Smart Building Infrastructure refers to the integrated network, automation, IoT, and data systems that enable a building to monitor, analyze, and optimize its environment and operations in real time. It is the digital backbone that allows intelligent buildings to deliver energy efficiency, occupant comfort, safety, security, and scalable connectivity.
Modern smart buildings rely on IP-based networks, Power over Ethernet (PoE), IoT sensors, Building Management Systems (BMS), cloud analytics, and cybersecurity to create dynamic, responsive environments.
🏢 Why Smart Building Infrastructure Matters
Enhanced Operational Efficiency
Unified control of HVAC, lighting, elevators, access, and energy
Predictive maintenance and downtime reduction
Streamlined facility management
Lower Energy Consumption & Carbon Goals
Advanced metering and occupancy-driven controls
AI energy modeling aligned with LEED/WELL standards
Better Occupant Experience
Optimized airflow and lighting
Seamless access control and digital services
Real-time space availability and room automation
Scalable Connectivity for Future Applications
Support for smart workspaces, digital twins, and robotics
Evolution to 5G/Wi-Fi 6 & sensor-rich environments
🏢 Core Components of Smart Building Infrastructure
1. Network & Connectivity Layer (Physical + Logical)
Smart buildings require robust, secure, low-latency networking:
Technology | Role |
|---|---|
Structured copper cabling (Cat6/Cat6A/Cat7) | High-bandwidth Ethernet backbone |
Fiber-optic cabling | High-speed backbone for data aggregation |
PoE/PoE+/PoE++ | Power + data for IoT devices |
Industrial Ethernet switches | Segmented, redundant network control |
Wi-Fi 6/6E, 5G, BLE | Wireless connectivity for end devices |
PoE (IEEE 802.3af/at/bt) is now essential in smart buildings for powering sensors, access points, lighting, cameras, displays, and access controllers.
2. IoT Sensors & Devices
Real-time data intelligence through:
Temperature, humidity, CO₂, and air quality sensors
Occupancy and motion sensors
Smart lighting and environmental controls
Security and access devices
Energy meters and sub-metering systems
3. Building Automation & Management
BMS / BAS (Building Management System) integrates:
HVAC
Lighting control
Fire & life safety systems
Video surveillance & access control
Smart elevators & parking systems
Protocols include BACnet, Modbus, KNX, MQTT, OPC UA, and IP-based convergence.
