
In today's fast-paced digital economy, agility and efficiency are not just advantages—they are necessities. Traditional data centers, with their "one-server, one-application" model, are often rigid, costly, and inefficient. This is where data center virtualization comes in, a transformative technology that is the bedrock of modern cloud computing and IT infrastructure.
But what exactly is it? In simple terms, data center virtualization is the process of creating a virtual (rather than physical) version of data center resources. This includes servers, storage, networking, and even desktops. By abstracting these resources from the underlying hardware, organizations can run multiple virtual systems and applications on a single physical machine.
This guide will demystify data center virtualization, explore its profound benefits, and highlight how cutting-edge hardware, including high-speed optical modules from LINK-PP, is crucial for its success. Whether you're an IT manager or a tech enthusiast, you'll learn why virtualization is a cornerstone of an efficient, scalable, and future-proof IT strategy.
➤ What is Data Center Virtualization, Really?
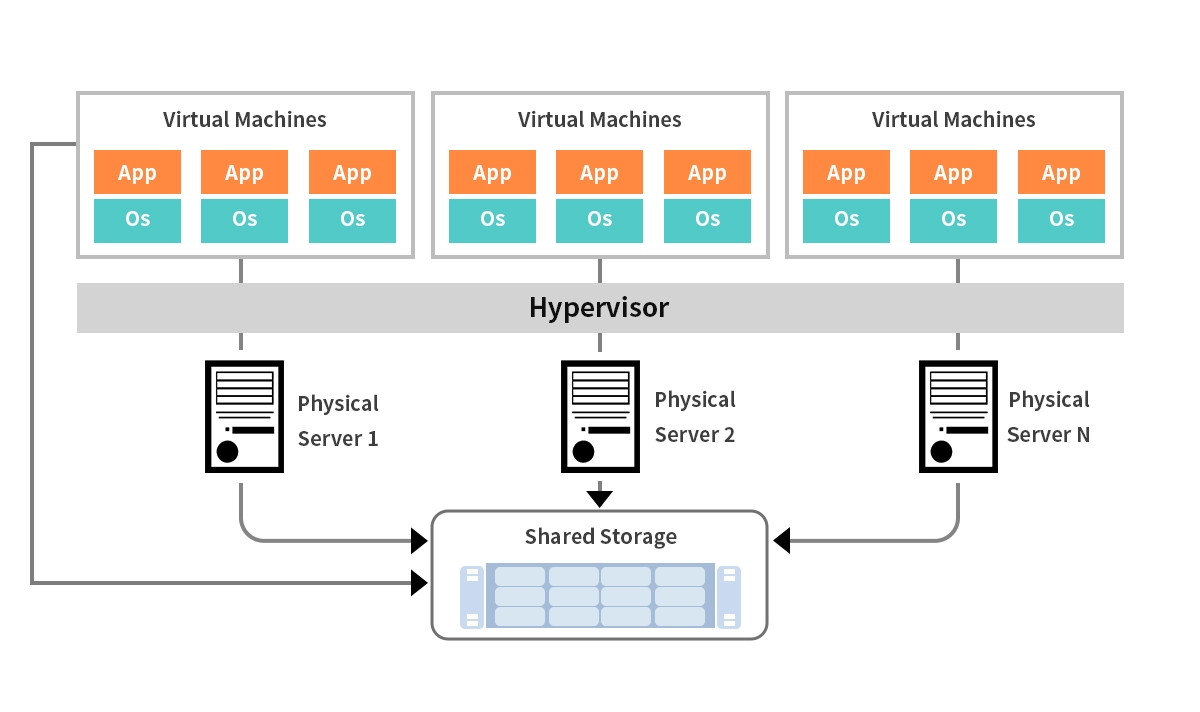
At its core, data center virtualization uses a software layer called a hypervisor to decouple physical hardware from the operating system and applications. The hypervisor (e.g., VMware vSphere, Microsoft Hyper-V) runs directly on the server hardware and allows you to create and run multiple virtual machines (VMs). Each VM acts like a complete, self-contained computer with its own OS and applications, all sharing the resources of the single physical host.
This process moves the data center from a static, hardware-centric environment to a dynamic, fluid pool of resources. This is fundamental for businesses looking to optimize IT infrastructure management and reduce operational costs.
➤ The Compelling Benefits: Why You Need to Virtualize
The shift to a virtualized data center isn't just a technical upgrade; it's a strategic business decision. The advantages are multi-faceted and impact both the bottom line and operational agility.
Benefit | Description | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|
Cost Reduction | Drastically lowers capital expenditure (CapEx) by reducing the number of physical servers, switches, and storage arrays needed. Also reduces operational costs (OpEx) for power, cooling, and physical space. | ✅ Significant savings on hardware and utility bills. |
Enhanced Agility & Speed | Provisioning a new server can be done in minutes instead of days or weeks. This accelerates application deployment and time-to-market for new services. | ✅ Faster response to business demands and opportunities. |
Improved Disaster Recovery & Business Continuity | VMs are encapsulated into files, making them easy to back up, replicate, and move. Technologies like live migration allow you to move running VMs between hosts with zero downtime. | ✅ Higher uptime and robust resilience against failures. |
Increased Efficiency & Utilization | Consolidates workloads from underutilized physical servers onto fewer machines, driving hardware utilization rates from 5-15% to 80% or higher. | ✅ Maximizes return on investment from existing hardware. |
Simplified Management | Centralized management consoles provide a single pane of glass for overseeing the entire virtual infrastructure, simplifying tasks and reducing administrative overhead. | ✅ Improved IT productivity and lower management complexity. |
➤ The Key Types of Data Center Virtualization
Virtualization extends beyond just servers. A fully virtualized data center encompasses several layers:
Server Virtualization: The most common form, where a physical server is divided into multiple isolated virtual servers.
