, routers, and servers. Data centers and big networks use them. They help connect equipment and move data fast.
What should you consider when choosing a pluggable optic?
Check the speed you need. Think about the distance and cable type. Make sure the module fits your device. Look at power use and if you can upgrade later.
What problems can pluggable optics solve?
Pluggable optics let you upgrade your network easily. You do not need to buy new equipment. You can fix broken links quickly. You save energy and money by using only what you need.




