
SFP (Small Form-factor Pluggable) modules play a critical role in high-speed data transmission across enterprise, data center, and telecom networks. While these hot-swappable optical transceivers are designed for flexibility and performance, improper handling or lack of maintenance can lead to failures, signal loss, or shortened module lifespan.
In this blog, we’ll explore professional and practical SFP module maintenance best practices, helping network engineers and IT professionals maintain optimal performance and reduce downtime.
Key Takeaways
Clean SFP Transceivers cages before every connection and at least monthly to prevent dirt buildup and signal loss, using proper tools like lint-free wipes and isopropyl alcohol.
Handle SFP modules carefully with anti-static precautions and store them with dust plugs to avoid damage and contamination that can cause failures.
Regularly monitor module performance and environmental conditions, and replace faulty modules promptly to maintain network stability and avoid costly downtime.
🔧 1. Minimize Plug and Unplug Cycles
Although SFP modules support hot-swapping, excessive plug/unplug cycles can wear down the gold-plated contacts inside the host equipment. Most modules are rated for 50 to 500 insertions. Always:
Power down when possible.
Avoid unnecessary removal.
Insert/remove gently and straight to avoid connector damage.
🧼 2. Keep Optical Interfaces Clean
Dust, oil, and debris are leading causes of signal degradation. Dirty fiber interfaces can lead to high insertion loss or link failure. To maintain optimal performance:
Use lint-free fiber wipes or fiber cleaning pens regularly.
Never touch the fiber ferrule or optical lens with bare fingers.
Keep dust caps on when not in use.
Clean both the SFP LC interface and fiber patch cables.
💡 Tip: Regular cleaning is especially important in high-density patch panel environments where airborne dust is common.
🌡️ 3. Monitor Operating Temperature
SFP modules typically operate within commercial (0°C to 70°C) or industrial (-40°C to 85°C) temperature ranges. Prolonged exposure to extreme heat can affect laser performance and internal electronics.
To ensure proper thermal conditions:
Keep devices in a well-ventilated rack.
Avoid blocking airflow around switches or routers.
Check for overheating using DDM (Digital Diagnostic Monitoring) if supported.
⚡ 4. Prevent Electrostatic Discharge (ESD)
Electrostatic discharge can irreparably damage sensitive optical components. Always:
Wear an ESD wrist strap when installing/removing modules.
Use antistatic trays or bags for storage.
Ground yourself before touching optical connectors.
🔍 5. Check Compatibility Before Use
Using incompatible modules can result in device recognition failure or suboptimal performance. Ensure:
Module data rate (1G, 10G, 25G, etc.) matches port requirements.
Wavelength and transmission distance suit the fiber type (single-mode vs multimode).
Module is vendor-compatible or specifically designed as a 3rd-party equivalent.
🗃️ 6. Store Unused Modules Properly
When not in use, SFP modules should be stored in:
Antistatic, sealed containers or original packaging.
Clean, dry, and temperature-controlled environments.
Separate compartments to avoid scratching or contamination.
📊 7. Use DDM to Monitor Module Health
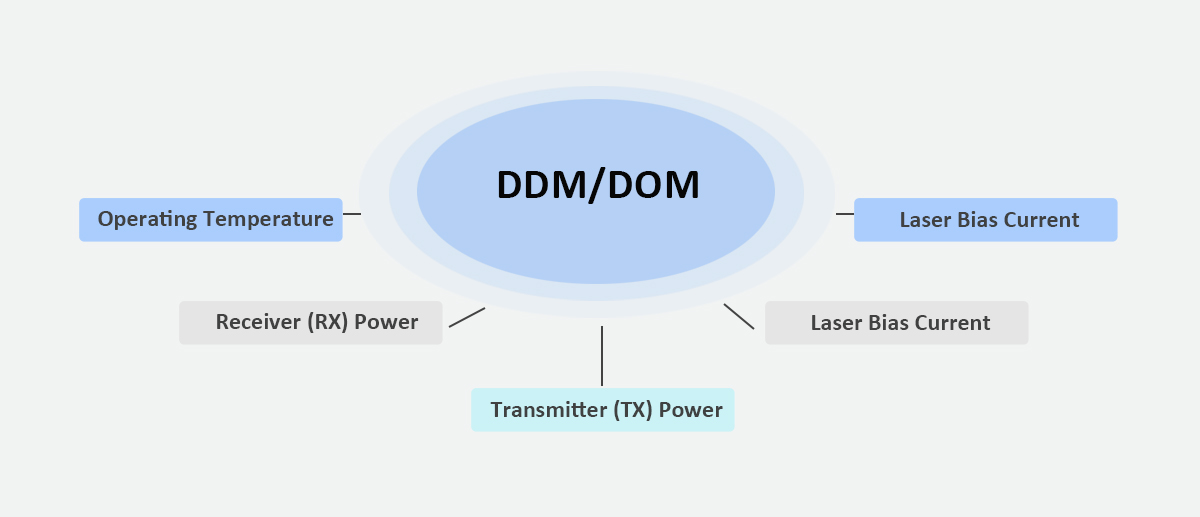
Many modern SFP modules support DDM (Digital Diagnostic Monitoring), which reports:
Laser bias current
TX/RX optical power
Module temperature
Supply voltage
Use this data to:
Detect performance degradation early.
Schedule proactive replacements.
Identify potential causes of signal issues.
🔄 8. Replace Aging Modules Before Failure
Even high-quality transceivers degrade over time. Gradual signal loss, high error rates, or unusual temperature readings may indicate:
Failing laser components
Fiber alignment drift
Connector oxidation
Maintain an inventory of backup modules and implement a lifecycle management policy for critical links.
✅ Conclusion
Maintaining your SFP optical transceivers properly is essential for achieving long-term network reliability and minimizing unplanned outages. By adopting these maintenance practices — from keeping connectors clean to monitoring internal diagnostics — you can protect your investment and keep high-performance links running at peak efficiency.
FAQ
How often should you clean SFP module connectors?
You should clean connectors before every connection or reconnection. In busy networks, monthly cleaning helps prevent signal loss and keeps your equipment running smoothly.
What tools do you need for SFP module maintenance?
Lint-free wipes
99% isopropyl alcohol
Fiber optic cleaning tools
Antistatic wrist strap
Dust plugs
Can you reuse a removed SFP module?
You can reuse SFP modules if they show no damage or contamination. Always inspect and clean them before reinstalling to ensure reliable performance.




