
In today’s interconnected digital landscape, securing network traffic isn't just an option—it's a necessity. At the heart of many robust security architectures lies a fundamental, yet powerful tool: the Access Control List (ACL). Whether you're a network administrator or an IT enthusiast, understanding ACLs is crucial for implementing effective security policies. This guide will demystify ACLs, explore their types and applications, and even touch upon their role in modern high-speed infrastructure, including insights from industry leaders like LINK-PP.
✅ Key Takeaways
Access control lists (ACLs) help you choose who can see or change things on a computer. This keeps your data safe.
Each ACL has access control entries (ACEs). These say what users or groups can do, like read or write files.
You should check your ACLs often. Make sure they fit what you need now. Take out any extra entries to keep things secure.
There are different kinds of ACLs for filesystems and networks. Each one helps protect data and control who gets in.
Using both access control lists and role-based access control together makes your systems safer.
✅ What is an Access Control List (ACL)?
An Access Control List (ACL) is a set of predefined rules used to control network traffic by filtering data packets entering or leaving a network interface. Think of it as a bouncer at a club, meticulously checking IDs against a guest list. The ACL, residing in routers, switches, or firewalls, inspects packet headers (like source/destination IP addresses, protocol, and port numbers) and decides whether to permit or deny passage.
ACLs are the cornerstone of network security and traffic management, providing a first line of defense by:
Enhancing Security: Blocking unauthorized access and potential threats.
Managing Traffic: Prioritizing critical applications (e.g., VoIP) and controlling bandwidth usage.
Improving Performance: Reducing unnecessary traffic on specific network segments.
✅ Types of ACLs: Standard vs. Extended
ACLs are primarily categorized based on the granularity of control they offer. The right choice depends on your specific network access control list configuration needs.
Feature | Standard ACL | Extended ACL |
|---|---|---|
Identification | Uses source IP address only. | Uses source & destination IP, protocol, and port numbers. |
Control Level | Basic, broad filtering. ("Who can access?") | Granular, precise filtering. ("Who can access what, and how?") |
Rule Range | Typically 1-99, 1300-1999 (Cisco-based). | Typically 100-199, 2000-2699 (Cisco-based). |
Best Use Case | Simple blocking/permitting of traffic from entire networks. | Securing specific services (e.g., HTTPS, SSH) between hosts. |
Placement | Close to the destination. | Close to the source of traffic. |
💡 Pro Tip: For most modern security needs, Extended ACLs are recommended due to their precision. Misconfigured ACLs can lead to security gaps or network outages, so thorough planning is key.
✅ How ACLs Work: The Packet-Filtering Process
The process is sequential and deterministic, often called "first-match." The device compares the packet against each rule in the ACL, from top to bottom.
Packet Arrival: A data packet arrives at an interface with an applied ACL.
Rule Evaluation: The router/switch checks the packet's header against the first ACL rule.
Match & Action:
If it matches a permit rule, the packet is forwarded.
If it matches a deny rule, the packet is dropped.
No Match: If the packet doesn't match any explicit rule, it hits the implicit "deny all" statement at the end of every ACL and is discarded. This is a critical security feature to remember.
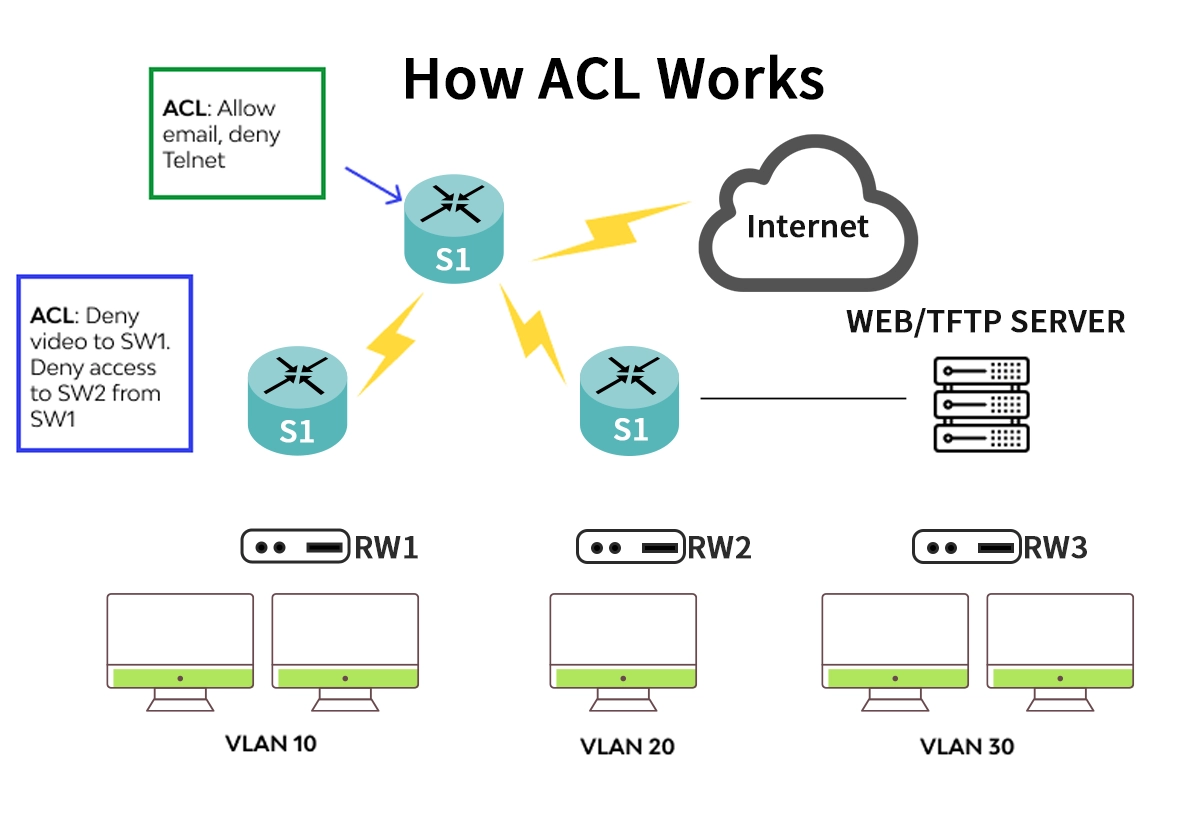
✅ Key Applications of ACLs in Modern Networks
Beyond simple filtering, ACLs enable sophisticated network management:
Security Policy Enforcement: Restrict access to sensitive subnets (e.g., finance servers) or block known malicious IPs.
Route Filtering: Control which routing updates are sent or received, improving network stability.
Quality of Service (QoS): Classify and mark traffic for priority handling, essential for optimizing network performance with ACLs.
