In the vast and intricate ecosystem of internet protocols, TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) often steals the spotlight. It's the reliable, methodical postman who ensures every package arrives, in order, and intact. But what about the need for speed? What about applications where a millisecond of delay is too much? Enter UDP (User Datagram Protocol), the lightning-fast, no-frills courier of the internet.
This deep dive will unpack everything you need to know about UDP, why it's critical for modern technology, and how the right hardware, like LINK-PP's advanced optical modules, can unlock its full potential.
📄 Key Takeaways
UDP lets you send data fast without making a connection. Use it when speed matters more than being sure all data arrives.
Each UDP packet is called a datagram and moves on its own. You can send data quickly, but some packets might not make it.
UDP works well for real-time apps like online games and live videos. These apps can lose a little data and still work fine.
Reading RFC 768 helps you learn UDP's rules and setup. This paper explains how UDP works and why it is simple.
Watch out for security problems with UDP. It does not have built-in checks or encryption, so use extra safety steps for private data.
📄 What is UDP? The Core Concept
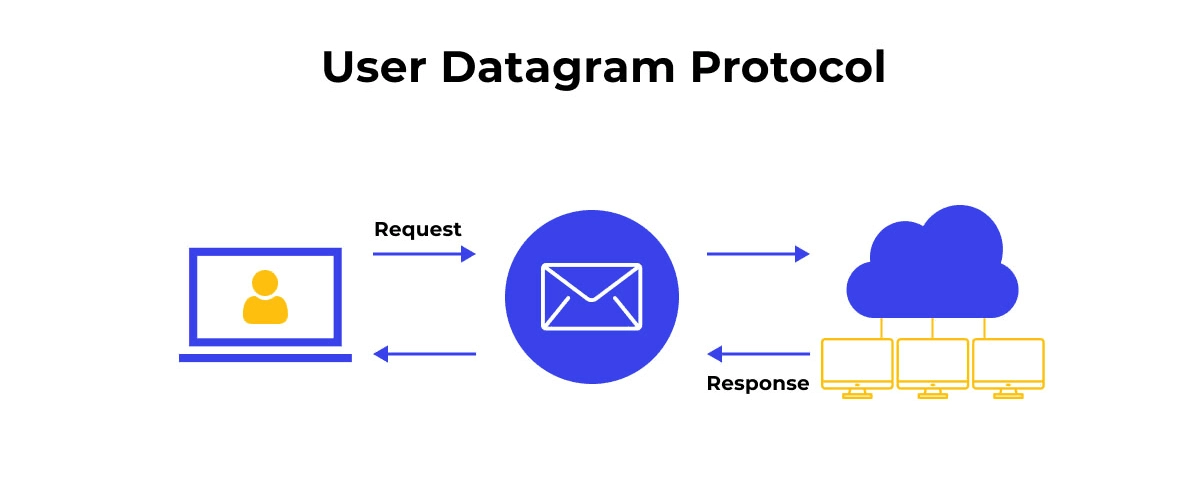
User Datagram Protocol (UDP) is one of the core members of the Internet Protocol suite, often juxtaposed with TCP. Its design philosophy is simple: minimalism. Defined in RFC 768, UDP provides a way for applications to send messages, known as datagrams, to other hosts on an IP network without the overhead of establishing a dedicated connection first.
Think of it as a shout in a crowded room versus a private, confirmed phone call. UDP is the shout—it's fast and efficient, but there's no guarantee the intended person heard it, nor is there a built-in mechanism for them to ask you to repeat it.
📄 UDP vs. TCP: A Head-to-Head Comparison
To truly appreciate UDP, we must contrast it with its more meticulous sibling, TCP. The table below breaks down their fundamental differences.
Feature | TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) | UDP (User Datagram Protocol) |
|---|---|---|
Connection | Connection-oriented (handshake) | Connectionless (no handshake) |
Reliability | High (acknowledgments & retransmissions) | Low (no delivery guarantees) |
Ordering | Guaranteed in-order packet delivery | No inherent ordering |
Speed & Overhead | Slower due to overhead | Very fast with minimal overhead |
Data Flow | Stream-based | Message (datagram) based |
Ideal Use Cases | Web browsing, email, file transfers | Live video, VoIP, online gaming, DNS |
As you can see, UDP's "weaknesses" are, in fact, its greatest strengths for specific low latency UDP applications.
