The backbone of our modern, hyper-connected world is Fiber to the Home (FTTH) technology. For ISPs, businesses, and even large-scale residential projects, choosing the right Passive Optical Network (PON) standard is a critical decision. The two giants in this arena are EPON and GPON.
But which one reigns supreme? The answer isn't a simple one, as it depends on your specific requirements for bandwidth, compatibility, and cost. In this showdown, we'll dissect EPON vs GPON to give you a clear, actionable understanding.
📄 A Tale of Two Protocols: The Core Difference
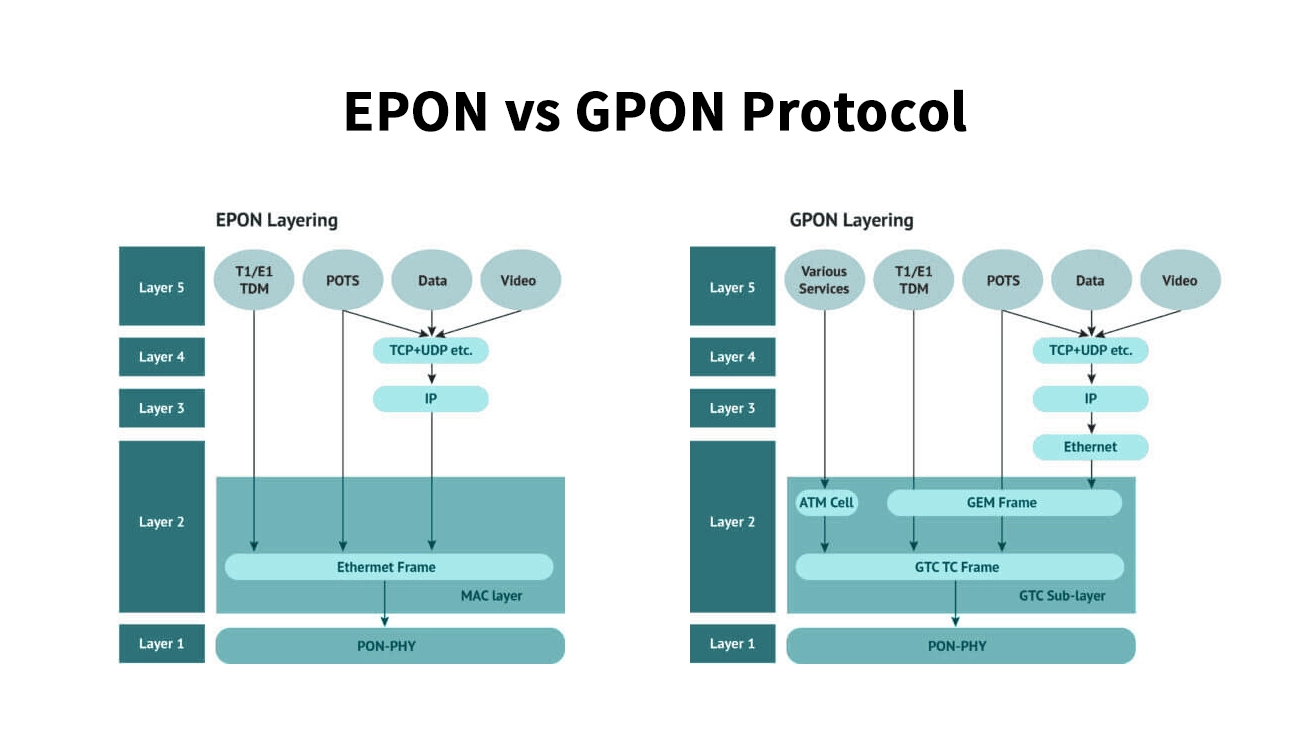
At their heart, the primary difference lies in the protocols they use.
EPON (Ethernet PON) leverages the IEEE 802.3ah standard. It's essentially Ethernet over fiber, making it a simple and elegant solution that integrates seamlessly with existing IP/Ethernet networks.
GPON (Gigabit PON) follows the ITU-T G.984 standard. It's a more complex, telecommunication-centric protocol that can natively carry multiple services (data, voice, video) using different encapsulation methods (ATM, GEM).
📄 Head-to-Head Comparison: EPON vs GPON
Let's put the key specifications side-by-side for a clearer picture.
