
Undersea fiber cables carry over 95% of global internet traffic. At the heart of these data transfer systems are high‑end optical transceivers, which convert electrical data into ultra‑modulated light signals, enabling reliable communication across thousands of kilometers.
Learn how high-performance optical transceivers empower ultra-long-haul submarine fiber networks through advanced DWDM and EDFA technologies. Explore LINK‑PP’s robust, compatible optical modules engineered for long-distance reliability and seamless integration.
LINK-PP Optics Transceivers are precisely calibrated and rigorously tested to ensure stable, accurate performance in advanced underwater optical systems.
🚢What Is a Submarine Cable System?
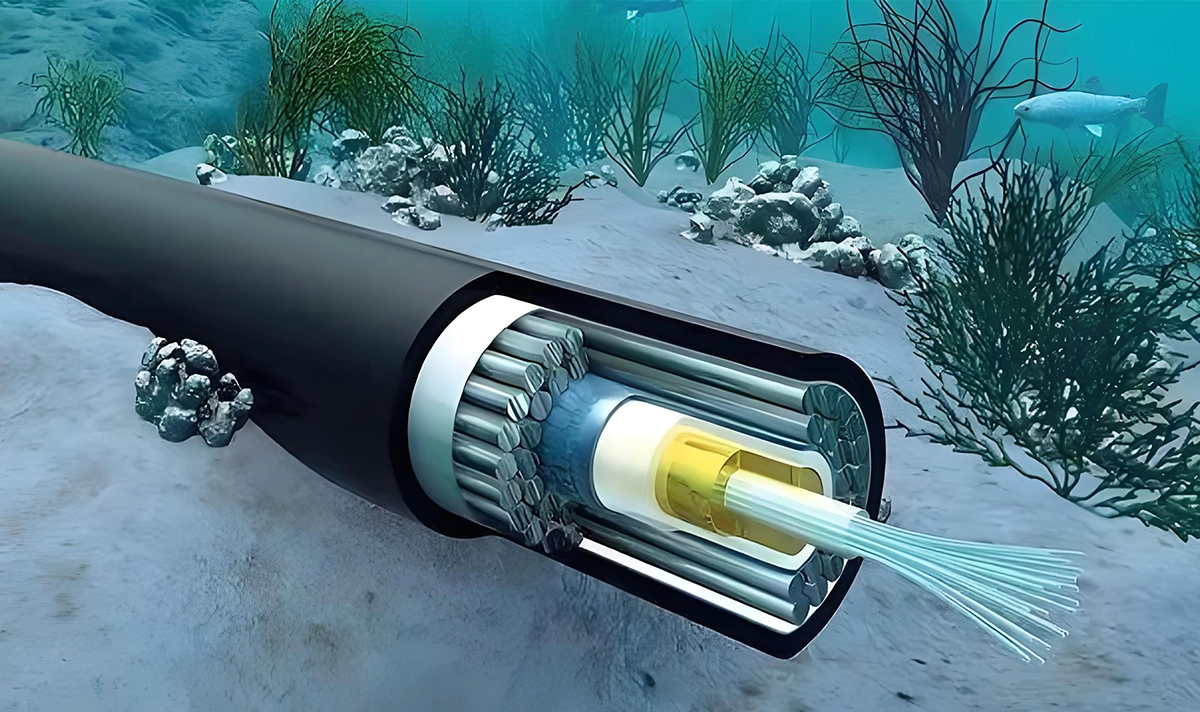
A submarine cable system is a network of fiber optic cables laid on the ocean floor to transmit data between countries and continents. These cables can span thousands of kilometers, crossing oceans and linking major communication hubs.
Key Components Include:
Optical fiber: Carries light signals over long distances.
Repeaters (Amplifiers): Strengthen the signal every 60–100 km.
Landing stations: Termination points where the system connects to terrestrial networks.
Optical transceivers: Interface between the electrical hardware and optical fiber.
The Challenge of Undersea Transmission
Submarine cables must overcome:
Extreme distances (> 5,000 km)
Signal attenuation and distortion
High-density wavelength demands for massive data throughput
The Role of Optical Transceivers

Optical transceivers are the gateways between electronic systems (like routers and switches) and optical fiber. Their main functions include:
✅ Electrical-to-optical signal conversion
Converts data signals into light for transmission through fiber.
✅ Optical-to-electrical signal conversion
At the receiving end, light signals are converted back to electrical signals for network devices.
✅ Support for WDM technology
Modern transceivers support Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM), allowing multiple data channels on different light wavelengths to be transmitted over a single fiber — vastly increasing capacity.
✅ Integration with optical amplifiers
To counter signal loss over long distances, transceivers work with EDFA (Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifiers) or Raman amplifiers placed along the cable.
You can trust LINK-PP optical transceivers to meet the highest standards for underwater optical wireless communication:
Requirement | Importance |
|---|---|
High output power | To ensure signal reaches across long distances |
Low power consumption | Reduces heat and enhances system longevity |
Thermal stability | Resists ocean temperature variations |
Optical precision | Ensures signal clarity across DWDM wavelengths |
Tip: When design submarine optical wireless communication systems, always consider the integration of optical transceivers, repeaters, and power systems. This approach guarantees high performance, reliability, and scalability for the submarine communication technologies.
LINK-PP Optical Transceivers for Submarine Applications
At LINK-PP, we provide industry-grade optical transceivers engineered for long-haul and submarine-compatible optical networks. Our modules offer:
Support for WDM systems
Up to 100G/200G/400G data rates
Excellent wavelength accuracy and signal stability
Custom calibration for undersea conditions
Compatibility with major brands and global standards
Our rigorous quality control includes:
Temperature cycling
Wavelength tuning and verification
Bit error rate (BER) testing under stress
Long-term burn-in tests
These measures ensure consistent, accurate operation — even in mission-critical submarine networks.
FAQ
Why are optical transceivers essential for submarine communication systems?
Optical transceivers convert electrical signals into optical signals for transmission through undersea fiber cables, and vice versa. Without them, data could not move between terrestrial network devices and submarine optical infrastructure.
How do you choose the right optical transceiver for a submarine cable?
Check wavelength compatibility.
Confirm data rate support.
Review power and temperature ratings.
Make sure it passes underwater reliability tests.
What’s the difference between a terrestrial and a submarine optical transceiver?
Submarine transceivers typically require greater optical output power, thermal stability, and coherent modulation support to handle the unique demands of long-distance, undersea environments. They also undergo stricter reliability testing.
See Also
What Is DWDM? Explaining Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing
Learn how DWDM technology enables high-capacity transmission over a single fiber — a cornerstone of modern submarine cable systems.Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifier (EDFA) in Optical Networks
Understand how EDFAs maintain signal strength over ultra-long-haul fiber routes, including undersea applications.Understanding What Is Bit Error Rate (BER)
Discover why low BER is critical for signal integrity in long-distance optical communications like submarine networks.