📄 Where UDP Shines: Real-World Applications
UDP isn't for sending an important contract, but it's perfect for a live conversation. Its architecture makes it indispensable for:
Real-Time Communication: Video conferencing (Zoom, Teams) and Voice over IP (VoIP) use UDP because waiting for a retransmitted, delayed packet is worse than just losing it. You'd rather hear a tiny skip than a long, awkward silence.
Online Gaming: In fast-paced games, player positions and actions are sent via UDP. A missed packet is less detrimental than the lag caused by TCP's error correction, which can ruin the gaming experience.
Domain Name System (DNS): When your browser looks up a website name, it uses UDP. The request and response are small and quick, and if it fails, it can simply be retried—no need for a complex connection.
Live Video Streaming: Services like live sports broadcasts prioritize getting the latest frame to your screen over ensuring every single pixel from 10 seconds ago is perfect.
IoT and Monitoring Systems: For sensors that send frequent, small status updates, UDP's low overhead is highly efficient.
When configuring your network for these UDP vs TCP reliability scenarios, choosing UDP is often the key to maintaining seamless, real-time performance.
📄 Optimizing UDP Performance: The Role of Hardware
While UDP is a software protocol, its performance is profoundly impacted by the underlying hardware. This is where high-quality networking components become non-negotiable. To minimize latency and jitter—the arch-enemies of real-time applications—you need hardware that can keep up with UDP's blistering pace.
This is a critical consideration for anyone building a robust network infrastructure for low latency UDP applications.
Boosting UDP with LINK-PP Optical Modules
For data to travel across networks, it must be converted from electrical signals into light pulses. This is the job of an optical transceiver module. The quality and capability of these modules directly influence the speed, integrity, and distance of your data transmission.
For demanding UDP-based applications, you need optical modules that offer not just high bandwidth but also exceptional signal clarity and low power consumption. LINK-PP's lineup of high-performance transceivers is engineered for precisely this purpose.
By integrating LINK-PP's reliable optics, you ensure that the physical layer of your network provides the cleanest, fastest possible pathway for those time-sensitive UDP datagrams. Whether you're building a data center for cloud gaming or a backbone for a large-scale VoIP system, the right module makes all the difference.
For instance, the LINK-PP SFP-10G-LR is a superb choice for 10Gbps long-reach connections, providing the stability needed for continuous UDP streams over kilometers of fiber.
📄 The Verdict: Is UDP Right for You?
UDP is not a one-size-fits-all solution, and it was never designed to be. It's a specialized tool for a specific set of problems.
Use TCP when you need 100% reliability and data integrity—like loading this web page, sending an email, or downloading a file.
Use UDP when you need blazing speed and low latency—like in live video, real-time gaming, or voice calls, where losing a few packets is acceptable.
Understanding this distinction is fundamental to designing efficient and responsive networked applications.
Ready to build a faster, more responsive network that leverages the raw power of UDP? The foundation starts with premium hardware. Visit the LINK-PP website [link-pp.com] to explore our full range of compatible optical transceivers and network solutions designed for high-performance, low-latency environments. Let's optimize your data flow together!
📄 FAQ
What makes UDP different from TCP?
UDP does not create a connection before sending data. You send each packet right away. TCP checks every packet and makes sure all data arrives in order. UDP gives you speed, while TCP gives you reliability.
What happens if a UDP packet gets lost?
If a UDP packet gets lost, you do not get a warning. UDP does not try to resend lost packets. Your application must handle missing data or ignore it.
What types of applications use UDP?
You find UDP in live video streams, online games, voice calls, and DNS lookups. These apps need fast delivery and can work even if some data does not arrive.
What is a UDP port?
A UDP port is a number that helps your device know where to send or receive data. Each service or app uses a different port to keep messages organized.


