
In the heart of every data center, server room, and network closet, an unsung hero works tirelessly to ensure operational continuity. Often overlooked next to flashy servers and sleek switches, the Power Distribution Unit (PDU) is the critical backbone of your infrastructure's power chain. Choosing the right PDU isn't just about plugging in equipment; it's a strategic decision impacting efficiency, uptime, and scalability. This comprehensive guide will demystify PDUs, explore their evolution, and help you select the perfect unit for your needs.
➤ Key Takeaways
A Power Distribution Unit (PDU) is important for giving power to many devices in data centers. It makes sure each device gets the right amount of power.
Using a PDU stops overloads and electrical dangers. It keeps your equipment safe and lowers the chance of downtime.
Pick the right PDU for your needs. Basic PDUs are simple. Metered PDUs let you check power use. Switched PDUs let you control power from far away. Intelligent PDUs have more features.
Check how much power you need before you pick a PDU. This helps make sure it can support your equipment now and later.
Setting up and organizing cables with a PDU can make your data center safer and work better.
➤ What is a PDU and Why Does It Matter?
A Power Distribution Unit (PDU) is a device designed to distribute reliable network power to multiple IT equipment components. Think of it as an advanced, rack-mounted power strip. However, modern PDUs have evolved far beyond simple distribution. They are pivotal for:
Organized Power Distribution: Efficiently power servers, storage, networking gear, and high-speed optics modules within a single rack.
Capacity Management: Ensuring the total power draw does not exceed the circuit's capacity.
Monitoring and Control: Providing real-time insights into power consumption, which is crucial for data center power monitoring and rack power management.
Remote Management: Allowing administrators to reboot locked-up equipment remotely, reducing downtime and operational costs.
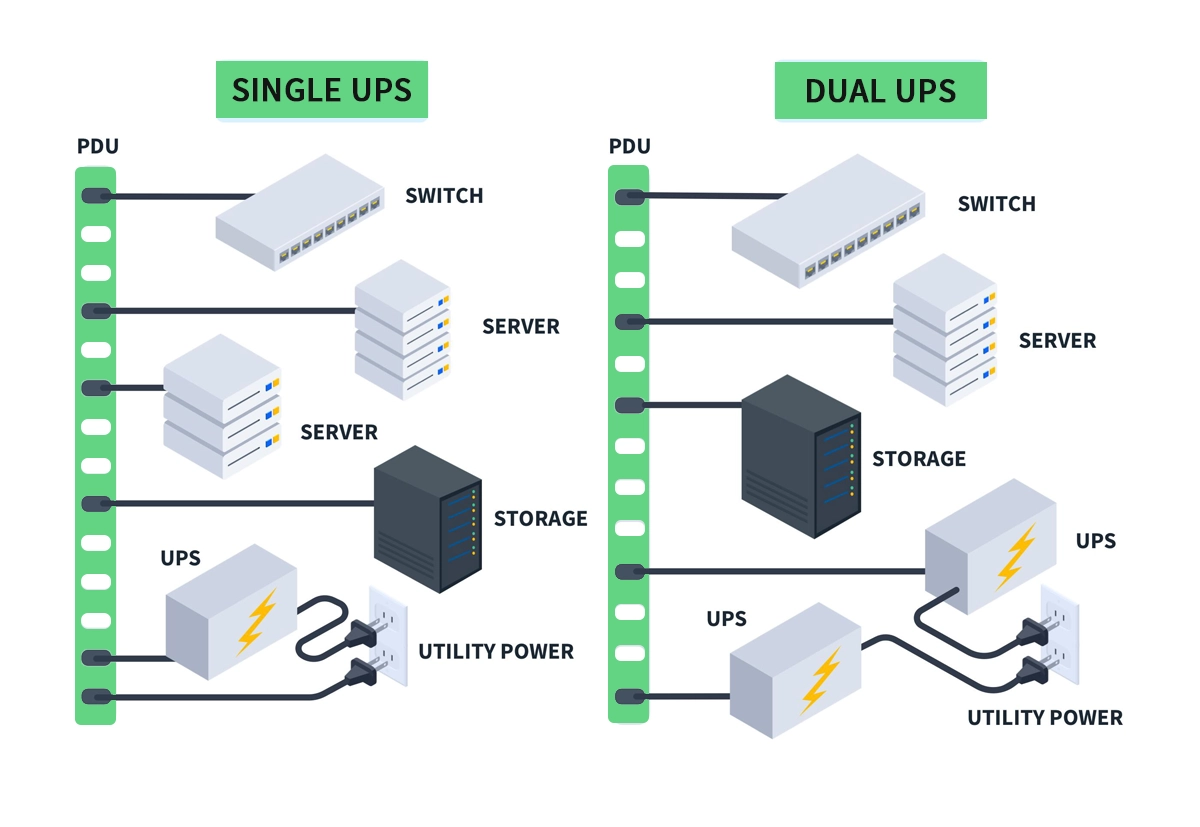
➤ Basic vs. Smart: Understanding PDU Types
Not all PDUs are created equal. They range from simple passive units to intelligent systems. The table below breaks down the primary categories:
Feature | Basic PDU | Metered PDU | Monitored PDU | Switched / Smart PDU |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Core Function | Power distribution only | Distribution + load monitoring | Distribution + detailed monitoring | Distribution + monitoring + remote outlet control |
Power Metrics | None | Aggregate current/load at unit level | Per-phase or aggregate voltage, current, power (kVA/kW) | Detailed per-phase & per-outlet metrics |
Outlet Control | No | No | No | Yes, individual outlet switching |
Network Management | No | No | Yes (read-only) | Yes (read/write) via SNMP, HTTP, SSH |
Primary Use Case | Simple racks with stable loads | Avoiding circuit overloads | Capacity planning, efficiency tracking | Remote power management, advanced data center power monitoring, and orchestration |
➤ The Game Changer: Capabilities of Smart/Intelligent PDUs
For modern, agile operations, Smart PDUs or Intelligent PDUs are indispensable. They transform power from a utility into actionable data and control. Key features include:
Real-Time Environmental Monitoring: Many units integrate sensors for temperature and humidity, providing a complete picture of rack health.
Power Sequencing: Define startup/shutdown order for equipment to prevent inrush current surges.
Alerts and Notifications: Receive instant alerts via email or SNMP trap when power thresholds or environmental conditions are breached.
