
In the relentless pursuit of faster data processing and analysis, modern data centers face an immense challenge: moving colossal amounts of information between servers, storage, and accelerators at unprecedented speeds. While Ethernet is the common workhorse, there's a specialized technology that dominates where raw speed and ultra-low latency are non-negotiable: InfiniBand.
This article dives deep into what makes InfiniBand the undisputed champion for AI workloads, machine learning training, and high-performance computing (HPC) clusters.
➣ Key Takeaways
InfiniBand is a fast and steady network technology. It is used in big data centers and supercomputers. It helps move data quickly with very little delay.
It uses a special way called RDMA. RDMA sends data straight between devices. This makes talking between devices faster and saves energy.
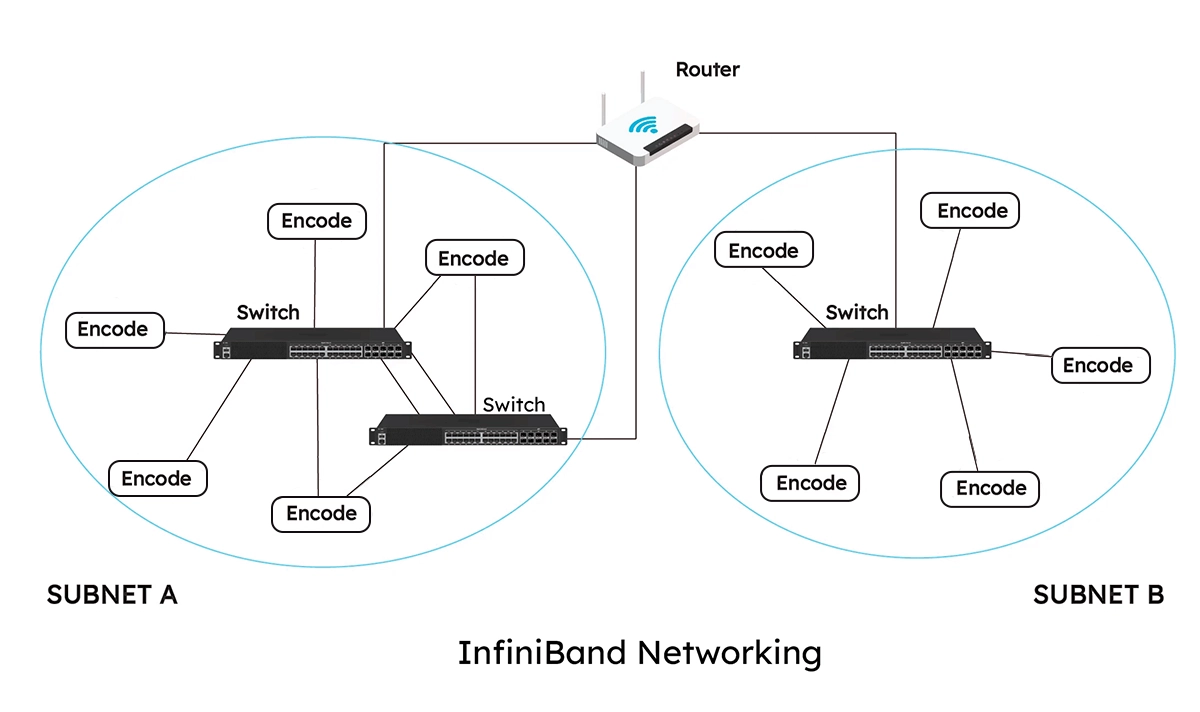
InfiniBand networks can grow by adding more devices. They do not slow down when more devices are added. This makes them good for small and big setups.
InfiniBand is much faster than Ethernet. It has lower waiting times too. This makes it great for high-performance computing and storage jobs.
Many scientists, engineers, and companies use InfiniBand. They use it for hard jobs like science research, cloud computing, and quick data storage.
➣ What Exactly is InfiniBand?
InfiniBand (IB) is a high-performance, channel-based interconnect architecture designed for data throughput and scalability in clustered computing. Unlike Ethernet's packet-switched network, InfiniBand uses a switched fabric topology, meaning every device can communicate with every other device simultaneously with minimal delay.
Its design philosophy is built from the ground up for one purpose: to move data as efficiently as possible between the critical components of a compute cluster.
