
In the world of fiber optics, the extinction ratio is a critical yet often overlooked parameter that can make or break signal integrity. This article explains what extinction ratio is, why it matters for reducing bit error rates in optical communication, and how it impacts optical module performance. We’ll also explore practical tips for optimization and introduce LINK-PP’s high-performance optical modules. Whether you’re an engineer or a tech enthusiast, you’ll gain insights into achieving reliable data transmission.
📝 Key Takeaways
Extinction ratio shows how well a system tells strong signals from weak ones. A high ratio means the signals are easier to see.
You can find extinction ratio with this formula: Power (On) divided by Power (Off). A bigger number means the signal is better.
A high extinction ratio makes the system work better. It helps stop mistakes when sending data and means fewer dropped calls.
Checking extinction ratio often helps you find problems early. This keeps your devices working well.
In things like fiber optics and lasers, a strong extinction ratio means data moves fast and pictures look clear.
📝 Introduction to Extinction Ratio
In optical communication systems, data is transmitted using light signals, where a logical "1" is represented by a high light power level and a logical "0" by a low level. The extinction ratio quantifies the distinction between these levels, defined as the ratio of the power during a "1" bit to the power during a "0" bit. Mathematically, it’s expressed as ER=P₁ / P₀, often converted to decibels (dB). A higher extinction ratio indicates a clearer signal, reducing the risk of errors—think of it as the contrast ratio in a display: sharper contrast means better readability.
Why is this important? In high-speed networks, such as 5G backhaul or data centers, a poor extinction ratio can lead to increased bit error rate (BER), degrading performance. With the growing demand for bandwidth, optimizing extinction ratio has become essential for fiber optic communication efficiency. According to industry standards, an extinction ratio above 10dB is typically desirable for many applications, but requirements vary based on factors like data rate and distance.
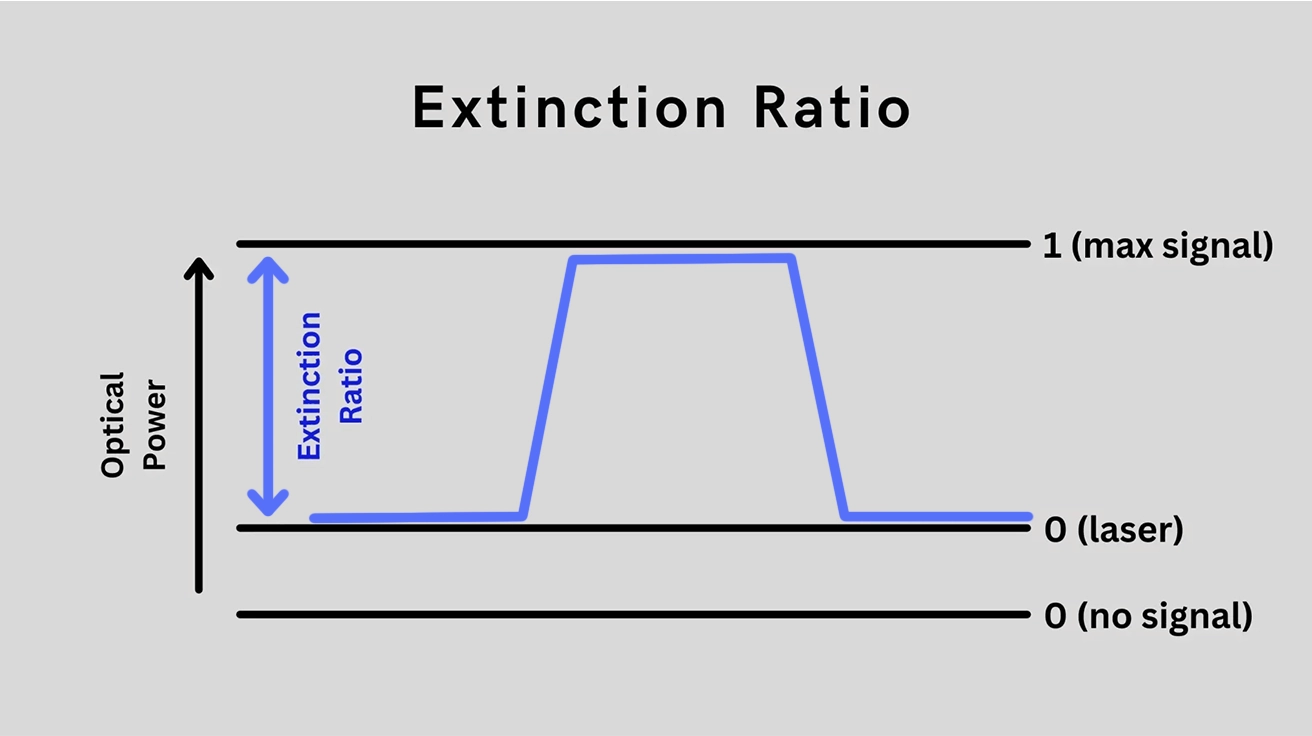
📝 Why Extinction Ratio Matters in Optical Systems
The extinction ratio plays a pivotal role in ensuring signal quality. Here’s why it’s a hot topic in optical engineering:
Impact on Bit Error Rate: A low extinction ratio blurs the line between 1s and 0s, causing the receiver to misinterpret signals. This elevates the BER, potentially leading to data loss. For instance, in long-haul transmission, even a slight degradation can accumulate over distance.
