1. What is DDM?
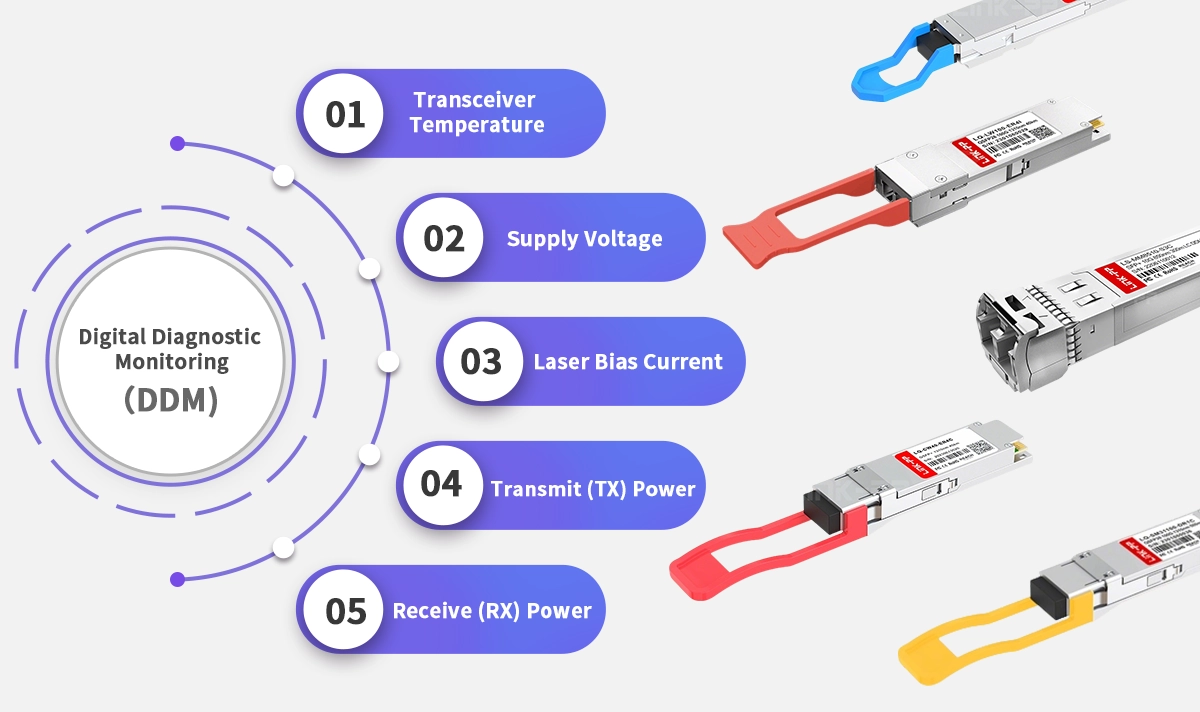
DDM stands for Digital Diagnostic Monitoring (also called Digital Optical Monitoring, or DOM). It refers to the function that allows network operators to access real-time operational information from optical transceivers. This includes key parameters like temperature, supply voltage, laser bias current, and transmit/receive optical power. These measurements help detect issues before they impact performance.
2. What is DDMI?
DDMI refers to the Digital Diagnostic Monitoring Interface—that is, the standardized mechanism (typically over I²C) defined by the SFF-8472 MSA through which DDM data is accessed. It’s this interface that enables host devices to poll the module’s diagnostic data consistently.
3. Side-by-Side Comparison
Term | Meaning | Focus |
|---|---|---|
DDM | Digital Diagnostic Monitoring (functionality) | What diagnostics are available |
DDMI | Digital Diagnostic Monitoring Interface | How diagnostics are accessed |
In short: DDM is the data, and DDMI is the pathway to retrieve it.
Why the Difference Matters
Clarity in Communication: Using the correct term helps technical teams understand whether you're referring to diagnostic capability (DDM) or the method to obtain it (DDMI).
Implementation Insight: When scouting or troubleshooting optical modules, knowing whether you’re dealing with a presentation layer (DDM) or interface layer (DDMI) helps avoid confusion
4. Applications in Practice
Real-Time Monitoring
DDM / DDMI enables ongoing access to metrics such as temperature, voltage, laser current, TX/RX power, vital for proactive maintenance.Standard Interface Compatibility
The SFF-8472 standard ensures modules from different vendors offer consistent diagnostic access via DDMI.Fault Detection & Alarming
Some systems recognize threshold violations indicated by DDM and trigger alarms via DDMI data retrieval.Simplified Troubleshooting
Through CLI or SNMP—accessing DDMI—technicians can quickly isolate failing or degraded modules.
5. LINK-PP Example: DDMI + DDM in Action

A real-world example of this synergy is LINK-PP’s LS-MM8532-S1C module—a 32 Gb/s SFP28 transceiver at 850 nm with 100 m reach and full DDMI support. This product enables the host device to read live diagnostics—via its DDMI interface—on temperature, voltage, laser bias, TX/RX power—illustrating the practical benefit of pairing both.
6. How This Helps You
Educated Purchasing: Confirm DDM functionality and DDMI compatibility in product specs.
Operational Confidence: Use DDMI to pull detailed diagnostics, allowing proactive responses before service impacts.
Universal Interoperability: Rely on SFF-8472-compliant DDMI and DDM across a broad array of transceiver brands, including LINK-PP.
7. Conclusion
Understanding the difference between DDM (the diagnostics) and DDMI (the interface) empowers better decision-making and more effective network maintenance. For robust performance and seamless diagnostics, explore LINK-PP’s range of DDMI-enhanced optical transceivers in their official product store.




