
In the world of fiber optics, where high-speed data transmission is king, some components work behind the scenes to make connectivity possible. The PLC Splitter (Planar Lightwave Circuit Splitter) is one such critical, yet often overlooked, device. It's the cornerstone of Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) networks and passive optical networks (PON), efficiently distributing optical signals to multiple users.
But what exactly is it, and how does it ensure your internet, TV, and phone services run smoothly? This guide will demystify the PLC splitter, compare it with alternatives, and explain its synergy with essential components like optical transceivers.
📜 Key Takeaways
A PLC Splitter takes one optical signal and splits it into many outputs. This helps share signals in fiber optic networks.
Pick the split ratio that matches what you need. Lower ratios work for fewer users. Higher ratios connect more users well.
Choose the connector type like SC, LC, or FC. This makes sure your network equipment works together. It also helps stop problems when installing.
Think about the splitter’s shape, like module, block, or tray. This helps it fit in your space and meets your needs.
A PLC Splitter makes the network work better and more reliably. It also helps the network grow easily when more users join.
📜 What is a PLC Splitter? A Deep Dive into the Technology
A PLC splitter is a passive optical device that takes a single input optical signal and divides it into multiple output signals. Unlike active electronic splitters, it requires no power, making it highly reliable and cost-effective. The magic happens inside a compact chip made of silica glass, where a series of optical waveguides are etched using sophisticated semiconductor-like technology.
📜 How Does a PLC Splitter Work?
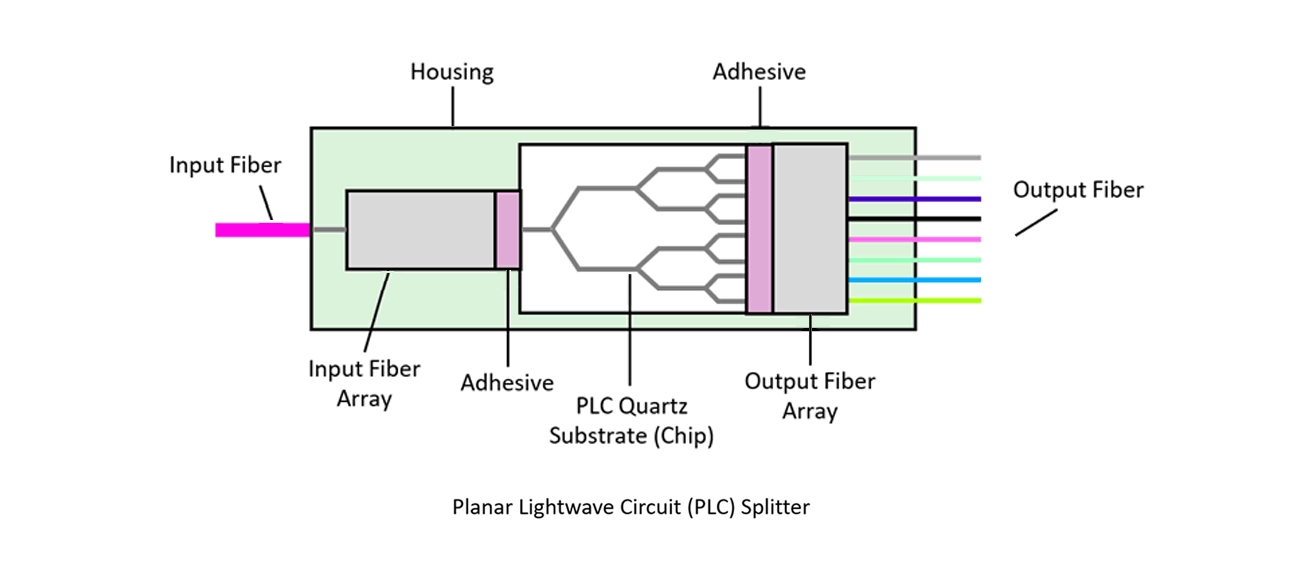
The principle is based on light propagation. When a light signal enters the splitter, it travels through these etched waveguides. The circuit is designed to divide the light's power equally (or in a specific ratio) among the output channels. For example, a 1x8 PLC splitter will divide one input signal into eight identical output signals, each carrying 1/8th of the original power.
Key advantages of this technology include:
High Reliability: No moving parts and no need for electrical power.
Compact Size: Ideal for space-constrained environments like distribution boxes.
Excellent Uniformity: The signal loss is very consistent across all output channels.
Wide Operating Wavelength Range: Works seamlessly with standard wavelengths like 1310nm, 1490nm, and 1550nm used in PON systems (GPON, EPON).
📜 PLC Splitter vs. FBT Splitter: Which One Should You Choose?
While both serve the same primary function, the technology behind them is different. The main alternative to PLC is the Fused Biconical Taper (FBT) splitter.
