In today's interconnected digital world, the ability to move files efficiently and securely is the lifeblood of businesses and IT operations. For decades, the File Transfer Protocol (FTP) has been the go-to solution. But as cyber threats evolve, a more secure alternative has risen to prominence: the SSH File Transfer Protocol (SFTP).
If you're still using FTP for critical transfers, you might be exposing your data to significant risks. This comprehensive guide will break down the key differences between FTP and SFTP, helping you make an informed decision. We'll also explore how your underlying network hardware, including high-performance LINK-PP optical transceivers, plays a crucial role in the performance and reliability of your file transfer operations.
🌐 What is FTP (File Transfer Protocol)?
FTP, or File Transfer Protocol, is one of the oldest protocols still in use on the internet. Developed in the early 1970s, its primary purpose is to transfer files between a client and a server on a computer network.
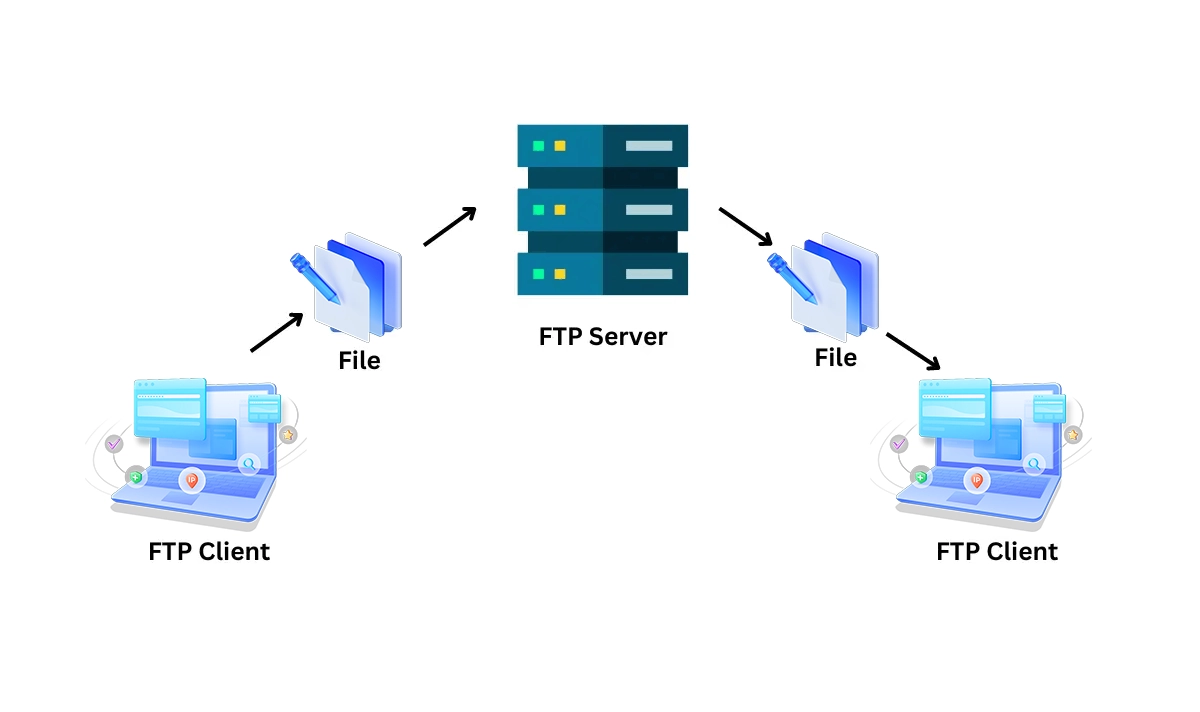
How FTP Works
FTP operates on a client-server model and uses separate control and data connections. The client initiates a connection to the server on port 21 (the command channel) to authenticate and send commands. When a file transfer is requested, a separate data channel is established (often on port 20) to move the actual files.
Key Characteristics of FTP:
Clear-Text Communication: Both commands and data are transmitted in plain text, including usernames and passwords.
Dual-Port Model: This can cause issues with firewalls and is less efficient.
Wide Compatibility: It's supported by almost all web hosts and operating systems.
While its simplicity and universality are advantages, its lack of security is a critical flaw in the modern era, making FTP security vulnerabilities a major concern for IT managers.
