In our hyper-connected world, a buffering video or a laggy video call is more than an inconvenience—it's a disruption. The demand for faster, more reliable, and lower-latency wireless connectivity has never been higher. Enter Multi-Link Operation (MLO), a cornerstone technology of the new Wi-Fi 7 (802.11be) standard that promises to solve these very challenges.
This comprehensive guide will demystify what MLO is, how it works, its profound benefits, and why it represents a quantum leap in wireless technology. We'll also explore the critical role of supporting hardware, including high-performance optical modules from industry leaders like LINK-PP.
💡 Understanding the Basics: What Exactly is MLO?
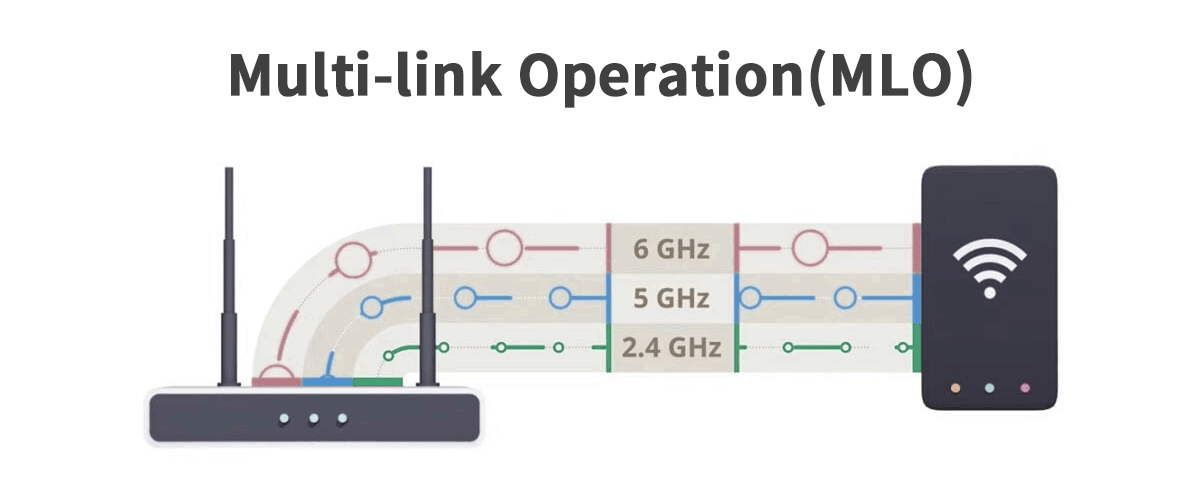
Traditionally, your Wi-Fi device (like a laptop or smartphone) connects to a router using a single radio link at a time—either the 2.4GHz, 5GHz, or 6GHz band. You might switch between them, but you're only using one.
Multi-Link Operation (MLO) shatters this limitation. It allows a device to establish and use multiple connections across different frequency bands simultaneously. Think of it as having several dedicated lanes on a highway instead of a single, congested one. Your data can be split, sent, and received over multiple paths at the same time, or one link can serve as an instant backup for another.
This fundamental shift is what makes MLO technology in Wi-Fi 7 a true game-changer for seamless connectivity.
💡 How Does Multi-Link Operation Work? A Technical Peek
At its core, MLO enables a Wi-Fi 7 access point (AP) and a Wi-Fi 7 client device to set up multiple links. These links can operate in different ways, managed by an intelligent controller:
Simultaneous Transmission and Reception: Data packets are sent and received over multiple bands at the same time, dramatically increasing total throughput.
Seamless Redundancy and Failover: If one link experiences interference or drops, the other links instantly take over without any noticeable interruption—perfect for critical applications.
Load Balancing: Traffic is dynamically distributed based on the real-time conditions of each band, optimizing overall network performance.
The key to achieving the benefits of multi-link operation for low latency is this coordinated, simultaneous use of spectrum resources, which was not possible in previous Wi-Fi generations.
