
In high-speed data centers and fiber optic networks, ensuring seamless connectivity is paramount. One critical yet often overlooked aspect is polarity in MTP/MPO systems. Polarity defines the path of light signals from transmitter to receiver, and getting it wrong can lead to network failures, signal loss, and costly downtime. As networks evolve with high-density fiber optic solutions, understanding polarity becomes essential for optimizing performance. This guide dives deep into the intricacies of MTP/MPO polarity, offering practical insights for professionals. We'll also explore how integrating the right optical modules, such as those from LINK-PP, can simplify deployment and enhance reliability.
➤ Key Takeaways
It is important to understand polarity. This helps signals move the right way in MTP/MPO systems. Always look at the key direction before you connect anything.
Make sure transmit (Tx) and receive (Rx) signals match. This keeps your data safe. Use tables to check each fiber spot.
Pick the right polarity method, like A, B, or C. Choose based on what your network needs. Each method has its own wiring setup. This changes how signals move.
Test your MTP/MPO connections often, especially after changes. This helps you find and fix polarity problems early. Fixing them early stops network trouble.
Write down your MTP/MPO setups. Keeping records helps you solve problems later. It also keeps your fiber network working well.
➤ What is Polarity in MTP/MPO Systems?
Polarity refers to the alignment of optical fibers within a connection to ensure that a transmitter (Tx) on one end communicates correctly with a receiver (Rx) on the other end. In MTP/MPO connectors, which house multiple fibers (typically 8, 12, 24, or more), polarity management is complex due to the array of fibers. These connectors are standardized by organizations like IEC and TIA, and improper polarity can break bidirectional communication, especially in parallel optics used for 40G, 100G, and beyond.
At its core, polarity ensures that each fiber pair matches Tx-Rx paths across the entire link. For instance, in a duplex system, fiber A must connect to fiber B, and vice versa. In MTP/MPO patch cords, this is achieved through keying mechanisms and cable configurations.
➤ Why is Polarity Critical in Fiber Optic Networks?
Signal Integrity: Correct polarity prevents crossed signals, reducing bit errors and ensuring data accuracy.
Network Efficiency: Misaligned polarity can halt network initialization, increasing deployment time.
Scalability: As networks adopt high-density fiber optic solutions, polarity mistakes become more costly to troubleshoot.
Compliance: Adhering to standards like TIA-568 ensures interoperability and future-proofing.
Ignoring polarity can lead to issues like link failure in data center interconnect (DCI) or cloud computing environments, where uptime is critical. Thus, mastering polarity is a best practice for any fiber optic professional.
➤ Polarity Types and Methods: A Comprehensive Overview
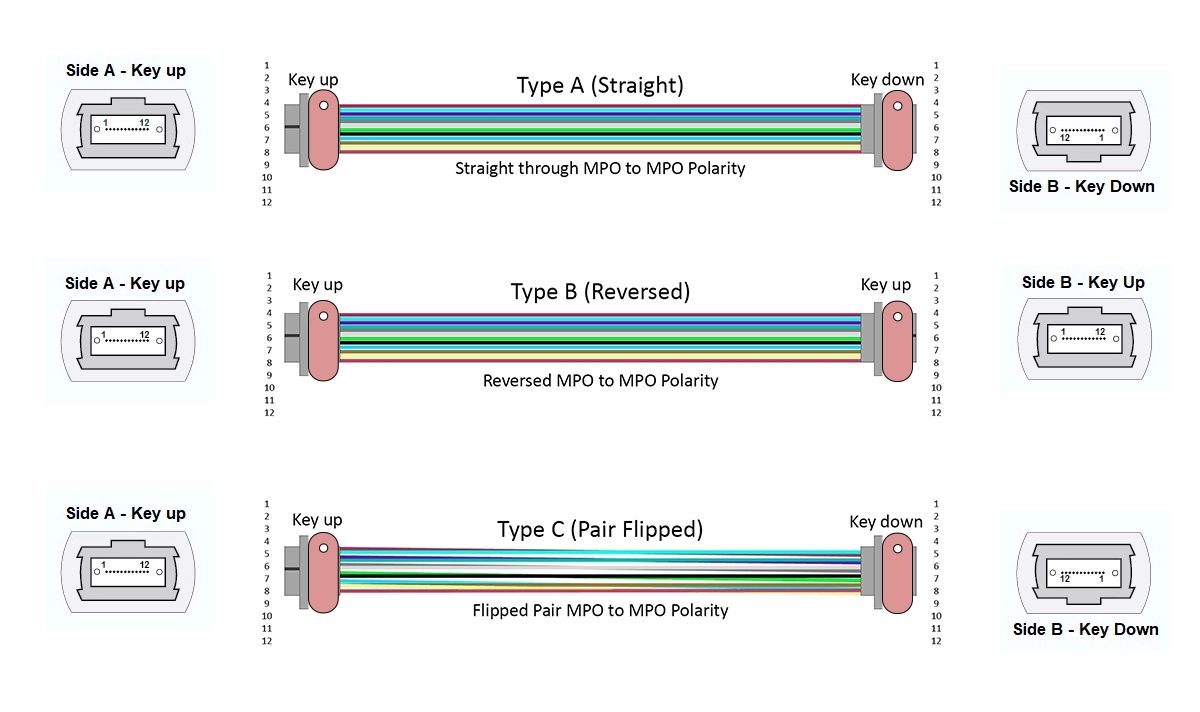
MTP/MPO systems use three primary polarity methods—Type A, Type B, and Type C—each suited for different applications. Understanding these is key to choosing the right MTP polarity for your setup.