🌐 What is SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol)?
SFTP, which stands for SSH File Transfer Protocol (or Secure File Transfer Protocol), is a completely different and far more secure program. It is a network protocol that provides file access, transfer, and management over any reliable data stream, secured by the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol.
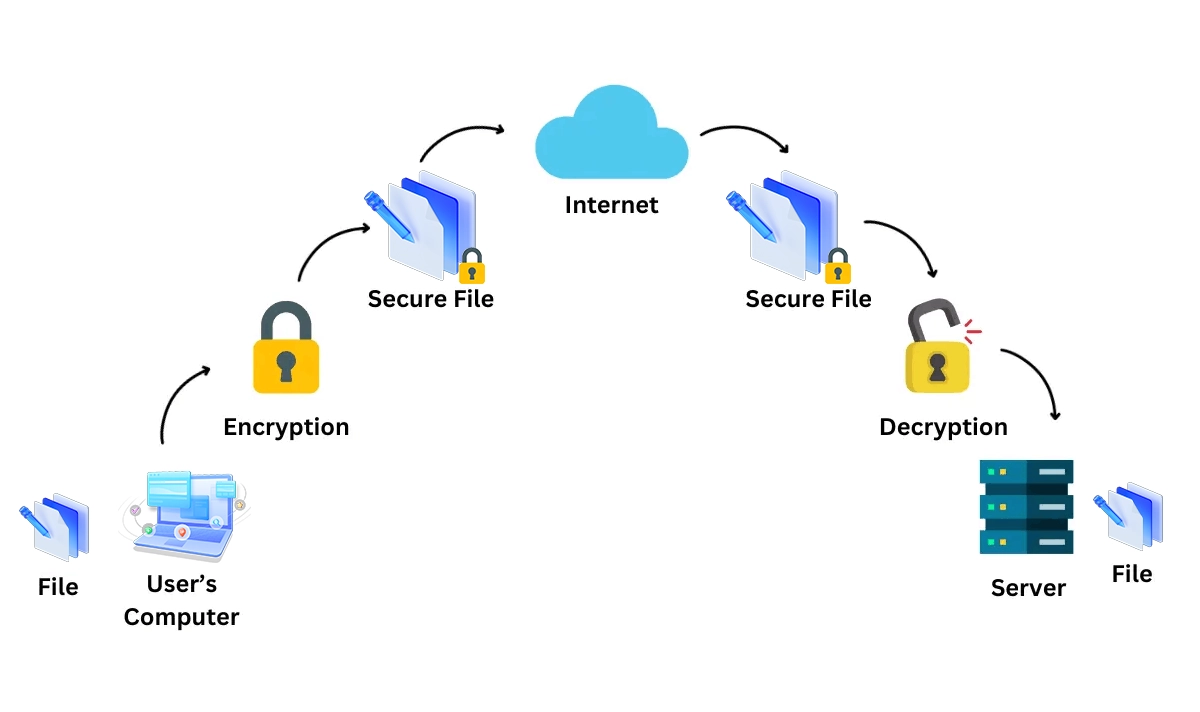
How SFTP Works
Unlike FTP, SFTP uses only a single connection. It tunnels the entire file transfer session—authentication, commands, and data—through a secure SSH channel, typically on port 22. This encryption ensures that all data passing between the client and server is protected from eavesdropping and tampering.
Key Characteristics of SFTP:
End-to-End Encryption: All data is encrypted using robust algorithms like AES.
Single Port Operation: Simplifies firewall configuration and enhances security.
Integrated Security: Leverages the proven security of SSH, including public key authentication.
For businesses looking for secure FTP alternatives or a reliable SFTP client for business, SFTP is the undeniable modern standard.
🌐 FTP vs SFTP: A Head-to-Head Comparison
To make the differences crystal clear, let's compare these two protocols across several critical dimensions.