The following table provides a clear comparison to help you make an informed decision:
Feature | PLC Splitter | FBT Splitter |
|---|---|---|
Technology | Planar waveguide circuit on a silica chip | Fused and tapered fibers |
Split Ratio Uniformity | Excellent (very consistent across ports) | Good, but can vary at higher split ratios |
Operating Wavelength | Wide (1260-1650nm), ideal for triple-play services | Limited to specific wavelengths (e.g., 1310nm & 1550nm) |
Size | Compact | Larger, especially for high split counts |
Cost | Cost-effective for higher split ratios (1x16, 1x32, 1x64) | More economical for lower split ratios (1x2, 1x4) |
Best For | High-density applications, PON networks, long-term stability | Simple applications, single-wavelength systems, budget-sensitive projects |
Verdict: For modern, scalable FTTH deployments requiring stability and support for multiple wavelengths, the PLC splitter is the superior choice.
📜 Key Applications: Where is a PLC Splitter Used?
The primary application of PLC splitters is in Passive Optical Networks (PON). They are deployed in the outside plant (OSP) in various configurations—centralized (in a single location) or cascaded (distributed in multiple points)—to split the signal from the Internet Service Provider's (ISP) central office to numerous end-users.
Other critical applications include:
CATV Network Distribution: Splitting a single video signal to multiple households.
Fiber Optic Test Equipment: Dividing a signal for monitoring and testing purposes.
Network Monitoring Systems: Enabling signal taps for security and performance analysis.
📜 The Critical Link: PLC Splitters and Optical Transceivers
A fiber network is an ecosystem, and the PLC splitter is just one part of the chain. Its performance is intrinsically linked to the quality of other components, especially the optical transceivers at each end of the link.
An optical transceiver (or fiber optic module) is the active device that converts electrical signals to optical signals and vice versa. In a PON system, an OLT (Optical Line Terminal) transceiver at the central office sends data downstream through the PLC splitter. At the user's home, an ONU (Optical Network Unit) transceiver receives this data and sends upstream data back.
Why does this partnership matter?
The PLC splitter introduces insertion loss—a deliberate attenuation of the signal. The quality and power budget of your transceivers must be high enough to overcome this loss and any additional loss from the fiber cable itself. Using low-quality transceivers with a high-split-ratio PLC splitter can lead to network instability and data loss.
For optimal performance, it's crucial to use reliable, compatible components. For instance, a LINK-PP SFP transceiver is engineered to deliver a stable and robust optical budget, ensuring clear signal transmission even after being split by a 1x32 or 1x64 PLC splitter. When planning your fiber network infrastructure, considering the compatibility between your PLC splitter specifications and your chosen transceivers is a non-negotiable step for success.
📜 Choosing the Right PLC Splitter: A Quick Guide
When selecting a PLC splitter, consider these factors:
Split Ratio: How many outputs do you need? (e.g., 1x4, 1x8, 1x32, 2x64).
Packaging Type: Bare fiber (for splicing), cassette-type (for patch panels), or plug-and-play modules (with connectors like SC/APC or LC/UPC).
Working Wavelength: Ensure it matches your system's requirements (e.g., 1310/1490/1550nm for GPON).
Quality and Standards: Choose manufacturers that adhere to Telcordia GR-1209-CORE standards for reliability.
For demanding applications requiring maximum performance, pairing a high-quality splitter with a premium optical transceiver module can significantly enhance your network's reach and reliability.
📜 Conclusion: Powering Connected Futures
The PLC splitter is a masterpiece of passive optical engineering, enabling the economic and efficient distribution of high-bandwidth services to millions worldwide. By understanding its role, benefits, and its symbiotic relationship with components like optical transceivers, network planners can build more robust and future-proof fiber infrastructures.
📜 FAQ
What does a PLC Splitter do in a fiber optic network?
A PLC Splitter divides one optical signal into several outputs. You use it to share a single signal with many users. This helps you keep each connection strong.
What split ratios can you find for PLC Splitters?
You can find split ratios like 1:2, 1:4, 1:8, 1:16, 1:32, and 1:64. You pick the ratio based on how many users you want to connect.
Tip: Always check the split ratio before you buy a splitter.
What types of connectors work with PLC Splitters?
You see SC, LC, and FC connectors most often. Each type fits different cables and devices. You choose the connector that matches your network setup.
What makes PLC Splitters reliable?
You get reliability from strong silica materials and precise design. The splitter keeps signals stable and works well in many environments.
Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
Silica material | Long lifespan |
Precise design | Stable signals |
What should you check before installing a PLC Splitter?
You need to check the split ratio, connector type, and packaging. Make sure the splitter fits your space and matches your cables. Clean connectors before installation for best results.




