
A local area network (LAN) connects your devices—like computers, printers, and phones—within a small area such as your home or office. You use a LAN to share files, access printers, and communicate quickly. Home WiFi and office networks are common examples. Fast, secure LANs help reduce delays and keep your data safe, especially as more devices connect every day.
🖧 What Is a Local Area Network (LAN)?
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a network system that connects computers and devices within a limited geographic area—such as a home, office, factory, or campus—to share resources like data, printers, and internet access. LANs are the foundation of most internal IT environments and are essential for efficient communication, collaboration, and data transfer within a defined space.
In enterprise and industrial applications, LANs are often built with high-speed Ethernet connections, robust switches, and reliable connectors and ethernet transformers—key components that LINK-PP specializes in providing.
🖧 Common LAN Examples
You see local area networks in many places every day. Here are some common examples:
Home Wi-Fi network: You connect your phones, laptops, smart TVs, and gaming consoles to the same wireless network at home. This setup lets you share internet access and stream videos easily.
Office network: In a business, employees use a LAN to access shared printers, files, and databases. This network helps everyone work together and keeps company data secure.
School or campus network: Schools use LANs to link classrooms, labs, and offices. Students and teachers can access learning materials, submit assignments, and use shared resources.
Small business network: Shops and small offices use LANs to connect cash registers, computers, and security cameras for smooth daily operations.
LANs form the backbone of modern digital life. Whether you work, study, or relax at home, a local area network helps you stay connected and productive. In industries ranging from manufacturing to telecom, a stable LAN infrastructure is non-negotiable. LINK-PP supports this reliability with high-performance integrated magnetics modules used in LAN switch and router designs.
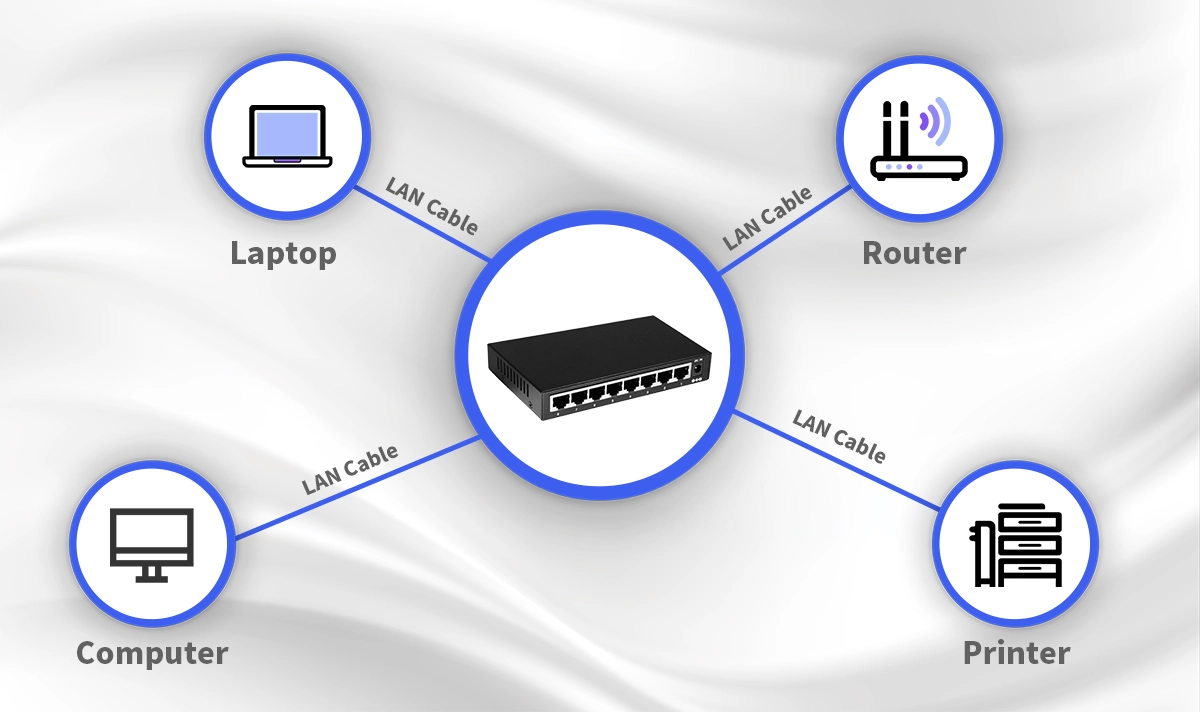
🖧 Key Components of a LAN
To set up a LAN, you need several key pieces of equipment. Each device plays a specific role in building your network and keeping it running smoothly.