Feature | FTP (File Transfer Protocol) | SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol) |
|---|---|---|
Security | ❌ Insecure. Transmits data and credentials in plain text. | ✅ Highly Secure. Full session encryption via SSH. |
Port Used | Port 21 (control) & Port 20 (data) | Port 22 (single connection) |
Authentication | Basic; username & password (sent in clear text). | Strong; supports passwords, SSH keys, and multi-factor. |
Firewall Friendly | ❌ No. The dynamic data port often gets blocked. | ✅ Yes. Uses a single, predictable port. |
Underlying Protocol | TCP/IP (native) | SSH (over TCP/IP) |
File Management | Basic transfer commands. | Advanced; includes permissions, listing, and remote editing. |
Speed | Can be slightly faster on local networks due to no encryption overhead. | Negligible overhead on modern hardware; essential for WAN/Internet. |
Compliance | Fails to meet standards like GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS. | Essential for meeting modern data privacy and security compliance. |
Verdict: For any file transfer involving sensitive data or traversing the internet, SFTP is the clear winner. The minor potential speed advantage of FTP is vastly outweighed by the catastrophic risks of a data breach.
🌐 The Hidden Factor: How Network Hardware Impacts Your Transfer Speed
When discussing FTP vs SFTP performance, most analyses stop at the software protocol level. However, your network's physical infrastructure is a critical, often overlooked, component. The speed and reliability of your file transfers are directly constrained by your network hardware, including switches, routers, and the transceivers they use.
This is where optical modules come into play. Also known as fiber optic transceivers, these small devices plug into network equipment to convert electrical signals into light pulses, enabling high-speed data transmission over fiber optic cables.
Why Your Optical Module Choice Matters for FTP and SFTP
Whether you're transferring large backup archives via FTP or syncing encrypted databases with SFTP, a slow or unreliable network link creates a bottleneck. High-quality optical modules ensure that:
Data Integrity: They minimize packet loss and errors, which is crucial for both protocols but especially for SFTP, where encrypted data streams are less tolerant of corruption.
Maximum Throughput: They support the highest possible data rates (e.g., 10G, 25G, 100G), allowing you to fully utilize your bandwidth for faster uploads and downloads.
Low Latency: They provide quick signal conversion, reducing delay, which improves the responsiveness of the transfer session.
For IT professionals building or upgrading their data center infrastructure for high-volume business file transfer solutions, investing in reliable hardware is non-negotiable.
Enhancing Your Infrastructure with LINK-PP Optical Modules
To achieve optimal performance for your file transfer services, you need optical transceivers you can trust. LINK-PP manufactures a range of high-performance, compliant optical transceivers designed for reliability and seamless integration.
A perfect choice for aggregating file transfer servers and ensuring smooth data flow is the LINK-PP SFP-10G-SR. This 10 Gigabit multimode module is ideal for short-range connections within a data center, offering low power consumption and robust performance. By deploying LINK-PP's hardware, you create a stable foundation that empowers both legacy FTP and modern SFTP transfers to run at their maximum potential, free from hardware-induced limitations.
🌐 Conclusion and Key Takeaways
The choice between FTP and SFTP is no longer a difficult one. While FTP has historical significance, its inherent security flaws make it unsuitable for modern use. SFTP provides a robust, encrypted, and firewall-friendly method for secure file sharing protocols, making it the definitive choice for any organization serious about data protection.
Remember:
Use FTP only for anonymous, public data on internal networks where security is not a concern.
Use SFTP for all other transfers, especially those involving sensitive information, compliance requirements, or traversal over the internet.
Your protocol choice is only one part of the equation. A high-performance network backbone, supported by quality components like LINK-PP optical modules, ensures that your secure transfers are not just safe, but also fast and reliable.
🌐 FAQ
What makes SFTP safer than FTP?
SFTP uses encryption to hide your files during transfer. FTP does not use encryption. Anyone can see your data if you use FTP. You keep your information private with SFTP.
Can you use FTP and SFTP on the same server?
Some servers support both FTP and SFTP. You choose which protocol to use when you connect. Always pick SFTP if you need to protect your files.
Which protocol works better with firewalls?
SFTP works better with firewalls. It uses only one port (22) for all data. FTP uses many ports, which can cause problems with firewalls.
Do you need special software for SFTP?
You need an SFTP client to connect securely. Many free SFTP clients exist. Some programs support both FTP and SFTP, so you can choose the best option for your needs.
When should you choose FTP over SFTP?
You should use FTP for public files or when security does not matter. SFTP is better for private or sensitive files. Here is a quick guide:
Use FTP for | Use SFTP for |
|---|---|
Public documents | Private documents |
Non-sensitive data | Sensitive data |




