
▷ What Is a VPN?
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a technology that creates a secure and encrypted connection over a public network such as the Internet. By establishing a “tunnel” between a user’s device and a remote server, VPNs protect sensitive data, ensure privacy, and allow users to access online resources as if they were connected to a private network.
VPNs are widely used by both individuals and enterprises to safeguard digital communications, especially when working remotely or transmitting data across untrusted networks.
▷ How VPNs Work
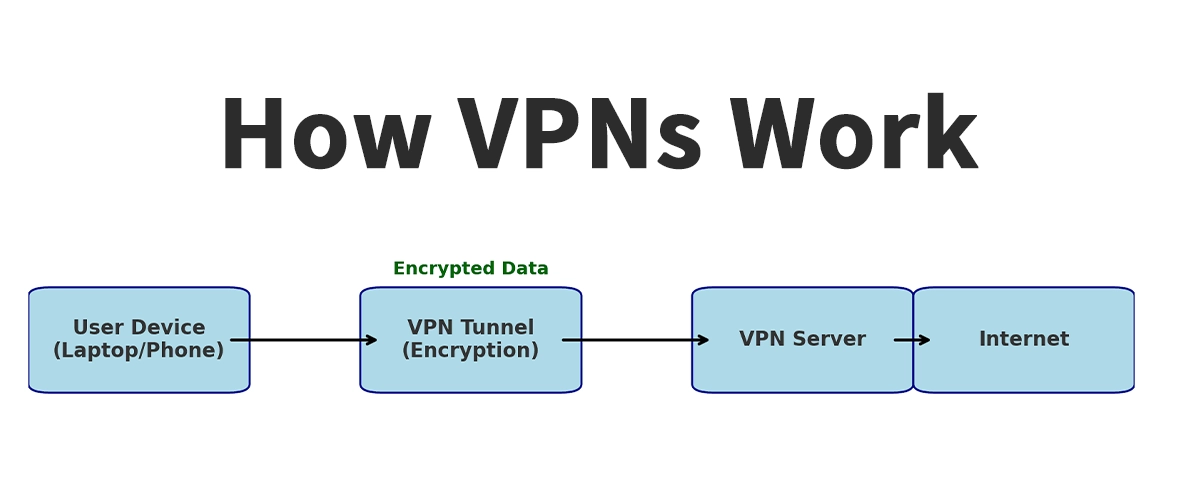
VPNs function through a process called tunneling. When a VPN connection is established, data packets are encapsulated and encrypted before being transmitted over the network. This process makes the traffic unreadable to unauthorized parties such as hackers or network administrators.
Key VPN protocols include:
PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol): One of the earliest VPN protocols, offering fast speeds but weaker security.
L2TP/IPsec (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol with IPsec): Provides stronger encryption by combining tunneling and IP security.
OpenVPN: An open-source protocol known for flexibility and strong security.
IKEv2/IPsec: Often used for mobile devices due to its stability when switching between networks.
▷ Benefits of Using a VPN
👉 Data Security: Protects information by encrypting traffic, reducing risks of data interception.
👉 Privacy Protection: Hides the user’s IP address, making online activity harder to track.
👉 Remote Access: Enables employees to connect securely to corporate networks from anywhere.
👉 Bypass Restrictions: Allows access to resources or websites that may be blocked in certain regions.
▷ VPN Applications in Business and Daily Life
Enterprises: Securely connect remote workers to internal applications and databases.
Individuals: Safeguard online transactions, streaming, and browsing on public Wi-Fi.
Service Providers: Ensure compliance with data protection regulations by encrypting customer traffic.
▷ VPN vs. Other Networking Technologies
While VPNs focus on security and privacy over the public Internet, other technologies such as MPLS or dedicated leased lines are often used for performance and predictable latency in enterprise networks. Many businesses deploy VPNs alongside these technologies to balance cost, flexibility, and security.
▷ Conclusion
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a cornerstone of modern cybersecurity and networking, ensuring privacy, secure remote access, and protection from cyber threats. As businesses increasingly adopt hybrid and remote work models, VPNs remain essential for safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining secure digital communications.


