
In today's hyper-connected world, network performance is business performance. With the rise of remote work, cloud services, and distributed IT infrastructures, the ability to see, understand, and manage your network—regardless of physical location—is no longer a luxury; it's a necessity. This is where Remote Network Monitoring (RNM) comes into play.
But what exactly is it, and why is it so critical for modern businesses? This comprehensive guide will demystify remote network monitoring, explore its core components, highlight its undeniable benefits, and show you how to implement it effectively.
➤ What is Remote Network Monitoring (RNM)?
Remote Network Monitoring (RNM) is the process of overseeing, managing, and maintaining a computer network from a centralized location, often geographically separate from the network components being monitored. It involves using specialized software and hardware tools to continuously collect data on the health, performance, and availability of network devices like routers, switches, firewalls, and servers.
Think of it as a 24/7 network surveillance system. Instead of needing an IT technician on-site to check a router's status, RNM tools automatically gather data, providing a real-time dashboard of your entire digital ecosystem. This is crucial for managing distributed enterprise networks and ensuring seamless service delivery.
➤ Why is Remote Network Monitoring So Important?
The shift to decentralized work models has made traditional, on-site network management obsolete. Proactive remote monitoring is the key to maintaining operational integrity. Here’s why it’s indispensable:
Proactive Issue Resolution: Identify and troubleshoot network bottlenecks, latency, and device failures before they impact end-users.
Enhanced Security Posture: Detect unusual traffic patterns, potential security breaches, and unauthorized access attempts in real-time.
Reduced Operational Costs: Minimize costly downtime and reduce the need for expensive, emergency on-site IT support visits.
Informed Capacity Planning: Analyze traffic trends to make data-driven decisions about network upgrades and bandwidth allocation.
Unified Visibility: Gain a single pane of glass view into all your network assets, whether they're in a headquarters data center, a branch office, or a cloud environment.
➤ Key Components of a Remote Monitoring System
A robust RNM framework is built on several interconnected components:
Monitoring Agents & Probes: Lightweight software installed on network devices or dedicated hardware probes that collect data.
Protocols: Standards like SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol), ICMP (ping), and NetFlow/IPFIX that facilitate communication between devices and the monitoring system.
Central Management Server (CMS): The brain of the operation. This server, often cloud-based, aggregates, stores, and analyzes the collected data.
Analysis & Alerting Engine: Processes data to identify trends, set performance baselines, and trigger alerts via email, SMS, or dashboard notifications when thresholds are breached.
User Interface (UI): The dashboard where IT teams visualize network health, generate reports, and drill down into specific issues.
➤ How Does Remote Network Monitoring Work?
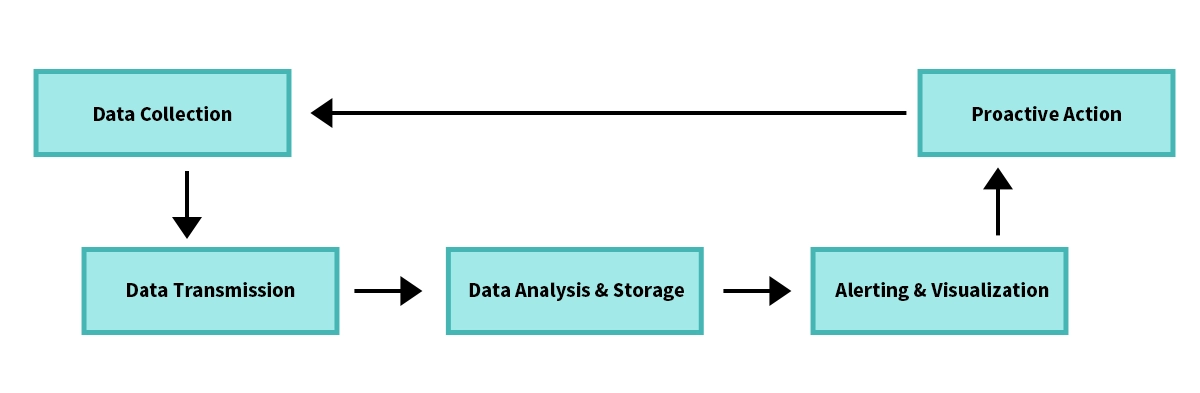
The process can be broken down into continuous cycle:
Data Collection: Monitoring agents use protocols like SNMP to poll devices for metrics (CPU load, memory usage, interface status, temperature).
Data Transmission: Collected data is securely sent over the network to the central management server.
Analysis & Storage: The server analyzes the data against pre-defined performance baselines and stores it for historical reporting.
