
As the world embraces 5G technology, telecom networks are evolving rapidly to deliver faster speeds, lower latency, and more reliable connectivity. Understanding what a telecom network is, how it works, and why it matters is essential for enterprises, service providers, and technology professionals planning for next-generation networks.
A telecom network is a system that connects devices and systems to transmit voice, data, and video. It consists of end devices (phones, computers, sensors), transmission media (fiber, copper, wireless links), switching and routing equipment, and management platforms. Together, these components ensure seamless communication across local, regional, and global distances.
📡 What Makes Telecom Networks Critical in the 5G Era?
a. Ultra-High Speed and Low Latency
5G networks provide speeds up to 10 Gbps and latency as low as 1 millisecond. This allows telecom networks to support bandwidth-intensive applications like AR/VR, cloud gaming, autonomous vehicles, and industrial automation.
b. Massive Device Connectivity
A telecom network under 5G can connect millions of devices per square kilometer, enabling the full potential of IoT in smart cities, factories, and transportation systems.
c. Network Slicing and Customization
Modern telecom networks can create multiple virtual networks over a single physical infrastructure. Each slice can be customized for different services, ensuring optimal performance for industrial, healthcare, or emergency communications.
d. Enhanced Reliability and Efficiency
Telecom networks in the 5G era are designed for high availability, ensuring that mission-critical applications remain online with minimal downtime.
📡 How a Telecom Network Works
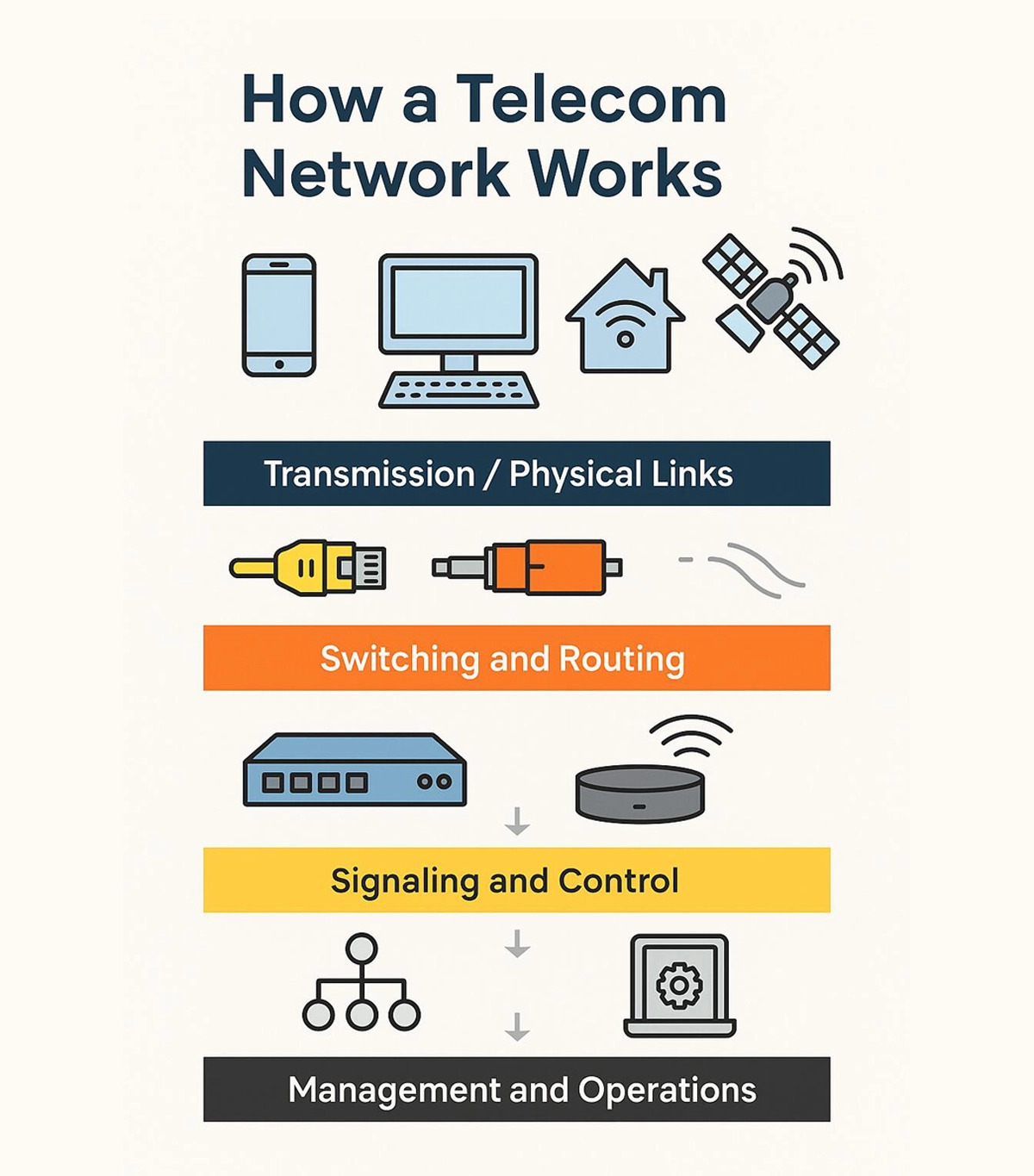
A telecom network operates through multiple layers:
Transmission / Physical Layer: Signals travel via copper cables, optical fibers, or wireless links.
Switching and Routing: Network nodes direct traffic efficiently from source to destination.
Signaling and Control: Protocols manage the setup, maintenance, and termination of communication sessions.
Management and Monitoring: Operations ensure the reliability, performance, and security of the network.
These layers work together to guarantee that data, voice, and video are delivered accurately and quickly.