Below is a table summarizing the key characteristics:
Polarity Type | Key Configuration | Common Use Case | Pros and Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
Type A | Straight-through; key up to key down on both ends. | Parallel optic links (e.g., 40G-SR4) | Pros: Simple deployment. Cons: Requires specific patch cords. |
Type B | Reversed; key up to key up, with fiber positions flipped. | Duplex applications (e.g., 10G-LR) | Pros: Compatible with standard duplex. Cons: Can be confusing to manage. |
Type C | Pair-flipped; each pair reversed within the connector. | Bidirectional systems (e.g., 100G-CWDM4) | Pros: Reduces cable bulk. Cons: More complex installation. |
These methods align with TIA-568 standards, and selecting the right one depends on factors like network architecture and equipment. For ensuring proper polarity in MTP patch cables, always verify the type labeled on connectors and use polarity testers.
➤ Practical Guide to Choosing the Right Polarity Method
To optimize polarity for MTP/MPO systems, follow these steps:
Assess Network Requirements: Determine if your setup uses parallel optics (e.g., 40G/100G) or duplex links. Parallel optics often require Type A, while duplex systems use Type B.
Map Fiber Paths: Use polarity diagrams to trace Tx-Rx paths, avoiding mismatches. Tools like polarity kits can help.
Select Compatible Components: Ensure cables, adapters, and modules match in polarity. For example, high-performance MTP/MPO trunks from brands like LINK-PP are pre-configured for ease.
Test and Validate: Employ optical testers to verify polarity before deployment, reducing downtime risks.
Common pitfalls include mixing polarity types in a single link—always standardize across your data center fiber infrastructure. For scalable solutions, consider modular polarity systems that allow reconfiguration.
➤ Integrating with Optical Modules: The LINK-PP Advantage
Optical modules, or transceivers, rely heavily on proper polarity to function. These modules convert electrical signals to optical ones and vice versa, and their connectors must align with MTP/MPO polarity schemes. Incorrect polarity can render a module non-functional, emphasizing the need for compatibility.
In high-speed optical modules, polarity is often pre-set based on the application. For instance, QSFP28 modules for 100G networks typically use Type A polarity for SR4 connections, while LR4 modules might require Type C for bidirectional traffic. When selecting modules, verify their polarity requirements in datasheets to avoid connectivity issues in fiber optics.
This is where LINK-PP excels by offering integrated solutions. Their optical modules are engineered with polarity in mind, simplifying deployment. A standout example is the LINK-PP QSFP28-100G-SR4 optical transceiver, designed with built-in Type A polarity alignment for seamless integration into MTP/MPO-based 100G networks. This module supports high-density data center applications and reduces installation errors through clear labeling and compliance with MSA standards. Additionally, LINK-PP SFP28-25G-SR modules provide versatile polarity options for duplex systems, catering to diverse network needs.
By choosing LINK-PP optical modules, professionals can leverage reliable fiber optic connectivity with minimized polarity concerns, enhancing overall network efficiency. Explore their product line for modules that support various polarity methods, ensuring compatibility with your existing infrastructure.
➤ Common Applications and Best Practices
Polarity management is vital in scenarios like:
Data Center Interconnects: For spine-leaf architectures using 400G DR4 modules, Type A polarity ensures reliable parallel links.
Telecommunications: In 5G fronthaul, Type B polarity supports duplex fiber deployments.
Enterprise Networks: Structured cabling with MTP/MPO fiber panels benefits from standardized polarity to reduce maintenance.
Best practices include:
Label all cables with polarity type (e.g., "Type A" or "B").
Use color-coded connectors for quick identification.
Train staff on polarity troubleshooting techniques to speed up repairs.
Source components from reputable brands like LINK-PP, which offer high-quality MTP/MPO solutions with clear documentation.
➤ Conclusion
Understanding polarity in MTP/MPO systems is not just technical jargon—it's a foundational skill for building robust fiber optic networks. By grasping polarity types, selecting appropriate methods, and integrating compatible components like LINK-PP optical modules, you can prevent errors and boost performance. Remember, in the era of cloud computing and IoT expansion, attention to details like polarity pays off in reliability and scalability. Stay proactive: keep learning, testing, and optimizing your setups for seamless connectivity.
For more insights on fiber optic best practices, explore our resources or contact experts to tailor solutions to your needs. Embrace polarity mastery, and let your networks shine!
➤ FAQ
What does polarity mean in MTP/MPO systems?
Polarity shows you how signals travel through your fiber cables. You use polarity to make sure each transmit signal matches the right receive spot. This keeps your network working without errors.
How do you check if your MPO cables have the correct polarity?
You look at the key direction on each connector. You match the transmit and receive positions using a simple table. You test the connection to make sure data flows as expected.
Why do you need different polarity methods?
You use different methods to match your network setup. Method A, B, and C help you connect devices with the right signal flow. You pick the method that fits your system best.
What should you do if you find a polarity problem?
You check each connector and adapter. You use polarity solutions like swapping patch cords or changing key direction. You test the system again to make sure the problem is fixed.
Can you change polarity without replacing all cables?
You can change polarity by using special adapters or patch cords. You do not need to replace every cable. You follow a step-by-step process to switch the signal direction.




