
When you pick between InfiniBand and Ethernet for your data center, your choice depends on what you need. InfiniBand is best for high-performance computing and jobs that need very low latency. Ethernet is good for most business workloads and works with many things. You should think about performance, cost, scalability, manageability, and if it will work in the future. InfiniBand vs Ethernet does not have one answer for everyone. Your business goals and technical needs should help you decide. So, which fabric is right for your workload? Let's dive into the ultimate comparison: InfiniBand vs Ethernet.
➤ The Core Difference: Philosophy & Design
At its heart, the difference is one of design philosophy.
InfiniBand (IB) is a purpose-built, lossless fabric designed from the ground up for high-throughput, ultra-low-latency communication in tightly-coupled clusters. It operates at the physical and link layers, offloading processing from the CPU directly to the network adapter.
Ethernet is the universal, flexible standard. Its strength lies in its ubiquity, interoperability, and the economies of scale it enjoys. With advancements like RoCE (RDMA over Converged Ethernet), it now competes directly with IB in performance-centric domains.
➤ Head-to-Head: Key Performance Indicators
Let's break down their performance across critical metrics in a clear comparison table.
Feature | InfiniBand | Ethernet (with RoCE) | Winner for... |
|---|---|---|---|
Latency | Extremely low, consistent (nanoseconds) | Low, but can be variable (microseconds) | InfiniBand (HPC, AI/ML) |
Throughput | Leading edge (e.g., NDR 400G, 800G upcoming) | Keeps pace (e.g., 400GbE, 800GbE) | Draw (Both are fast) |
CPU Offload | Advanced (Transport layer offload to NIC) | Good (Depends on NIC Smartness) | InfiniBand |
Scalability | Excellent within a single fabric/subnet | Excellent, built for global networks | Ethernet (General Use) |
Congestion Control | Built-in, precise, and adaptive | Requires DCQCN/PFC configuration | InfiniBand (Easier) |
Cost | Higher (Specialized hardware) | Lower (Commoditized hardware) | Ethernet |
Management | Centralized (Subnet Manager) | Distributed (Protocols like BGP) | Depends on Need |
When to Choose InfiniBand? 🏎️
InfiniBand is the undisputed champion for applications where latency and consistency are non-negotiable. Its superior congestion control and CPU offloading make it ideal for:
AI and Deep Learning Training: Training massive models like LLMs (Large Language Models) requires synchronized communication across thousands of GPUs. Any latency causes GPUs to sit idle, wasting valuable compute resources.
High-Performance Computing (HPC): Scientific simulations, weather modeling, and genetic sequencing involve millions of messages between nodes. InfiniBand’s low latency ensures these calculations finish in hours, not days.
High-Frequency Trading (HFT): Where every microsecond (or nanosecond) counts.
When to Choose Ethernet? 🚛
Ethernet wins on flexibility, cost, and its universal nature. It's the default choice for:
General-Purpose Data Centers: Web services, enterprise applications, and storage networking (NAS, iSCSI).
Cloud Infrastructure: Its interoperability and scalability are perfect for multi-tenant environments.
Cost-Sensitive Deployments: Where ultimate performance is secondary to budget constraints.
RoCE (RDMA over Converged Ethernet) Environments: For organizations that want RDMA performance but need to leverage their existing Ethernet skills and infrastructure. Proper configuration is key here.

➤ The Critical Role of Optical Transceivers
No discussion about high-speed networking is complete without mentioning the components that make the physical connection possible: optical transceivers and DAC/AOC cables. Whether you're running InfiniBand or Ethernet, choosing the right, high-quality optical module is paramount for signal integrity, power efficiency, and overall network reliability.
This is where compatibility becomes crucial. For a seamless, high-performance network, you need transceivers that are fully compatible with your switches and NICs. This is a core strength of LINK-PP.
For instance, a common and powerful setup for an NDR 400G InfiniBand network would utilize the LINK-PP 400G QSFP-DD transceiver module, designed for both high density and exceptional thermal performance. For 200GbE/HDDR networks, the LINK-PP LQ-M85200-SR4C 200G QSFP56 form factor is a popular and reliable choice, offering a perfect balance of speed and power efficiency.
Using quality, compatible InfiniBand optical modules or Ethernet transceivers from a trusted supplier like LINK-PP prevents link flapping, ensures error-free data transmission, and protects your significant investment in switches and adapters.
➤ Conclusion: It’s About the Workload
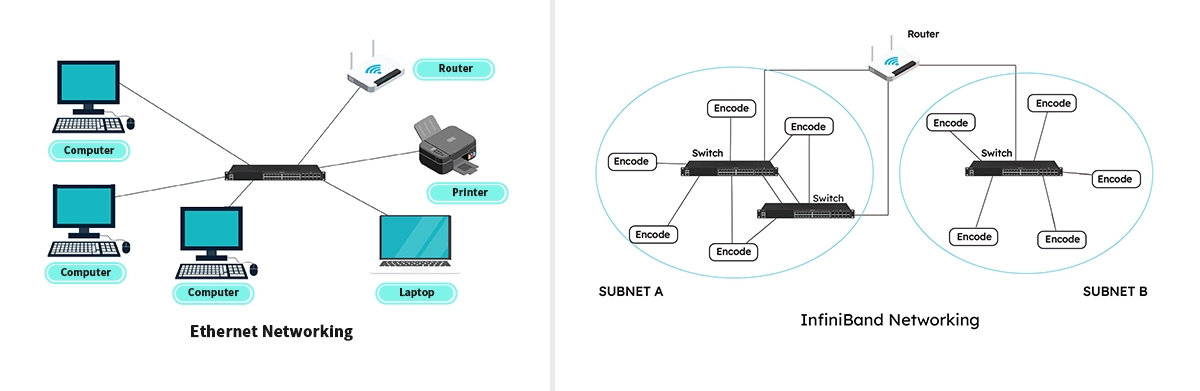
So, who wins the battle of InfiniBand vs Ethernet?
Choose InfiniBand if you are building a specialized, performance-maximizing cluster for AI, HPC, or any workload where every nanosecond of latency translates directly into cost or time savings.
Choose Ethernet (especially with RoCE) for its flexibility, lower cost, and ubiquity. It’s perfect for general data center use, cloud environments, and is rapidly closing the performance gap for more demanding applications.
The lines will continue to blur with technologies like Ultra-Ethernet on the horizon. The best choice depends entirely on your specific technical requirements and business objectives.
➤ FAQ
What is the main difference between InfiniBand and Ethernet?
InfiniBand is used in high-performance computing. It gives very low latency and high bandwidth. Ethernet is good for most business needs. It works with many devices and is easy to manage.
Which network is easier to manage in a data center?
Ethernet is easier for most people to manage. Most IT teams already know how to use Ethernet. InfiniBand needs special training and skills. You might need experts to set up and support it.
Can you use both InfiniBand and Ethernet in one data center?
Yes, you can use both networks together. Many data centers use InfiniBand for fast computing jobs. They use Ethernet for regular business work. Using both gives you speed and flexibility.
Which option is more cost-effective for most businesses?
Ethernet usually costs less money. There are many vendors and cheaper hardware for Ethernet. InfiniBand costs more but gives top performance for special jobs.
Is InfiniBand better for AI and machine learning?
InfiniBand gives faster speed and lower latency for AI training. It moves big data sets quickly. Ethernet works for many AI jobs, but InfiniBand is better for top performance.