💡 The Tangible Benefits: Why MLO is a Big Deal
The advantages of implementing MLO are transformative for both home users and enterprises. Here’s a quick comparison:
Feature | Traditional Wi-Fi (Pre-MLO) | Wi-Fi 7 with MLO | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|---|---|
Speed & Throughput | Limited to one band's maximum speed. | Aggregated speed from multiple bands. | Faster downloads, uploads, and data transfers. |
Latency | Variable; susceptible to interference on a single band. | Extremely low and predictable latency. | Ideal for gaming, VR, and real-time collaboration. |
Reliability | A weak or congested link causes drops. | High resilience with instant failover. | No more dropped Zoom calls or gaming sessions. |
Efficiency | Inefficient band switching. | Intelligent traffic management across links. | Optimized network performance for all connected devices. |
For businesses looking to improve network performance with multi-link operation, this means a more robust infrastructure capable of handling IoT devices, high-density deployments, and mission-critical operations without a hitch.
💡 The Role of Optical Modules in a Robust MLO Ecosystem
While MLO focuses on the wireless "last mile," its performance is heavily dependent on the backbone network that supports the access points. This is where high-speed, reliable optical modules become indispensable.
An MLO-capable Wi-Fi 7 AP generates a massive aggregate data stream from its multiple radio links. To prevent the wired uplink from becoming a bottleneck, these APs require high-bandwidth fiber connections. Optical transceivers, such as SFP+, SFP28, and QSFP28, are the components that convert electrical signals from the AP's port into light signals for transmission over fiber optic cables.
Why does this matter for MLO?
A true multi-gigabit wireless backhaul solution is needed to feed data to and from the MLO radios. If the AP's connection to the core network is slow, the benefits of MLO are lost. High-performance optical modules ensure that the wired backbone can keep up with the wireless speed, delivering a truly end-to-end high-performance experience.
For network architects building future-proof systems, choosing the right optical partner is crucial. LINK-PP offers a range of certified, high-performance optical transceivers designed for these demanding applications. A perfect example is the LINK-PP SFP28-25G-LR, which provides a robust 10Gbps link over single-mode fiber with low power consumption and high reliability—exactly the kind of stable, high-bandwidth foundation a powerful MLO network requires.
Integrating LINK-PP's compatible optical components ensures your entire network infrastructure, from the core to the wireless edge, is optimized for the future of high-speed connectivity.
💡 Real-World Applications of MLO Technology
Where will you feel the impact of MLO the most?
Competitive Gaming & eSports: Eliminate lag spikes for a competitive edge.
Augmented & Virtual Reality (AR/VR): Enable high-resolution, untethered experiences with flawless tracking.
Hybrid Work & Teleconferencing: Crystal-clear video and audio with no dropouts, even when others are streaming.
Enterprise & Industrial IoT: Reliable connectivity for hundreds of devices in smart factories and offices.
Instant Data Backups and Syncing: Large files sync in the background faster and more reliably.
💡 Conclusion: The Future is Multi-Linked
Multi-Link Operation is not just an incremental update; it's a foundational shift that makes Wi-Fi more reliable, faster, and smarter. As Wi-Fi 7 devices become ubiquitous, understanding and leveraging MLO for enterprise networks will be key to maintaining a competitive advantage.
The full potential of MLO is unlocked when the entire network stack—from the wireless radios to the optical backhaul—is designed for performance. This is where a strategic partnership with a proven hardware provider makes all the difference.
Ready to future-proof your network and harness the power of Wi-Fi 7 and MLO?
Explore LINK-PP’s comprehensive portfolio of networking solutions, including our high-performance optical transceivers, to ensure your infrastructure is ready for the next generation of connectivity.
🔗 Contact LINK-PP Experts Today to design a network that leverages MLO for unparalleled performance and reliability.
💡 FAQ
What is a WiFi multi-link operation?
Multi-link operation lets you use more than one wi-fi band at the same time. You get faster speeds and a more stable connection. Your device can send and receive data over several wi-fi channels together.
What does a mlo-enabled ssid mean?
A mlo-enabled ssid is a wi-fi network name that supports multi-link operation. You connect to one wi-fi name, but your device uses many wi-fi bands. This gives you better wi-fi performance.
What devices support WiFi multi-link operation?
Devices that support wi-fi multi-link operation include some new phones, laptops, and routers. You need both your device and your router to support wi-fi 7 for multi-link operation to work.
What benefits do you get from WiFi multi-link operation?
You get faster wi-fi speeds, lower lag, and more reliable connections. Multi-link operation helps your wi-fi work better in busy places. You see smoother streaming and gaming.
What should you check before using a mlo-enabled ssid?
You should check if your device and router support wi-fi 7 and multi-link operation. Look for wi-fi 7 labels and mlo-enabled ssid in the product details. This helps you get the best wi-fi experience.