Network Virtualization: This involves abstracting network resources to create virtual networks that are independent of the underlying physical hardware. Technologies like Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and network function virtualization (NFV) fall under this category, enabling more flexible and automated network management.
Storage Virtualization: Pools physical storage from multiple network storage devices to make it appear as a single, centralized storage unit. This simplifies storage management and improves utilization.
Desktop Virtualization (VDI): Hosts desktop operating systems on a central server, allowing users to access their personal desktops remotely from any device.
➤ How Does It All Work? The Role of the Hypervisor
The magic of virtualization is enabled by the hypervisor. Think of it as a super-efficient traffic controller for your server's resources (CPU, memory, storage).
Type 1 (Bare-Metal) Hypervisor: Installed directly on the physical server hardware. It is highly efficient and is the preferred choice for enterprise data centers. Examples: VMware ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V, Citrix Hypervisor.
Type 2 (Hosted) Hypervisor: Runs as an application on top of an existing operating system (like Windows or macOS). It's more common for development and testing. Examples: Oracle VM VirtualBox, VMware Workstation.
The hypervisor allocates the necessary resources to each VM, ensuring they operate in complete isolation from one other. This isolation is key to security and stability within a virtualized server environment.
➤ Navigating the Challenges and Considerations
While powerful, virtualization introduces new complexities that must be managed:
Performance Overhead: The hypervisor layer can introduce a slight performance overhead. Proper resource allocation and monitoring are essential.
Security in a Shared Environment: A compromised hypervisor could potentially affect all VMs on the host. A robust security strategy must include the virtual layer.
Increased Network Complexity: Virtual networks and the high volume of East-West traffic (between VMs within the data center) demand a highly reliable and fast physical network backbone.
➤ The Unsung Hero: High-Speed Optical Modules in a Virtualized World
This is where the physical and virtual worlds converge in a critical way. In a highly virtualized data center, the volume of data moving between servers, storage, and switches is immense. This internal "East-West" traffic is the lifeblood of VM communication, live migrations, and storage access.
To support this low-latency, high-bandwidth demand, the physical network infrastructure must be top-tier. High-speed optical transceivers are the crucial components that convert electrical signals from servers and switches into light pulses for transmission over fiber optic cables. They are the workhorses that enable the high-speed spine of the modern data center.
Without reliable, high-performance optical transceivers, the entire virtualized environment could be bottlenecked, leading to sluggish VM performance and failed live migrations. For seamless data center network performance, investing in quality optics is non-negotiable.
This is a key area where a brand like LINK-PP excels. Their optical modules are engineered to meet the rigorous demands of virtualized and cloud environments. For instance, the LINK-PP 400G QSFP-DD DR4 transceiver is an excellent choice for spine-leaf architectures, providing the massive bandwidth required for dense VM environments. Its high density and low power consumption make it ideal for organizations looking to scale their virtual infrastructure without compromising on performance or efficiency. Integrating such high-caliber components ensures that your virtualized data center can handle today's workloads and is ready for the future.
➤ The Future of Data Center Virtualization
The evolution is far from over. Virtualization is the foundation for even more advanced paradigms:
Containers and Kubernetes: Offering even greater agility and density than VMs for microservices-based applications.
Hyperconverged Infrastructure (HCI): Tightly integrates compute, storage, and networking into a single, software-defined appliance, further simplifying the data center.
Edge Computing: Virtualization technologies are being deployed at the edge to bring processing power closer to where data is generated.
AI-Driven Operations: AI and machine learning are being used to autonomously manage and optimize virtualized environments, predicting demand and preventing issues before they occur.
➤ Conclusion: Virtualize to Future-Proof
Data center virtualization is no longer an optional technology; it is a fundamental component of a modern, efficient, and resilient IT strategy. By abstracting resources from hardware, it delivers unparalleled cost savings, agility, and operational simplicity.
Success, however, depends on a holistic approach. It requires not just robust software but also a powerful and reliable physical network infrastructure. Partnering with trusted hardware providers for components like LINK-PP's high-performance optical transceivers ensures that your virtualized environment is built on a solid foundation, ready to power your business forward.
➤ FAQ
What is a virtual machine?
A virtual machine is a program that works like a real computer. You can use it to run apps and save files. You can make many virtual machines on one server.
What makes data center virtualization different from traditional data centers?
You use software to make virtual resources, not just hardware. This means you can do more jobs with fewer machines. You can control everything from one spot.
What do you need to start data center virtualization?
You need a server, a hypervisor, and tools to manage things. You also need a plan for your virtual machines. Training helps you learn how to use the tools.
What are the main risks of data center virtualization?
You might have security problems if you do not protect your virtual machines. You can also see slow systems if you run too many jobs on one server. Good planning helps you stop these problems.
What is a hybrid environment in data center virtualization?
A hybrid environment lets you use your own data center and the cloud. You can move virtual machines back and forth. This gives you more options and makes things easier.




