
For years, Gigabit Ethernet (1Gbps) has been the reliable backbone of our connected world. But as our digital appetites grow—with 4K/8K streaming, immersive cloud applications, IoT sprawl, and bandwidth-intensive remote work—the 1Gbps ceiling is beginning to feel stifling. Enter Multi-Gigabit Ethernet, the unsung hero poised to revolutionize wired networks without demanding a complete infrastructure overhaul.
This technology isn't just about raw speed; it's about intelligent, adaptable connectivity. Let's dive into what Multi-Gig Ethernet is, why you need it, and how it's shaping the future of networking.
📑 Key Takeaways
Multi-gig ethernet makes your network faster. You do not need new cables. It works with CAT5e and CAT6 cables you already have. This helps you save money because you do not need to buy new cables.
Pick the speed that fits what you do. Use 2.5Gbps for gaming. Use 5Gbps if you move big files. Use 10Gbps for powerful computers at work.
You may need an upgrade if things are slow. Slow downloads, lag in games, or many devices online are signs. If you see these problems, think about getting multi-gig ethernet.
Use multi-gig switches and routers for fast connections. This setup makes streaming, gaming, and work better.
Check how your network works now. If you pay for fast internet but it is still slow, you may need to upgrade your network.
📑 What is Multi-Gig Ethernet? Breaking the 1 Gigabit Barrier
Multi-Gig Ethernet is a collective term for network technologies standardized under IEEE 802.3bz, supporting speeds of 2.5Gbps (2.5GBASE-T) and 5Gbps (5GBASE-T) over standard twisted-pair copper cabling. It seamlessly bridges the gap between 1 Gigabit and 10 Gigabit Ethernet, offering a perfect balance of performance, cost, and infrastructure compatibility.
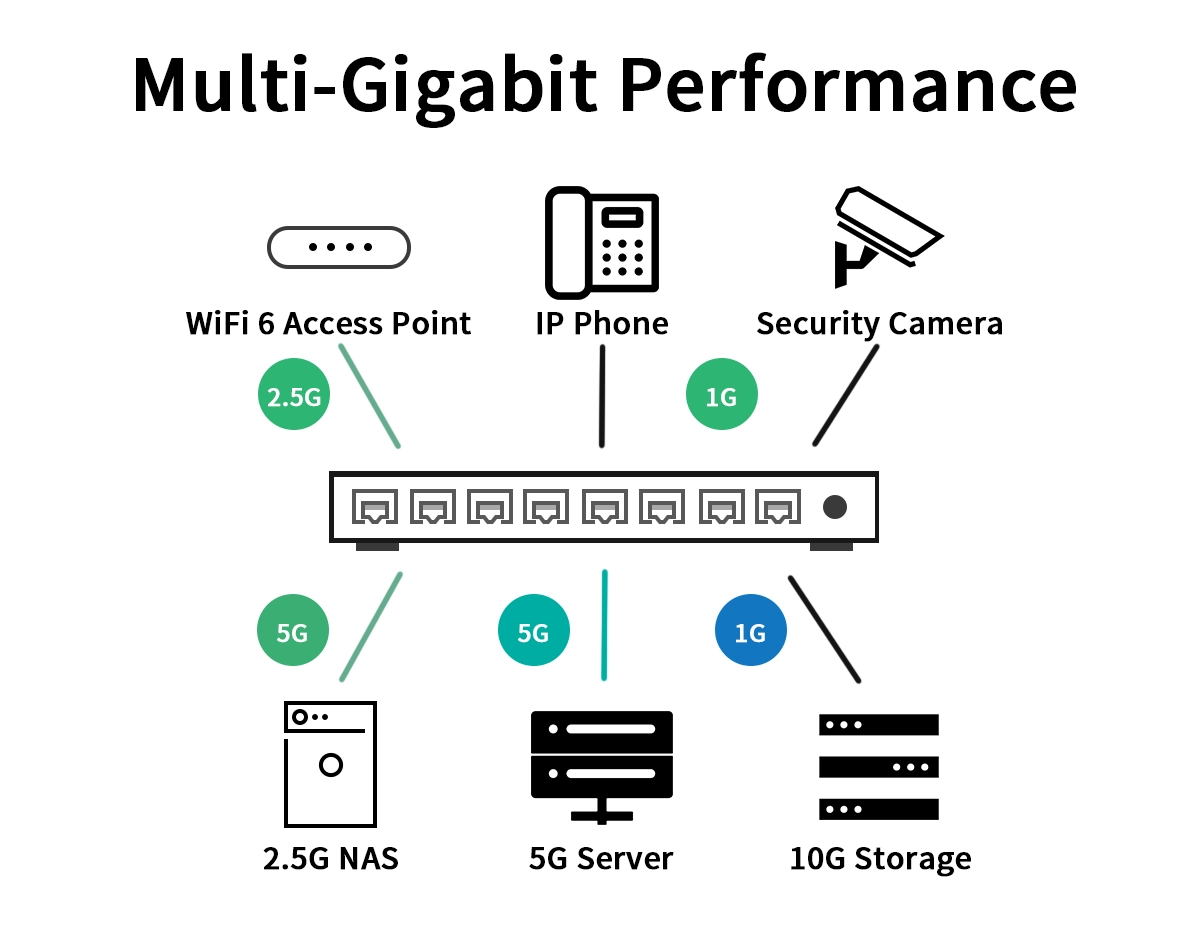
Why Multi-Gig? The Need for Speed Between 1G and 10G
For years, the jump from 1G to 10G was a costly leap requiring expensive Cat 6a/7 cabling. Multi-Gig solves this by utilizing the often-untapped potential of the Cat 5e and Cat 6 cabling already installed in millions of buildings.
