In our always-online world, a few milliseconds can feel like an eternity. Whether you're a gamer eliminated before you can react, a professional frustrated by a laggy video call, or a customer abandoning a slow-loading website, you've experienced the effects of network latency.
But what exactly is this invisible force that dictates the speed of our digital interactions? In this comprehensive guide, we'll demystify network latency, explore its root causes, and provide a practical guide on how to reduce network latency for a smoother, faster online experience.
➤ Key Takeaways
Network latency is the wait you feel when data moves on a network. Lower latency means your internet is faster. It helps things like gaming and video calls work better.
You can check network latency with tools like 'ping.' A low ping, under 50ms, shows good speed. A high ping, over 150ms, can cause problems.
To lower latency at home, get closer to your Wi-Fi router. Try using a wired connection. Close apps you are not using. These easy steps can make your internet faster.
Getting new network equipment, like routers and cables, can lower latency a lot. New devices work quicker and move more data.
Check your network often to find latency problems early. Use tools to test speed. Make changes when needed to keep your internet working well.
➤ Defining Network Latency: It's More Than Just Speed
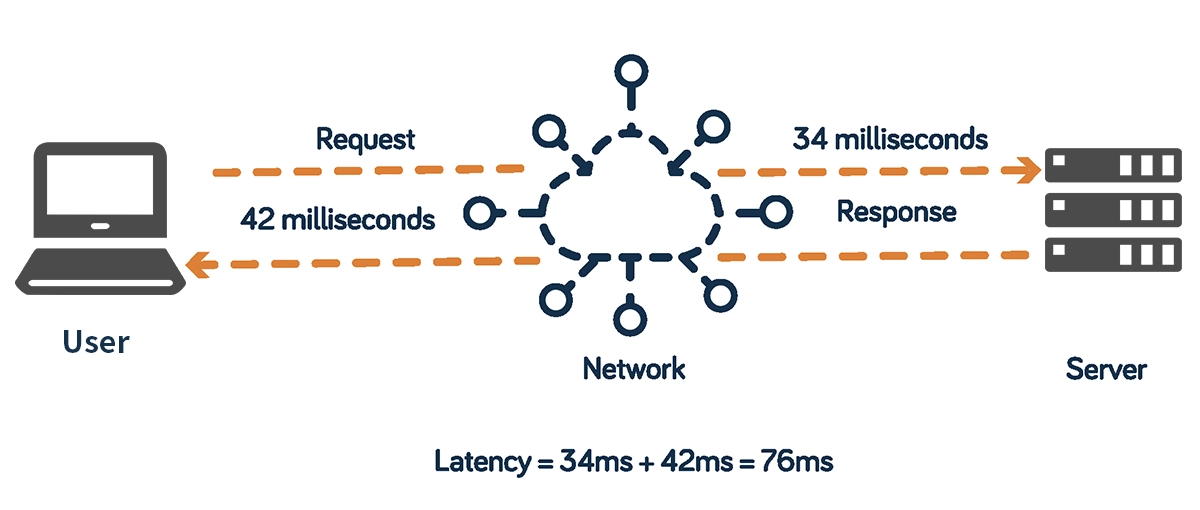
Network latency is the time it takes for a data packet to travel from its source to its destination and back again. Often measured as "Ping" in diagnostic tools, it's the digital equivalent of the delay between asking a question and hearing the answer.
It's crucial to distinguish latency from bandwidth, as they are often confused:
Feature | Latency | Bandwidth |
|---|---|---|
What it measures | Time (Delay) | Volume (Capacity) |
Analogy | The speed of a single car on a highway. | The number of lanes on a highway. |
Primary Concern | Responsiveness. How long until the first byte of data arrives? | Throughput. How much data can be transferred in a given period? |
Measured In | Milliseconds (ms) | Megabits per second (Mbps) or Gigabits per second (Gbps) |
A high-bandwidth connection can still suffer from high latency. You can have a 10-lane highway (high bandwidth) with a 30-minute delay at a toll booth (high latency).
➤ The Main Culprits: What Causes Network Latency?
Understanding how to lower network latency and improve performance starts with knowing its common causes:
Propagation Delay: The fundamental limit—the time dictated by the speed of light as data travels through a cable or fiber. This is unavoidable over long distances.
