
🌐 Introduction: What is IEEE 802.3af?
IEEE 802.3af, commonly known as Power over Ethernet (PoE), is the original international standard that enables electrical power to be transmitted alongside data over standard Ethernet cables. Ratified in 2003, this technology allows devices such as IP phones, wireless access points, and cameras to receive both power and data through a single Cat5 (or higher) cable — eliminating the need for separate power adapters.
🌐 Technical Overview and Power Specifications
The IEEE 802.3af standard defines how power is delivered from a Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE), such as a PoE switch or injector, to a Powered Device (PD) like an IP camera or VoIP phone.
Maximum power output at PSE: 15.4 W
Available power at PD (after cable loss): 12.95 W
Operating voltage: 44–57 V DC (nominal 48 V)
Supported cable: Cat5 or higher (using two of the four twisted pairs)
The power is transmitted via the spare pairs (pins 4–5 and 7–8) or data pairs (pins 1–2 and 3–6), depending on the configuration.
🌐 Key Features and Advantages
Single Cable Solution – Reduces installation complexity and cost by combining power and data in one cable.
Centralized Power Management – Power can be controlled, monitored, and managed centrally through the Ethernet switch.
Safe Power Detection – The system intelligently detects whether a device supports PoE before supplying power, preventing damage to non-PoE equipment.
Scalable and Reliable – Simplifies network expansion and ensures consistent performance across enterprise and industrial environments.
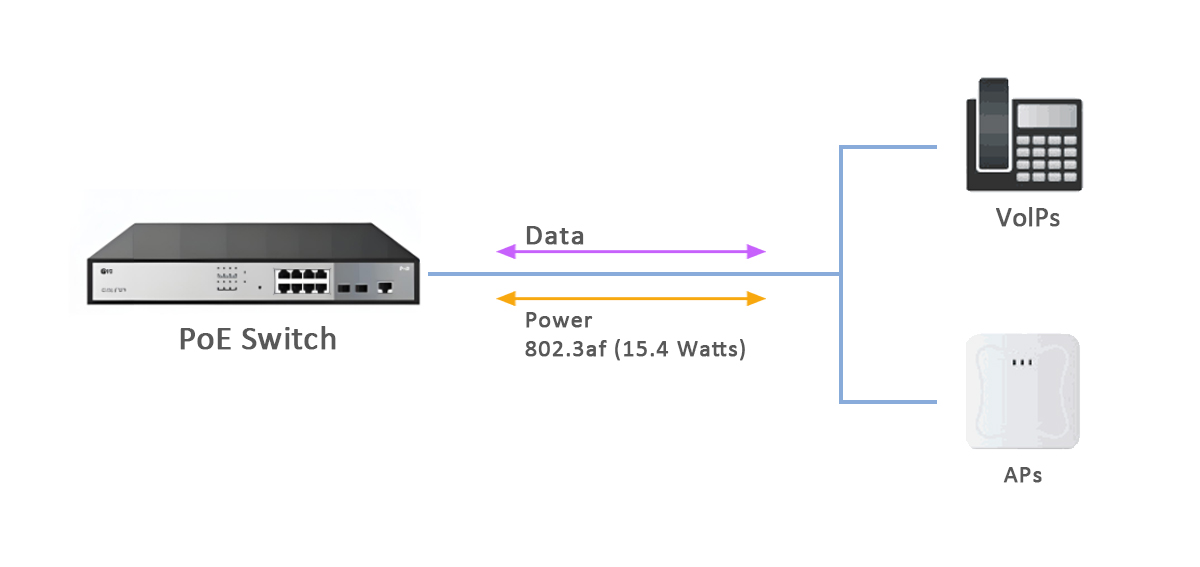
🌐 Typical Applications of IEEE 802.3af PoE
The 802.3af standard is ideal for low to medium-power devices, including:
IP Phones – Unified communications without external adapters.
Wireless Access Points (WAPs) – Streamlined deployment in ceilings or remote areas.
Surveillance IP Cameras – Reliable power supply for security systems.
IoT Gateways and Sensors – Simplified installation in smart building systems.
By delivering nearly 13W of usable power, IEEE 802.3af PoE meets the needs of most lightweight network endpoints.
🌐 PoE vs PoE+ (IEEE 802.3at): What’s the Difference?
While IEEE 802.3af provides up to 15.4 W of power, the later IEEE 802.3at (PoE+) standard doubles this capability to 30 W, enabling higher-performance devices such as PTZ cameras and advanced Wi-Fi 6 access points.
In practice:
PoE (802.3af): Ideal for low-power devices (phones, basic APs)
PoE+ (802.3at): Designed for higher-power devices (HD cameras, multi-radio APs)
Both standards are backward compatible, meaning PoE+ switches can safely power PoE devices.
🌐 LINK-PP PoE Solutions for IEEE 802.3af Networks

To achieve stable power and data transmission in accordance with IEEE 802.3af, high-quality Ethernet magnetics are essential.
, a leading manufacturer of network connectivity components, offers reliable and cost-effective PoE magnetic solutions.
🔹 PoE RJ45 Magnetics Jack:
Designed for IEEE 802.3af/at applications, featuring integrated magnetic transformers that ensure isolation, noise suppression, and consistent 15.4W power delivery.🔹 PoE Magnetics Transformer Modules:
The LINK-PP PoE LAN Transformer provides reliable data transmission and efficient Power over Ethernet (PoE) functionality.
By using LINK-PP components, OEMs and network integrators can ensure high reliability, superior EMI performance, and full IEEE compliance.
🌐 Conclusion
The IEEE 802.3af (PoE) standard revolutionized Ethernet networking by combining power and data transmission in a single, efficient infrastructure. It remains the foundation of modern PoE technologies, enabling cost-effective, flexible, and scalable network deployments worldwide.
For businesses and integrators seeking reliable hardware for PoE-enabled designs, LINK-PP’s PoE RJ45 Magnetics and PoE Transformer provide robust performance, ensuring safe and efficient power delivery across a wide range of devices.