Virtual Terminal Access: Limit which IP addresses can establish telnet or SSH sessions to the network device itself.
For organizations implementing a zero-trust network model, ACLs are indispensable tools for enforcing the principle of least privilege at the network layer.
✅ ACLs and High-Speed Network Infrastructure: The Role of Optical Modules
As network speeds skyrocket with the adoption of 400G and beyond, the efficiency of packet processing becomes paramount. This is where high-performance hardware, including advanced optical modules, intersects with ACL functionality.
High-speed switches and routers performing ACL checks at line rate require immense processing power. The optical modules that facilitate these connections must provide flawless, low-latency data transmission to ensure security policies don't become a bottleneck. In data centers and service provider networks, configuring ACL for data center security often involves securing traffic flowing through these high-capacity links.
This is where partnering with a reliable hardware provider makes a difference. For instance, LINK-PP's high-performance optical transceivers are engineered to support the demanding requirements of modern, ACL-secured networks. A module like the LINK-PP 400G QSFP-DD DR4 ensures reliable and secure high-density connectivity, providing the stable foundation upon which granular ACL policies are executed without compromising speed. Implementing precise ACLs to manage east-west traffic in a data center is more effective when the underlying hardware, such as LINK-PP's 100G/400G modules, guarantees integrity and performance.
✅ Best Practices for Implementing ACLs
Plan Before Configuring: Document your security goals and traffic flows.
Follow the Principle of Least Privilege: Start with "deny all," then add only necessary permit rules.
Place ACLs Strategically: Place extended ACLs as close to the source as possible to conserve network resources.
Be Specific with Rules: Use specific IP addresses and port ranges instead of "any" where possible.
Organize & Optimize Rules: Place the most frequently matched rules at the top to improve device efficiency.
Test Thoroughly: Apply ACLs in a test environment first and monitor logs (like ACL hits) after deployment.
Review Regularly: Periodically audit ACLs to remove obsolete rules and adapt to new threats.
Avoiding common mistakes, such as overly permissive rules or incorrect rule order, is vital for maintaining a strong security posture and preventing common ACL configuration errors.
✅ Conclusion
Access Control Lists (ACLs) remain a vital, foundational technology for network security and management. From basic traffic filtering to enabling complex, zero-trust architectures, their utility is undeniable. As networks evolve with higher speeds and greater complexity, the synergy between intelligent software policies (like ACLs) and robust hardware (exemplified by providers like LINK-PP) becomes increasingly critical.
By mastering ACL concepts and implementing ACL best practices, you can build more secure, efficient, and controllable networks. Remember, a well-designed ACL is not just a filter; it's a clear statement of your network's security policy.
✅ FAQ
What is an access control list?
You use an access control list to set rules for who can see or change files and network resources. This helps you keep your data safe from unwanted access.
What does an access control entry do?
An access control entry gives specific rights to a user or group. You use it to allow or deny actions like reading, writing, or running files.
What problems can happen with access control lists?
You might set the wrong permissions. This can let people see or change things they should not. Always check your rules to avoid mistakes.
What is the difference between filesystem and network access control lists?
Filesystem ACL | Network ACL |
|---|---|
Controls files | Controls traffic |
Sets file rights | Filters data |
What should you check when managing access control?
You should review your rules often. Remove old entries. Make sure only trusted users have access. This keeps your system safe.


