Power Over Ethernet (PoE) is a revolutionary technology that combines power and data transmission through a single Ethernet cable. This simplifies connectivity for modern devices. PoE eliminates the need for separate power outlets, making it an essential solution in environments like offices, schools, and hospitals. Its reliability supports industrial applications, powering devices such as IP cameras and sensors, even in harsh conditions.
How Power Over Ethernet Works

Mechanism of PoE
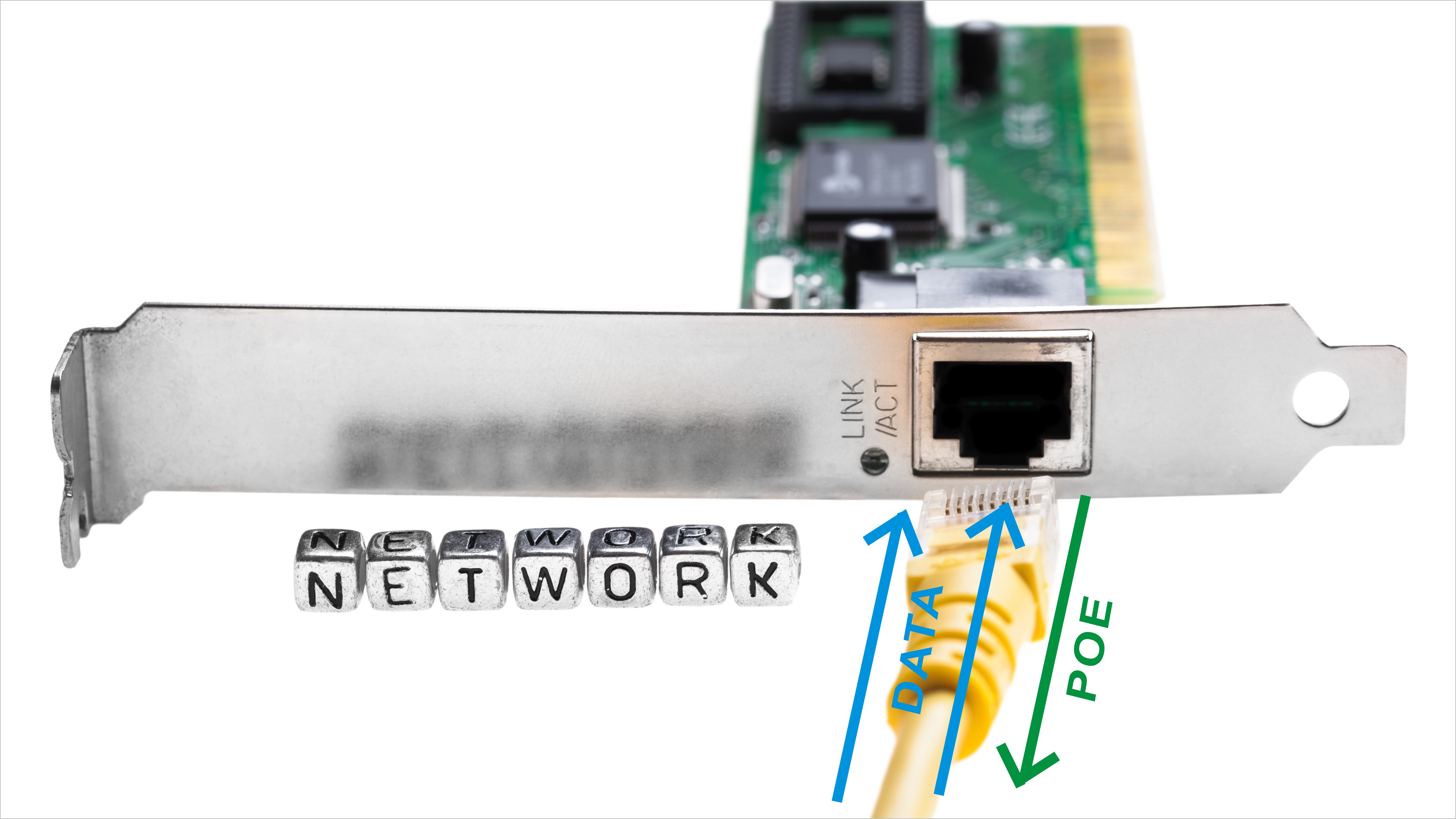
Power over Ethernet (PoE) enables the transmission of both electrical power and data over standard Ethernet cables, such as Cat5e or Cat6. This technology eliminates the need for separate power sources, simplifying installations and reducing clutter. The process begins with Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE), such as a PoE-enabled switch or injector, which injects electrical current into the Ethernet cable. The cable then delivers this current to a Powered Device (PD), such as an IP camera or VoIP phone.