Power Efficiency: A higher extinction ratio often requires more laser power, but it improves sensitivity, allowing for longer reaches without amplifiers. This balances power consumption and performance—a key consideration in green data centers.
Compatibility with Modulation Formats: Advanced formats like PAM4 (used in 400G Ethernet) demand precise extinction ratios to maintain integrity. As networks evolve, extinction ratio specifications tighten.
To illustrate, consider the table below, which shows typical extinction ratio requirements for different applications:
Application | Data Rate | Typical ER Requirement (dB) | Key Challenge |
|---|---|---|---|
Short-Reach Data Center | 10Gbps | 8 - 10dB | Power efficiency |
Long-Haul Telecom | 100Gbps | 12 - 15dB | Signal attenuation over distance |
5G Wireless Front-haul | 25Gbps | 10 - 12dB | Interference mitigation |
This table highlights how extinction ratio needs scale with complexity. For professionals, monitoring this metric is part of optical performance optimization.
📝 Measuring and Improving Extinction Ratio
Accurate measurement is crucial. Tools like optical oscilloscopes or BER testers assess extinction ratio by comparing P₁ and P₀. Best practices include:
Calibrating Equipment: Use certified instruments to avoid errors.
Controlling Temperature: Laser output can drift with heat, affecting the ratio. Active cooling in modules helps stabilize it.
Optimizing Driver Circuits: Adjusting laser bias currents can enhance extinction ratio without sacrificing longevity.
📝 The Role of Extinction Ratio in Optical Modules
Optical modules (or transceivers) are the workhorses of fiber networks, converting electrical signals to light and vice versa. The extinction ratio is a core specification here, directly influencing module reliability. In high-speed optical transceivers, a superior extinction ratio ensures cleaner eye diagrams, which are visual representations of signal quality.
This is where LINK-PP excels. As a leader in high-performance optical modules, LINK-PP integrates advanced laser technology to maintain optimal extinction ratios even under demanding conditions. For example, the LINK-PP LS-SM3125-40C is engineered for extended-reach applications, boasting an extinction ratio of up to 12 dB. This makes it ideal for data center interconnects (DCI) where low BER is non-negotiable. By choosing modules like these, you address extinction ratio requirements in transceivers proactively, reducing downtime.
Moreover, LINK-PP’s focus on optical module compatibility means their products adhere to industry standards, ensuring seamless integration. When selecting a module, always verify the extinction ratio specs—it’s a small detail with big implications for network health.
📝 Conclusion and Next Steps
Extinction ratio (ER) isn’t just a technical jargon; it’s a gateway to robust optical communication. From minimizing errors to enabling future-proof networks, its importance can’t be overstated. As you refine your systems, remember that components like LINK-PP optical modules can be game-changers.
📝 FAQ
What does a low extinction ratio mean for your device?
A low extinction ratio makes it hard for your device to tell "on" from "off." You may notice more mistakes or weak signals. If you see these problems, check your system.
What tools can you use to measure extinction ratio?
You can use a photodetector, oscilloscope, or polarizer. These tools help you see the difference between "on" and "off."
Tip: Always use tools that are set up right for the best results.
What causes extinction ratio to drop?
Dust, dirty lenses, or broken parts can make extinction ratio lower. Clean your devices and look for damage.
Doing regular checks helps keep extinction ratio high.
What is a good extinction ratio value?
A good extinction ratio depends on your system. Most optical systems work best with values over 10dB.
Note: Higher values mean signals are clearer and there are fewer mistakes.
What happens if you ignore extinction ratio?
If you do not check extinction ratio, your device may send mixed signals. This can make data slow, calls drop, or cause mistakes. Always check extinction ratio to keep your technology working well.