| Common Challenge | How a Smart PDU Solves It |
| :--- | :--- |
| "Which server in rack A7 is causing the spike?" | Per-outlet power metering identifies the exact device. |
| "A network switch on a remote site is frozen." | Remote outlet reboot restores service without a truck roll. |
| "Are we optimizing power capacity in our racks?" | Historical trend data informs right-sizing and prevents over-provisioning. |
➤ Powering the High-Speed Network: PDUs and Optical Modules
As network speeds catapult to 400G and 800G, the supporting infrastructure must evolve. High-density switches loaded with optical transceiver modules demand more precise power delivery and management. This is where the synergy between advanced PDUs and quality optics becomes critical.
Modern high-speed optical modules, while becoming more efficient per bit, still contribute significantly to a switch's overall thermal design power (TDP). A Smart PDU provides the granular visibility needed to accurately attribute power consumption. For instance, when deploying a high-density 400G switch populated with optics, administrators can monitor its exact power draw in real-time, ensuring it stays within the rack's PDU branch circuit limits.
Furthermore, for setups requiring direct-attach copper or active optical cables for short-reach, high-speed connections, ensuring stable, clean power from the PDU minimizes signal integrity risks. When selecting components for a high-performance rack, consider a holistic power strategy that pairs a reliable, monitored PDU with quality, power-efficient optics. For example, integrating a LINK-PP 400G DR4 module into your core switch requires assurance that the power infrastructure can support the aggregate load reliably and provide data for optimization. Brands like LINK-PP engineer their fibre optic modules for optimal performance-per-watt, a factor that directly influences your rack power management decisions.
➤ How to Choose the Right PDU: A Quick Selection Guide
Assess Your Needs: Do you need basic power, monitoring, or control? Start with your operational and data center power monitoring requirements.
Calculate Power Capacity: Sum the maximum power requirements of all equipment in the rack, then add a margin (typically 20-30%). Choose a PDU with a corresponding amperage rating (e.g., 30A, 60A).
Determine Plug Types: Match the PDU's input plug (e.g., NEMA L6-30P, IEC 309) to your facility's outlet and its output receptacles (C13, C19) to your equipment cords.
Consider Form Factor: Select between vertical (0U) or horizontal (1U/2U) mounting based on your rack space and cable management preferences.
Plan for the Future: Opt for a unit with some spare outlets and consider stepping up to a Monitored or Switched PDU for future-proof flexibility, especially if managing remote power distribution is a goal.
➤ Conclusion: More Than Just a Power Strip
Today's Power Distribution Unit is a strategic management tool integral to data center infrastructure efficiency and network uptime. From ensuring the basic orderly flow of electricity to enabling sophisticated remote power management and proactive capacity planning, the right PDU is a cornerstone of a resilient IT environment.
For organizations looking to build or modernize their infrastructure, investing in intelligent power distribution from the start pays dividends in reduced operational risk, lower energy costs, and enhanced control. Partnering with providers that understand the entire ecosystem—from reliable PDU solutions to high-performance components like LINK-PP's optical transceivers—ensures a cohesive, efficient, and future-ready data center.