Inside the PD, a splitter separates the power from the data to ensure they do not interfere with each other. This separation allows the device to operate efficiently while maintaining reliable data transmission. PoE systems are designed to deliver power safely, typically at 48 volts DC, and automatically stop power delivery when the PD is disconnected. This mechanism ensures energy efficiency and prevents waste.
Components of PoE Systems
A PoE system consists of several key components that work together to deliver power and data seamlessly:
Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE): This component provides power to the Ethernet cable. Examples include PoE switches and injectors.
Powered Devices (PD): These devices receive power and data from the Ethernet cable. Common examples are wireless access points, IP cameras, and smart lighting systems.
Ethernet Cables: These cables transmit both power and data. Category 5e cables are the minimum requirement, but Category 6 or 6A cables are recommended for better performance.
Splitters: These are used in non-PoE devices to separate power from data, enabling compatibility with PoE systems.
The interaction between these components ensures that PoE systems operate efficiently, even in complex environments. For instance, the universal connectivity grid (UCG) design simplifies cable routing and enhances flexibility during installation.
PoE Standards
Standard | Power | Suitable Applications |
|---|---|---|
IEEE 802.3af (PoE) | Up to 15.4W per port | Low-power devices (IP cameras, VoIP phones) |
IEEE 802.3at | Up to 25.5W per port | Advanced IP cameras, video-conferencing equipment |
IEEE 802.3bt (PoE++/4PPoE) | Up to 51W (Type 3) and 71.3W (Type 4) per port. | High-demand devices (laptops, digital signage) |
IEEE 802.3bu | up to 50W | Automotive and industrial applications |
These standards ensure compatibility and safety across PoE-enabled devices, allowing you to choose the right solution for your needs.
Compatibility with Non-PoE Devices
You might wonder if PoE works with non-PoE devices. The answer is yes, but with some additional components. A PoE splitter can separate power from data, enabling non-PoE devices to function seamlessly. PoE injectors also provide a solution by delivering power to devices that lack built-in PoE support. PoE switches, on the other hand, automatically detect compatible devices and supply power without damaging non-PoE equipment.
However, keep in mind that cable length can affect PoE performance. Long cables may establish Ethernet links but fail to deliver sufficient power. Devices with higher power requirements may also limit the effective cable length. To ensure optimal performance, consider using high-quality components like LINK-PP's Integrated RJ45 Connectors and LAN Transformers, which support PoE functionality and enhance reliability.
💡 Tip: When integrating PoE into your network, always verify the power requirements of your devices and the capabilities of your PoE equipment.
Advantages of Power Over Ethernet
Cost Savings: Reduces expenses for electrical outlets and professional installers by delivering power over existing network cabling.
Installation Flexibility: Allows network devices to be placed where power outlets are unavailable, optimizing coverage for Wi-Fi access points and surveillance cameras.
Centralized Power Management: Enables remote power cycling and monitoring of devices via the network switch or midspan, improving uptime and simplifying maintenance.
Enhanced Safety: Low-voltage (typically 44–57 V DC) operation reduces risk of electrical hazards compared to AC power installations.
Scalability: Supports a wide range of devices (VoIP phones, LED lighting, building sensors) without separate power infrastructure, simplifying network expansion.
Disadvantages of Power Over Ethernet
Power Limitations: PoE systems have power delivery limits, which can restrict their use for high-energy devices. For example, the IEEE 802.3af standard provides up to 15.4 watts, while the more advanced IEEE 802.3bt standard delivers up to 90 watts. Devices like laptops or large displays often require more power than PoE can supply.
Initial Costs: While PoE simplifies installations, the upfront costs can be higher compared to traditional setups. PoE switches and injectors are more expensive than standard network equipment. If you’re upgrading an existing network, you might also need to replace non-PoE-compatible devices, adding to the expense. Although PoE reduces long-term operational costs, the initial investment can be a barrier for small businesses or budget-conscious projects. Planning your network carefully can help you balance these costs with the benefits of PoE.
Security Concerns: PoE networks introduce potential cybersecurity risks that you should consider. Modernizing PoE systems for physical security, such as IP cameras, can expose vulnerabilities.
🔒 Tip: Regularly audit your PoE network to identify and address potential vulnerabilities before they become serious issues.
LINK-PP’s Integrated RJ45 Connectors and LAN Transformers Supporting PoE
Models like the LPJ1253AHNL and LPJM96282AGNL are engineered for PoE and PoE+ applications, featuring integrated magnetics that ensure signal integrity and compliance with IEEE standards.
These connectors support speeds up to 10G Base-T and are suitable for devices like digital cameras, routers, and network firewalls.
LINK-PP's LAN transformers are designed to handle PoE, PoE+, and PoE++ applications, ensuring efficient power transmission and minimal signal loss.
They support various speeds, including 10/100M/1/2.5/5/10G, making them versatile for different network requirements.
By integrating these components, LINK-PP provides reliable solutions for modern networking needs, ensuring compatibility with the latest PoE standards and applications.