Transmission Delay: The time it takes to push the data packet onto the network medium. Larger packets take longer to "load onto the truck."
Processing Delay: The time routers and switches take to examine the packet's header, check routing tables, and decide where to send it next.
Queueing Delay: When network equipment is congested, packets are held in buffers (queues) before they can be processed and sent, much like cars waiting at a traffic light.
For businesses and data centers looking for low latency network solutions, addressing these delays at the hardware level is paramount.
➤ The Real-World Impact of High Latency
The effects of latency extend far beyond a single buffering video.
Gaming: In competitive online games, high latency (or "lag") means your actions are delayed, putting you at a severe disadvantage.
Video Conferencing: High latency causes awkward pauses, frozen screens, and people talking over each other, crippling effective communication.
Finance: In high-frequency trading, milliseconds of latency can mean the difference between a profitable trade and a multi-million dollar loss.
Web Browsing & E-commerce: A delay of just 100 milliseconds can reduce conversion rates by up to 7%, as users quickly lose patience with slow-loading pages.
➤ How to Reduce Network Latency: A Practical Guide
Reducing latency often requires a multi-faceted approach. Here are some of the most effective strategies:
Use a Wired Connection: Ethernet cables provide a more direct and stable connection than Wi-Fi, which is susceptible to interference and signal degradation.
Leverage a CDN (Content Delivery Network): CDNs cache website content on servers geographically closer to your users, drastically reducing propagation delay.
Optimize Routing: Implement efficient routing protocols and use Tier-1 internet providers to ensure data takes the shortest possible path.
Prioritize Traffic with QoS (Quality of Service): Configure your network to prioritize latency-sensitive traffic like VoIP and video calls over less critical data.
Upgrade Your Hardware: Outdated routers, switches, and network interface cards can be significant bottlenecks. This leads us to a critical component for modern, high-speed networks.
➤ The Role of Optical Transceivers in Minimizing Latency
When every microsecond counts, the hardware inside your network switches and servers becomes critically important. This is where optical transceivers, or optical modules, come into play.
An optic module is the component that converts electrical signals from a network device into optical signals for transmission over fiber optic cables, and vice-versa. The performance of these modules directly impacts latency, signal integrity, and overall network reliability.
Key attributes of a low-latency optic module include:
High Data Rate: Modules that support 100G, 400G, and beyond can process data much faster.
Advanced DSP (Digital Signal Processing): Efficient signal processing reduces the time needed to encode and decode data.
Quality Components: Superior manufacturing and components ensure minimal signal degradation and lower error rates, preventing retransmissions that increase latency.
For network engineers seeking a reliable and high-performance partner, LINK-PP offers a range of cutting-edge transceivers designed to meet the demands of modern data centers and enterprise networks. A standout solution for high-density, high-speed applications is the LINK-PP 400G QSFP-DD DR4 module. This optic provides a robust, low-latency connection perfect for spine-leaf architectures and data center interconnects, ensuring your backbone network operates at peak efficiency.
➤ Conclusion: Mastering Latency for a Faster Future
Network latency is an unavoidable aspect of digital communication, but it is not an insurmountable obstacle. By understanding its causes—from propagation delay to hardware bottlenecks—you can take informed steps to mitigate it.
From simple fixes like using an Ethernet cable to strategic investments in CDNs and high-performance hardware like LINK-PP's 400G optics, every reduction in milliseconds counts. In today's competitive landscape, optimizing for low latency network performance is not just a technical goal; it's a business imperative that enhances user experience, drives engagement, and fuels growth.
➤ FAQ
What is a good network latency for gaming?
For gaming, you wide area networkt latency below 50 milliseconds. Lower latency lets you react quickly in games. High latency can cause lag and make games harder.
What tools can you use to check network latency?
You can use the ping command on your computer. Online ping testers are also helpful. Network monitoring apps let you see latency and watch for changes.
What causes sudden spikes in network latency?
Network congestion can cause latency spikes. Old hardware or too many devices can also be a problem. You might see higher latency when lots of people use the network.
What steps help you lower network latency at home?
Try moving closer to your router. Use wired connections instead of Wi-Fi. Close apps you are not using. Restart your router and update your device software. These steps can help your internet work faster.


