
🔄 Introduction: The Growing Power of Ethernet
Power over Ethernet (PoE) has revolutionized how modern networks deliver both data and electrical power over a single cable.
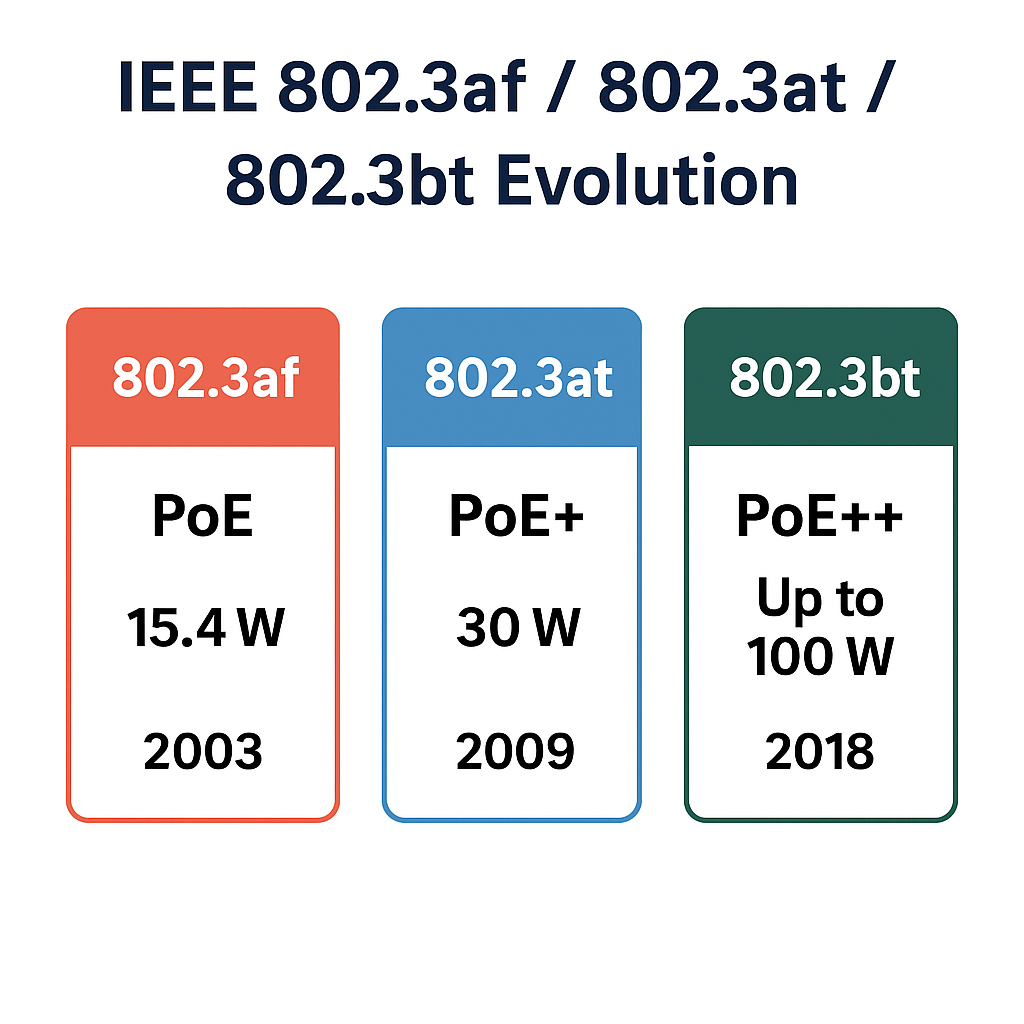
From powering IP phones to high-performance access points and displays, PoE standards—IEEE 802.3af, 802.3at, and 802.3bt—define how much power can safely and efficiently travel through Ethernet cables.
As connected devices demand higher wattage, PoE technology has evolved to keep pace — moving from PoE (15.4W) to PoE+ (30W) and finally PoE++ (up to 100W).
🔄 Overview of PoE Standards
Attribute / Standard | IEEE 802.3af | IEEE 802.3at | IEEE 802.3bt (Type 3) | IEEE 802.3bt (Type 4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Common Name | PoE | PoE+ | PoE++ | PoE++ |
IEEE Release Year | 2003 | 2009 | 2018 | 2018 |
PSE Output Power | 15.4W | 30W | 60W | 100W |
PD Power Available | 12.95W | 25.5W | 51W | 71–90W |
Power Pairs Used | 2 pairs | 2 pairs | 4 pairs | 4 pairs |
Typical Cable Type | Cat5 or higher | Cat5e or higher | Cat5e/Cat6 | Cat6/Cat6A |
Key Applications | VoIP phones, IP cameras, wireless APs | PTZ cameras, dual-band APs, thin clients | Wi-Fi 6 APs, LED lighting, building automation | Digital signage, IoT gateways, mini PCs |
🔄 Technical Comparison and Power Delivery
1. IEEE 802.3af (PoE)
Introduced in 2003, the first official Power over Ethernet standard.