➣ InfiniBand vs. Ethernet: A Head-to-Head Comparison
Why choose InfiniBand over a more common technology like high-speed Ethernet? The answer lies in the specific demands of cutting-edge computational tasks. The following table breaks down the key differences:
Feature | InfiniBand | High-Speed Ethernet |
|---|---|---|
Latency | Extremely Low (nanoseconds) | Higher (microseconds) |
Throughput | Extremely High (HDR 400Gbps, NDR 800Gbps) | High (400GbE available) |
Protocol Efficiency | Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) enables direct memory-to-memory transfer, bypassing the CPU & OS. | Relies on TCP/IP stack, which involves more processing overhead and CPU utilization. |
Traffic Management | Lossless Fabric with built-in congestion control. No packet drops. | Can be lossy, relying on protocols like PFC to manage congestion, which can add complexity. |
Primary Use Case | AI/ML, HPC, Scientific Simulation (performance-critical) | General Data Center, Cloud, Enterprise Networking (versatility-critical) |
Cost | Higher | Generally Lower |
➣ Where InfiniBand Truly Shines: Key Applications
InfiniBand's architecture makes it the backbone of the world's most powerful supercomputers and AI research facilities.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Training massive neural networks requires synchronizing data across thousands of GPUs. InfiniBand’s ultra-low latency and high bandwidth prevent GPUs from sitting idle, dramatically reducing training times from weeks to days.
High-Performance Computing (HPC): Scientific simulations in fields like genomics, climate modeling, and astrophysics involve trillions of calculations. InfiniBand's lossless fabric and RDMA ensure these calculations happen in perfect sync without data transfer bottlenecks.
High-Frequency Trading (HFT): In trading, microseconds matter. The near-instantaneous data transmission provided by InfiniBand can provide a significant competitive advantage.
➣ The Unsung Hero: Why Quality Optical Transceivers Matter
A high-performance InfiniBand network is only as strong as its weakest link. This is where optical transceivers come in. These small but mighty devices convert electrical signals from the switch into optical signals for transmission over fiber optic cables.
Using reliable, high-quality InfiniBand optical transceivers is critical for maintaining signal integrity, minimizing latency, and ensuring error-free data transmission over longer distances. Inferior optics can lead to data corruption, retransmissions, and increased latency, completely negating the advantages of your expensive InfiniBand infrastructure.
For a seamless and optimized network, it's essential to choose compatible, high-performance optics from a trusted supplier.
➣ Optimizing Your InfiniBand Fabric with LINK-PP
This is where LINK-PP establishes itself as a key partner for data center operators. LINK-PP provides a comprehensive range of high-compatibility, performance-optimized optical transceivers designed specifically for modern InfiniBand infrastructures.
For instance, integrating the LINK-PP QSFP-DD NDR 400G InfiniBand Optical Transceiver into your Mellanox Quantum-2 platform ensures you achieve the full 400Gbps (HDR) throughput with exceptional reliability. This module is engineered for low power consumption and high thermal stability, which are essential for maintaining performance in dense server racks.
When you're looking for reliable InfiniBand compatible transceivers or a cost-effective 400G optical module, LINK-PP offers solutions that meet rigorous OEM standards without the premium price tag, ensuring your network performs at its peak without unnecessary overhead.
➣ Conclusion: Is InfiniBand Right for You?
InfiniBand is not a one-size-fits-all solution. For most general-purpose enterprise networking, high-speed Ethernet remains a versatile and cost-effective choice.
However, if your business is pushing the boundaries of what's possible in AI, deep learning, or large-scale scientific computing, the performance benefits of InfiniBand are undeniable. Its superior latency, bandwidth, and efficiency directly translate into faster results, higher productivity, and a stronger competitive edge.
Ready to unlock the full potential of your high-performance computing cluster?
➡️ Contact LINK-PP expert to find the perfect InfiniBand solution for your infrastructure. Ensure your network's backbone is built with reliability and speed in mind.
➣ FAQ
What makes InfiniBand faster than Ethernet?
InfiniBand uses RDMA and its own protocol. Devices send data right to memory. The network skips extra steps that Ethernet needs. This means InfiniBand has less waiting and more speed.
Can InfiniBand work with Ethernet devices?
InfiniBand cannot link straight to Ethernet devices. Each network uses different hardware and rules. Some places use gateways or adapters to connect both. These tools help move data between InfiniBand and Ethernet.
Is InfiniBand only for supercomputers?
InfiniBand works best in supercomputers and labs. Many data centers use it for storage and cloud jobs. Small offices do not need InfiniBand. Ethernet is enough for their work.
Does InfiniBand need special cables?
Yes, InfiniBand uses its own cables. These cables help keep speeds high and waiting low. The cables keep data safe and moving fast. Users must pick the right cables for their InfiniBand gear.
How does InfiniBand keep data safe?
InfiniBand checks for mistakes when sending data. The network uses backup paths if one path breaks. This helps stop data loss. Many companies trust InfiniBand for big jobs because it keeps links steady.