Key Drivers for Adoption:
High-Speed Wi-Fi 6/6E & Wi-Fi 7 Access Points: A single Wi-Fi 6E AP can easily saturate a 1Gbps uplink. Multi-Gig (2.5G/5G) ensures your wireless network isn't throttled by its wired backbone.
Bandwidth-Intensive Applications: Video production, CAD/CAM workstations, network-attached storage (NAS), and virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI).
Future-Proofing: A pragmatic, scalable investment that prepares your network for next-generation devices without a complete rewiring project.
📑 Multi-Gig vs. Traditional Ethernet: A Quick Comparison
Feature | Fast Ethernet (100M) | Gigabit Ethernet (1G) | Multi-Gig Ethernet (2.5G/5G) | 10 Gigabit Ethernet (10G) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
IEEE Standard | 802.3u | 802.3ab | 802.3bz | 802.3an |
Common Cable Used | Cat 5 | Cat 5e/6 | Cat 5e/6 (Up to 100m) | Cat 6a/7 |
Typical Use Case | Legacy/Basic Connectivity | General Office, VoIP | High-speed Wi-Fi Uplinks, NAS, Workstations | Data Centers, Backbone |
Infrastructure Cost | Very Low | Low | Moderate (Mostly Switches/NICs) | High |
📑 The Critical Role of the RJ45 Magjack in Multi-Gig Systems
At the physical heart of any copper Ethernet connection is the RJ45 Magjack (Magnetics Module + Jack). This unsung hero is far more than just a port; it's a sophisticated component providing:
Electrical Isolation & Signal Integrity: Protects sensitive circuitry from voltage surges and electromagnetic interference (EMI).
Impedance Matching & Noise Cancellation: Crucial for maintaining clean, high-frequency signals required for Multi-Gig speeds over longer cable runs.
PoE Support: Many modern Magjacks are designed to handle Power over Ethernet (PoE++) efficiently, delivering up to 90W to devices like APs and cameras.

For a reliable Multi-Gig or even 10Gig connection, selecting a high-performance, standards-compliant Magjack is non-negotiable. Inferior components can lead to data errors, reduced range, and link instability. For engineers designing robust networking equipment, specifying quality components like the LINK-PP 2.5G Series RJ45 Magjack (e.g., Model LPJM230125BENL) ensures optimal signal integrity and compliance with IEEE 802.3bz standards. This makes the LINK-PP RJ45 Magjack an ideal choice for next-generation switches, routers, and network interface cards demanding future-proof connectivity.
📑 Deploying Multi-Gig: What You Need to Know
Check Your Cabling: While Multi-Gig works on Cat 5e (for shorter 2.5G runs) and Cat 6, a certified Cat 6a installation guarantees full performance across all Multi-Gig speeds up to 100 meters.
Upgrade Your Switches: You'll need a Multi-Gigabit switch (often labeled as NBASE-T or Multi-Gig) that supports 1G/2.5G/5G/10G ports. These are now widely available from major networking brands.
Update Endpoint Adapters: Ensure your PCs, NAS, and servers have compatible Multi-Gig NICs (Network Interface Cards). Many newer motherboards already include 2.5G Ethernet ports.
Consider Your Use Case: Deploy Multi-Gig ports first at aggregation points for Wi-Fi APs and for power users. A full-scale upgrade can be done progressively.
📑 Looking Ahead: The Future is Multi-Gig
Multi-Gigabit Ethernet is not a niche technology—it's becoming the new mainstream for enterprise and prosumer networks. It elegantly solves the "last-meter" bandwidth crunch, especially with the proliferation of Wi-Fi 7 devices and high-performance edge computing.
Ready to Supercharge Your Network?
Upgrading to Multi-Gig is one of the most impactful network improvements you can make. By leveraging existing cables and strategically investing in new switches and adapters, you can unlock tremendous performance gains. For OEMs and designers, partnering with reliable component manufacturers like LINK-PP for critical parts such as high-speed RJ45 Magjacks ensures your hardware delivers consistent, high-performance Multi-Gig Ethernet connectivity that users can count on.
📑 FAQ
What is the difference between multi-gig ethernet and regular ethernet?
Multi-gig ethernet goes faster than 1Gbps. Regular ethernet is usually only 1Gbps. Multi-gig ethernet moves data quicker. Your network can handle more devices. You can send bigger files with multi-gig ethernet.
What equipment do you need for multi-gig ethernet?
You need a multi-gig switch and the right cables. CAT5e or CAT6 cables work well. Your devices must have multi-gig network ports. Some computers need a new network card. Your setup works best with new hardware.
What are multi-gig internet plans?
Multi-gig internet plans give speeds over 1Gbps. You can stream and game much faster. Sharing files is quicker with these plans. Multi-gig ethernet networks work well with these plans. All your devices get better performance.
What devices benefit most from multi-gig ethernet?
Gaming PCs and smart TVs work better with multi-gig ethernet. Network storage and video editing stations also benefit. You get faster downloads and smoother streaming. File transfers are quicker. Offices with many users see better network speed.
What cables work with multi-gig ethernet?
CAT5e cables can go up to 5 Gbps. CAT6 cables can reach 10 Gbps for short runs. Check your cables for any damage. Using the right cable gives you the best speed.