Delivers up to 15.4W from the Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE), with 12.95W available at the Powered Device (PD) after cable losses.
Uses two pairs of Ethernet wires for power and data.
Ideal for low-power devices like IP phones and basic cameras.
2. IEEE 802.3at (PoE+)
Released in 2009 to support higher-power devices.
Provides up to 30W from the PSE and 25.5W to the PD.
Still uses two pairs, but increases the current flow per pair for more wattage.
Common in PTZ surveillance cameras, dual-radio access points, and touch panels.
3. IEEE 802.3bt (PoE++)
Published in 2018, this latest standard introduces Type 3 and Type 4 classes.
Utilizes all four wire pairs, significantly improving efficiency and reducing heat loss.
Supports up to 100W output, enabling entirely new classes of powered devices:
4K/8K displays
LED lighting systems
Industrial IoT gateways
Mini PCs and NUCs
Includes intelligent power negotiation and cable temperature management to ensure safe operation.
🔄 Backward Compatibility
All PoE standards are backward compatible:
A PoE++ (802.3bt) switch can safely power PoE+ or PoE devices, automatically adjusting voltage and current.
However, older PoE or PoE+ switches cannot power newer PoE++ devices requiring >30W.
This flexibility makes network upgrades seamless — existing infrastructure can evolve gradually.
🔄 Real-World Applications
Application Type | IEEE 802.3af (PoE) | IEEE 802.3at (PoE+) | IEEE 802.3bt (PoE++) |
|---|---|---|---|
IP Phones / Entry Cameras | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
Wireless Access Points | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
PTZ Security Cameras | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
LED Lighting / Displays | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
Industrial IoT Gateways | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
Mini PCs / NUCs | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
🔄 LINK-PP PoE Magnetics Solutions

To ensure reliable signal transmission and power efficiency, LINK-PP provides a full range of PoE magnetics modules and RJ45 connectors compatible with all IEEE PoE standards.
🔹 LPJG0926HENL — PoE+ RJ45 Jack, IEEE 802.3af/at Compliant
🔹 LPJK6072AONL — PoE RJ45 with Integrated Magnetics for WAPs
🔹 LPJMP95282AGNL — PoE++ (802.3bt) Magnetics Jack for 10G Applications
🔹 LP41223NL — PoE+ LAN Transformer for 10/100Base-T Networks
All products feature high isolation voltage, low insertion loss, and excellent EMI suppression, supporting robust PoE system design for telecom, industrial, and networking equipment.
👉 Explore LINK-PP’s full PoE portfolio: www.l-p.com
🔄 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Is IEEE 802.3bt backward compatible with PoE and PoE+?
Yes. IEEE 802.3bt equipment automatically detects and adjusts to legacy devices, ensuring safe interoperability across all PoE generations.
2. Can PoE+ or PoE++ damage non-PoE devices?
No. All IEEE PoE standards include power detection and negotiation mechanisms. Power is only delivered when a valid powered device (PD) signature is detected.
3. What cable category is recommended for PoE++?
For optimal power efficiency and minimal heating, use Cat6 or Cat6A cables, especially for 4-pair (802.3bt) deployments.
4. How far can PoE transmit power?
All PoE standards support up to 100 meters (328 feet) per Ethernet segment, following the IEEE 802.3 specifications.
5. What’s the main advantage of upgrading to IEEE 802.3bt (PoE++)?
It enables high-power devices such as LED lighting, displays, and mini computers to operate through Ethernet alone — simplifying installation, reducing costs, and centralizing power management.
🔄 Conclusion
From IEEE 802.3af’s modest 15W to 802.3bt’s powerful 100W, the PoE family has evolved to meet the rising energy demands of today’s smart networks.
Whether you’re designing access points, IP surveillance, or industrial automation systems, understanding these standards ensures optimal compatibility and performance.
LINK-PP’s PoE Magnetics Solutions empower engineers to build reliable, efficient, and fully compliant PoE systems—driving the next generation of intelligent network infrastructure.