📡 Challenges Facing 5G Telecom Networks
a. Infrastructure Upgrades
Deploying 5G requires dense small-cell networks, upgraded core and edge components, and expanded fiber or optical transport.
b. Spectrum Management
Efficiently using high-frequency mmWave bands and managing interference is technically challenging and requires careful planning.
c. Cost and Complexity
Building and maintaining 5G networks involves high capital expenditure and coordinated efforts among operators, vendors, and regulators.
d. Security Concerns
Increased connectivity and network slicing introduce new cybersecurity risks, requiring advanced monitoring and protection mechanisms.
📡 LINK‑PP Connectivity Solutions for 5G Networks
Reliable hardware is essential for modern telecom networks. LINK‑PP offers high-performance connectivity solutions:
RJ45 Connectors – for high-speed Ethernet connectivity in edge devices, base stations, and industrial networking.
Optical Transceivers (SFP/SFP28/QSFP) – support high-speed, low-latency links in 5G backhaul, data centers, and backbone networks.
Industrial-Grade Components – built to withstand extreme temperatures, vibration, and EMI, suitable for outdoor or industrial 5G deployment.
These products ensure signal integrity, interoperability, and network reliability, supporting robust telecom infrastructures.
📡 Future Outlook
5G adoption is driving telecom networks toward greater speed, capacity, and versatility. Edge computing, IoT, and smart industry applications will continue to expand network demands. Telecom networks must adapt to deliver high performance, low latency, and secure connectivity. LINK‑PP’s components remain vital for building scalable, reliable, and future-ready telecom networks.
📡 Conclusion
Telecom networks are the backbone of digital communication, connecting devices and enabling global information exchange. In the 5G era, these networks present both opportunities—faster speeds, massive connectivity, network slicing—and challenges—infrastructure complexity, spectrum management, and security. High-quality connectivity solutions from LINK‑PP, including RJ45 connectors and optical transceivers, play a key role in ensuring that modern telecom networks meet the demands of today and tomorrow.