Feature | EPON (IEEE 802.3ah) | GPON (ITU-T G.984) |
|---|---|---|
Upstream/Downstream | 1Gbps / 1Gbps (Symmetrical) | 2.5Gbps Down / 1.25Gbps Up (Asymmetrical) |
Protocol | Native Ethernet | ATM & GEM Encapsulation |
Split Ratio | Typically 1:32 | Up to 1:128 |
Reach | ~20 km | ~20 km (up to 60 km with extensions) |
Cost | Generally lower due to Ethernet simplicity | Historically higher, but costs have normalized |
Market Adoption | Strong in Asia, specific enterprise networks | Dominant in North America & Europe |
Breaking Down the Battle: Key Decision Factors
1. Bandwidth & Symmetry:
GPON offers a higher raw downstream speed (2.5Gbps), which is great for downloading and streaming. Its asymmetrical nature mirrors typical consumer usage.
EPON provides a symmetrical 1Gbps. This is a significant advantage for businesses and power users who rely on heavy upstream traffic, such as cloud backups, video conferencing, and hosting servers.
2. Scalability & Split Ratio:
GPON traditionally supports a higher split ratio (up to 1:128), meaning a single fiber from the central office can serve more end-users, potentially improving ROI for ISPs in dense areas.
EPON typically uses a 1:32 split, which can translate to more dedicated bandwidth per user.
3. Cost & Efficiency:
EPON often has a cost advantage. Its use of standard Ethernet equipment reduces complexity and cost for both the Optical Line Terminal (OLT) and Optical Network Unit (ONU).
GPON costs have decreased significantly and are now highly competitive, making the total cost of ownership (TCO) a closer call than before.
📄 The Future is 10G: The Rise of XG/XGS-PON and 10G-EPON
The evolution continues with 10-gigabit technologies. XGS-PON (symmetrical 10Gbps) and 10G-EPON are the natural successors. A key advantage of upgrading your network with future-proof optical modules is that many of these next-generation systems can coexist on the same fiber as GPON and EPON, protecting infrastructure investments.
📄 Why Your Optical Transceiver Choice is Critical
Often overlooked, the optical module (or transceiver) is the heart of your PON system. It's the component in the OLT and ONU that converts electrical signals to light and vice versa. The performance and compatibility of these modules directly dictate your network's stability, reach, and speed.
Using generic or low-quality modules can lead to intermittent connectivity, data loss, and increased latency. For mission-critical applications, investing in reliable, MSA-compliant modules is non-negotiable. This is where specifying proven manufacturers becomes essential. For instance, ensuring you source the right compatible SFP+ optical transceiver for your OLT chassis can be the difference between a flawless rollout and a troubleshooting nightmare.
For robust performance in both EPON and GPON applications, the LINK-PP PON optical module is an excellent choice, designed for reliability and broad compatibility. When planning for future 10G upgrades, the LINK-PP XGS-PON module offers a seamless path forward without overhauls. Choosing the right supplier like LINK-PP ensures you avoid the common pitfalls of sourcing compatible optical modules for legacy PON equipment.
📄 Conclusion: So, Which One Should You Choose?
The EPON vs GPON debate doesn't have a single winner.
Choose GPON if: You are an ISP in a market where it's the standard, you need to serve a very high number of users from a single port (high split ratio), and your primary focus is downstream bandwidth.
Choose EPON if: You prioritize cost-effectiveness, need symmetrical bandwidth for upstream-heavy applications, or are building a network that integrates seamlessly with a standard Ethernet infrastructure.
Ultimately, the best choice hinges on your local market, specific use case, and long-term scalability plans.
📄 FAQ
What is the main difference between GPON and EPON?
You will see that GPON offers higher download speeds, while EPON gives you equal upload and download speeds. GPON works well for large networks. EPON fits best with Ethernet systems.
Which technology is better for home internet?
You should choose GPON if you want faster downloads for streaming or gaming. EPON works well if you want simple setup and equal speeds for uploads and downloads.
Can I upgrade from EPON to GPON easily?
You can upgrade, but you may need new equipment. GPON uses different technology, so you cannot just swap one for the other. Always check with your provider before making changes.
Which is more cost-effective for businesses?
You will find EPON usually costs less to set up, especially if you already use Ethernet. GPON can save money for large networks because it connects more users with one fiber.
How do I decide between GPON and EPON for my project?
You should look at your speed needs, number of users, and budget. GPON gives higher download speeds and supports more users. EPON is easier to manage with Ethernet and costs less for smaller projects.