Switches: These devices connect multiple computers or printers within your LAN. A network switch directs data to the right device, reducing congestion and improving speed.
Routers: Routers link your LAN to other networks, such as the internet. They manage traffic between your local network and the outside world.
Access Points: You use these to add wireless capability to your LAN. Access points let laptops, phones, and tablets connect without cables.
Ethernet Cables: These cables form the backbone of a wired LAN. They carry data quickly and reliably between devices.
Network Interface Cards (NICs): Every device on your LAN needs a NIC to connect, whether wired or wireless.
Component | Function |
|---|---|
Switch | Directs data between devices within the LAN |
Router | Connects the LAN to external networks like the internet |
Ethernet Cables | Physical wiring (e.g., Cat5e/Cat6) that links devices |
Interfaces for connecting Ethernet cables to devices | |
Access Points | Extend wireless LAN coverage for mobile and IoT devices |
Servers/Clients | Provide or request resources across the network |
🖧 Wired LAN vs. Wireless LAN
You can build a local area network using either wired or wireless technologies. Each type has its own strengths and best use cases. Wired LANs use physical cables, such as Ethernet, to connect devices. Wireless LANs use radio waves, like Wi-Fi, to link your devices without cables.
Here is a comparison of the latest wired and wireless LAN technologies:
Feature | Wired LAN | Wireless LAN |
|---|---|---|
Maximum Speed | Higher, Up to 40 Gbps(CAT8 cables) | Lower, Theoretical up to 1 Gbps (Wi-Fi 6/7), practical 25-600 Mbps |
Stability | More stable and interference-free | Prone to interference and environmental factors |
Installation | Requires physical cabling and setup | Quick and flexible installation, no cables needed |
Security | Physically secure, less vulnerable | Requires strong encryption and monitoring |
Mobility | Limited by cabling infrastructure | Easily expandable with access points |
Emerging Tech | Cat8 cables, 10/40 Gbps Ethernet | Wi-Fi 6, Wi-Fi 7, 5G narrowing speed gap |
Wired LANs give you faster and more stable connections. You often see them in places where speed and reliability matter most, like offices or data centers. Wireless LANs offer flexibility and easy setup, which makes them popular in homes and open workspaces. Many modern networks use both types to balance speed, reliability, and mobility.
Tip: For gaming or video editing, use a wired LAN for the best performance. For mobile devices or flexible workspaces, a wireless LAN gives you more freedom.
You might also see advanced equipment in larger networks, such as firewalls for security or fiber optic cables for higher speeds. The right equipment depends on your needs, the size of your network, and your desired speed.
🖧 Common LAN Topologies
LAN topology refers to how devices are arranged and connected. The most common types include:
Star Topology: All devices connect to a central switch or hub (most common today)
Bus Topology: A single backbone cable connects all devices (outdated but still seen in legacy systems)
Ring Topology: Each device connects to two others in a closed loop
A star topology using LINK-PP RJ45 integrated connectors allows for easier troubleshooting, faster data transfer, and better fault isolation.
🖧 Applications of LAN in Modern Networks
LANs are deployed in:
Corporate offices for file sharing, VoIP, and internal collaboration
Factories and automation lines for machine-to-machine communication
Campus networks across schools or hospitals for seamless connectivity
Smart homes to control lighting, entertainment, and security systems
As edge computing and IoT expand, the LAN continues to evolve. Devices like Gigabit switches, PoE-powered IP cameras, and networked industrial sensors all rely on reliable LAN connections.
FAQ
What devices can you connect to a LAN?
You can connect computers, printers, smartphones, smart TVs, and gaming consoles. Many smart home devices also work on your LAN.
How do you keep your LAN secure?
Use strong passwords, enable encryption, and update your devices often. Set up a firewall to block unwanted access.
Can you use both wired and wireless connections in one LAN?
Yes! You can mix Ethernet cables and Wi-Fi. This setup gives you flexibility and supports many types of devices.
See Also
Essential Information Everyone Should Understand About Power Over Ethernet