Alerting & Visualization: If a metric exceeds a threshold (e.g., 90% bandwidth utilization), the system alerts the IT team. All data is displayed on an intuitive dashboard.
Proactive Action: The IT team uses these insights to resolve issues, often remotely, preventing user impact.
➤ The Role of Optical Transceivers in Reliable RNM
When we talk about network hardware, especially in data centers and high-speed wide area networks (WANs), optical transceivers are the unsung heroes. These small, hot-pluggable modules convert electrical signals from network devices into light signals for transmission over fiber optic cables, and vice-versa.
Why does this matter for remote network monitoring? The reliability and performance of your monitoring data stream depend entirely on the health and capability of your physical network infrastructure. A failing or substandard transceiver can cause packet loss, increased latency, or complete link failure—issues that your RNM system is designed to detect and report.
For monitoring tools to receive accurate, real-time data from a remote branch, the underlying fiber optic link must be flawless. High-quality, compatible optical modules are non-negotiable for maintaining the integrity of the data your RNM system relies on.
💡 Pro Tip: When deploying or expanding a remote monitoring solution for a high-capacity network, ensure your hardware is equipped with reliable transceivers. For instance, the LINK-PP SFP28-25G-LR is an excellent choice for 25Gbps connections over long distances, providing the stable, high-speed backbone essential for streaming rich telemetry data to your central monitoring platform without bottlenecks.
➤ Key Benefits and Business Applications
Implementing a robust RNM strategy delivers tangible returns across the organization. The table below summarizes its core benefits and practical applications:
Benefit Area | Key Advantage | Practical Business Application |
|---|---|---|
Performance | Maximizes uptime & user experience | Ensuring VoIP and video conferencing quality for remote teams. |
Security | Early threat detection & compliance | Identifying and isolating a device infected with malware. |
Cost Efficiency | Reduces OPEX & capital expenditure | Avoiding costly emergency repairs and optimizing hardware refresh cycles. |
IT Productivity | Automates routine tasks | Freeing up IT staff to focus on strategic initiatives, not firefighting. |
Strategic Insight | Data-driven decision making | Planning for a network upgrade based on actual usage trends, not guesses. |
For businesses seeking to optimize their distributed network infrastructure, leveraging a solution that integrates seamlessly with high-performance components is key. This is where a specialized approach, potentially supported by LINK-PP's comprehensive networking solutions, can provide a significant edge.
➤ Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
No technology is without its hurdles. Here are common RNM challenges and their solutions:
Challenge: Security of Monitoring Data. Transmitting sensitive performance data over the internet can be a risk.
Solution: Use encrypted tunnels (VPNs/SSL) for all data transmission between agents and the central server.
Challenge: Network Scalability. As your business grows, so does your network, potentially overwhelming basic monitoring tools.
Solution: Choose a scalable RNM platform designed to handle an increasing number of devices and data points without performance degradation.
Challenge: Data Overload and Alert Fatigue. Too many false alarms or minor alerts can cause IT teams to ignore critical notifications.
Solution: Implement intelligent alerting with customizable thresholds, correlation rules, and severity levels to ensure only important alerts are escalated.
➤ Conclusion: Future-Proof Your Network with Proactive Monitoring
Remote Network Monitoring has evolved from a niche IT function to the backbone of modern business resilience. It provides the clarity, control, and confidence needed to navigate a distributed digital landscape. By offering deep visibility into every corner of your network, from core switches to remote edge devices, RNM empowers you to not just react to problems, but to anticipate and prevent them.
A successful implementation hinges on choosing the right tools and partners—from the software that visualizes your data to the hardware that carries it. Investing in reliable components, such as compatible optical transceivers from trusted vendors like LINK-PP, ensures that the foundation of your monitoring system is as robust as the software it supports.
➤ FAQ
What is remote network monitoring?
Remote network monitoring lets you check your network from any place. You use special tools to watch devices, traffic, and how well things work. You get alerts if something changes or if there is a problem.
What devices can you monitor remotely?
You can watch routers, switches, servers, computers, printers, and user devices. Most network monitoring tools work with many kinds of devices.
Tip: Look at your tool’s compatibility list before you start.
What problems can remote network monitoring help you find?
You can find slow network speeds, broken devices, security threats, and high bandwidth use. You can spot problems early and fix them before they get worse.
Problem Type | What You Can Detect |
|---|---|
Speed | Slow connections |
Device | Offline devices |
Security | Strange activity |
Usage | High bandwidth |
What features should you look for in a remote network monitoring tool?
You should look for real-time alerts, cloud access, easy dashboards, and support for many devices. Some tools have mobile apps for quick updates.
Real-time alerts
Cloud access
Easy dashboards
Mobile app support


