
Ever wonder how a beam of light traveling through a hair-thin glass fiber transforms into your binge-watching session, online gaming marathon, or crystal-clear Zoom call? The magic happens inside a small, often overlooked box in your home or office: the ONU.
This unsung hero of fiber optic internet is the critical endpoint that bridges the gap between your provider's vast light-based network and your familiar electronic devices. Understanding what an ONU is and how it functions can empower you to make better decisions about your home network setup. Let's dive in!
📝 What is an ONU? Breaking Down the Acronym
ONU stands for Optical Network Unit. In simple terms, it's a device that receives the optical signal from your Internet Service Provider (ISP) via a fiber optic cable and converts it into electrical signals that your router, computer, phone, and other devices can understand and use.
Think of it as a highly sophisticated translator. It speaks the "language of light" from the internet backbone and translates it into the "language of electricity" that your gadgets use.
📝 ONU vs. ONT vs. Modem: What’s the Difference?
This is where many people get confused. The terminology often overlaps, but there are subtle distinctions, primarily based on the device's location and final destination.
Feature | ONU (Optical Network Unit) | Traditional Cable Modem | |
|---|---|---|---|
Network Type | Fiber-to-the-X (e.g., FTTB, FTTC) | Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) | Coaxial Cable (Cable Internet) |
Typical Location | In a building's comms room (MDU) | Inside your home/office | Inside your home/office |
Function | Converts optical signal for multiple users | Converts optical signal for a single user | Converts RF signal to digital data |
Medium | Fiber Optic Cable | Fiber Optic Cable | Coaxial Cable |
In practice, the term ONT is often used for a unit that serves a single subscriber (e.g., in your apartment), while ONU can refer to a device that serves multiple users (e.g., in a fiber-to-the-building scenario). However, many ISPs and manufacturers use these terms interchangeably for consumer equipment. Both are fiber optic modems, distinct from traditional DSL or cable modems.
📝 How Does an ONU Work? A Simple Step-by-Step Process
The entire process is a marvel of modern engineering, yet it can be broken down into a few key steps:
Signal Reception: The ONU receives a beam of modulated light carrying vast amounts of data from your ISP's central office (OLT).
Optical-to-Electrical Conversion: A photodiode inside the ONU converts this stream of light photons into an electrical signal.
Processing & Demarcation: The device processes this signal, separating the data into different types (internet, voice, IPTV).
Distribution: Finally, the ONU routes these signals to the appropriate ports—Ethernet for your router or computer, POTS for your analog phone, and coaxial for TV service.
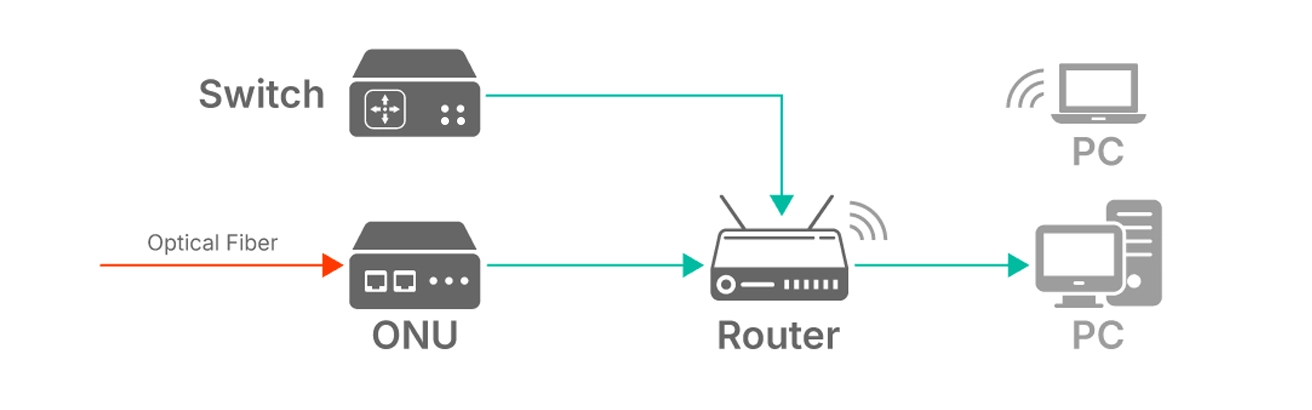
📝 Types of ONUs: Choosing the Right One for Your Needs
Not all ONUs are created equal. Your needs will determine the best type for you. When considering your options, it's crucial to understand the different types of ONU devices available.
Bridge ONU: A basic unit that purely converts the fiber signal to Ethernet. It requires a separate router to create a Wi-Fi network. Ideal for users who want to use their own high-end router.
Wi-Fi ONU (Router ONU): An all-in-one unit that combines the fiber modem, a router, and a wireless access point. This is the most common type provided by ISPs for its convenience and space-saving design.
GPON ONU: Adheres to the Gigabit-capable Passive Optical Network (GPON) standard, a popular technology for ultra-fast broadband access that offers high efficiency and bandwidth.
📝 Key Features to Consider When Buying an ONU
If you're purchasing your own ONU instead of renting from your ISP, here’s what to look for:
Compatibility with ISP: This is the most critical factor. Ensure the device supports the standard (e.g., GPON, EPON) and is approved by your provider.
Port Configuration: How many Ethernet (LAN) ports do you need? Do you require a telephone (VoIP) port for landline service?
Wi-Fi Standards: For all-in-one units, look for Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) for the best performance, range, and ability to handle multiple devices.
Management Interface: A user-friendly interface allows you to change settings, set up port forwarding, and manage your connected devices easily.
Upgrading to a capable ONU can future-proof your connection and potentially improve your network's stability and speed.
📝 The Critical Link: ONUs and Optical Transceivers
To truly understand how an ONU connects, we must talk about its "eyes": the optical transceiver module. This small, hot-swappable component is the physical interface that sends and receives light pulses over the fiber. It handles the crucial tasks of electro-optical conversion (electrical signals to light) and photodetection (light back to electrical signals).
Many modern, carrier-grade ONUs designed for business or fiber internet installation in multi-dwelling units feature pluggable transceiver slots, such as SFP or SFP+. This design offers immense flexibility. Instead of replacing the entire ONU, you can simply swap the optical transceiver to change the fiber connector type (e.g., SC, LC) or upgrade the technology (e.g., from GPON to XGS-PON) for more bandwidth.
For instance, a ONU can be equipped with a specific GPON SFP module, allowing for easy integration into different network setups. This modular approach is a key consideration for future-proofing your network infrastructure, making devices like those from LINK-PP a versatile choice for evolving needs.
📝 Final Thoughts: The Gateway to Your Digital World
The ONU is far more than just a "modem." It is the essential gateway that unlocks the immense potential of fiber optic technology, delivering the high-speed, low-latency internet we have come to rely on. By understanding its role, you can better appreciate the technology behind your screen and make informed choices to optimize your home network.
📝 FAQ
What does an ONU look like?
You usually see an ONU as a small box with indicator lights and several ports. Some models sit outside your home, while others stay inside near where the fiber cable enters.
What happens if your ONU stops working?
If your ONU fails, you lose your internet connection. You should check the power and cables first. If the problem continues, contact your internet provider for help or a replacement.
What devices connect to an ONU?
You can connect routers, computers, smart TVs, and game consoles to an ONU. Most ONUs have Ethernet ports for wired connections. Some models also support phone lines.
What should you do before replacing your ONU?
You should check if your new ONU matches your network type and speed. Ask your internet provider for a list of supported models. Always follow setup instructions to avoid connection issues.