4. Cloud, Edge & Digital Twin Platforms
Real-time analytics & machine learning
Predictive maintenance
Digital twin simulations
Scalable dashboards & mobile control
5. Cybersecurity Architecture
Secure-by-design with:
VLAN segmentation for OT and IT networks
Zero-Trust access control
Encrypted device communication
Firmware + patch hardening
🏢 Smart Building Infrastructure Architecture
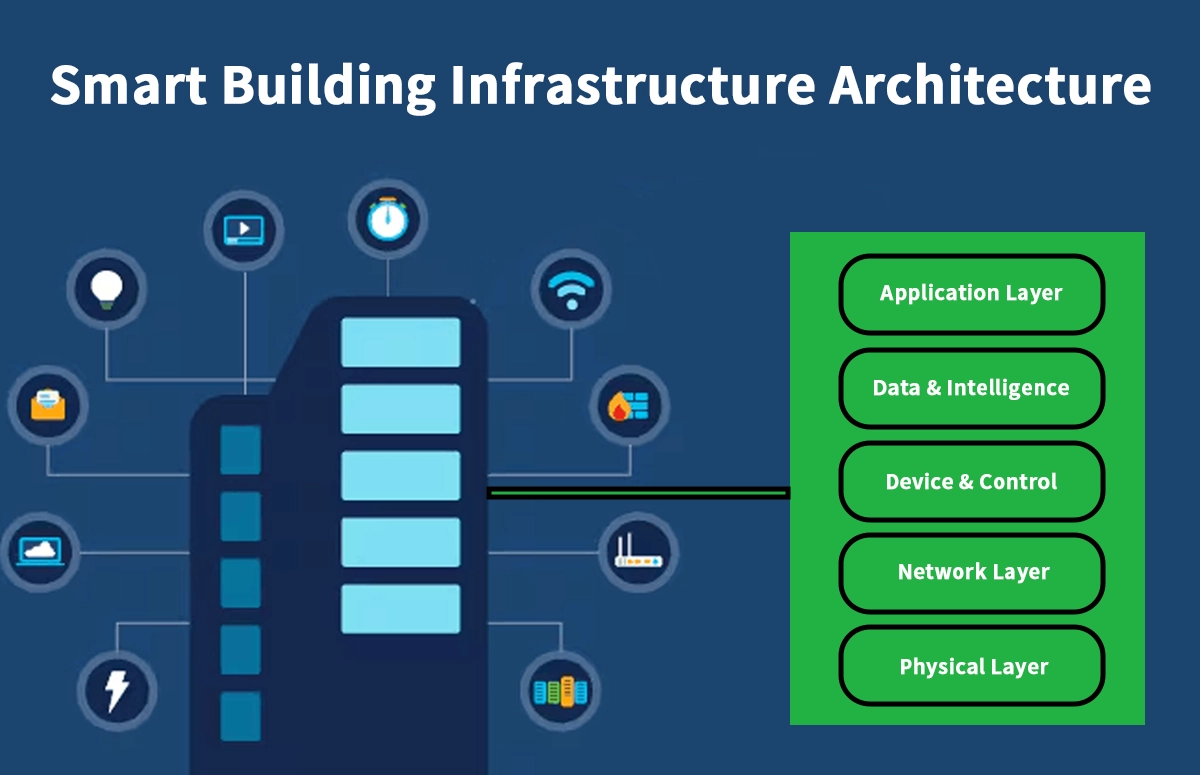
Layered Architecture Model
Layer | Function |
|---|---|
Application Layer | BMS, security, energy platforms |
Data & Intelligence Layer | |
Device & Control Layer | Sensors, controllers, gateways |
Network Layer | Ethernet, fiber, wireless, PoE |
Physical Layer | Power, cabling, structured media |
🏢 Key Standards & Compliance
IEEE 802.3 (Ethernet & PoE)
ASHRAE 135 / BACnet
ISO/IEC 11801 (Structured cabling)
TIA-568 / TIA-862-B (Intelligent building cabling)
LEED, WELL, ISO 50001 (Green building standards)
These standards ensure reliable performance, energy efficiency, and interoperability.
🏢 LINK-PP Connectivity Solutions for Smart Building Infrastructure

Smart buildings depend on high-performance Ethernet and PoE-ready connectivity.
LINK-PP provides LAN magnetics, PoE RJ45 connectors, and fiber transceiver solutions designed for:
PoE wireless access points
IP surveillance & access control
Smart lighting & environmental sensors
Industrial automation controllers
Edge gateways and switches
Example Product Lines for Smart Buildings
Integrated RJ45 MagJack with PoE/PoE+ support
PoE MagJack modules for APs and IP cameras
10G/2.5G/1G Ethernet magnetics for BMS controllers
SFP / SFP+ optical modules for fiber backbones
Industrial-grade RJ45 connectors for harsh environments
LINK-PP products are widely used in enterprise networks, data centers, smart campuses, and intelligent buildings where reliability and EMI performance are critical.
🏢 Conclusion
Smart Building Infrastructure forms the digital and electrical foundation for intelligent building ecosystems. Through IP-based networks, PoE, sensors, structured cabling, BMS integration, and secure cloud control, buildings can achieve:
Higher energy efficiency
Greater comfort & safety
Long-term scalability
Improved operational performance
As the world accelerates toward AI-driven, low-carbon, connected environments, smart building foundations are essential for every modern property.




