
Have you ever been in a crucial video conference where voices cut out, or in an intense online game where your character suddenly teleports? These frustrating experiences are often the direct result of a common but elusive network problem: packet loss.
In our always-connected world, understanding packet loss is key to maintaining productivity and enjoying seamless digital experiences. This comprehensive guide will demystify packet loss, explore its causes and impacts, and provide actionable solutions—including the role of high-performance hardware like LINK-PP optical modules.
➤ What Exactly is Packet Loss?
At its core, the internet communicates by breaking data—whether it's an email, a video stream, or a voice call—into small chunks called "packets." These packets travel across various networks (like routers and switches) from the source to your device, where they are reassembled.
Packet loss occurs when one or more of these data packets fail to reach their destination. It's like a postal service losing letters from a mailed package; if too many are missing, the final product is incomplete or corrupted.
Packet loss is typically measured as a percentage. For most applications, a packet loss rate of below 1-2% is acceptable. However, for real-time services like VoIP (Voice over IP) and online gaming, even 0.5% can be disruptive.
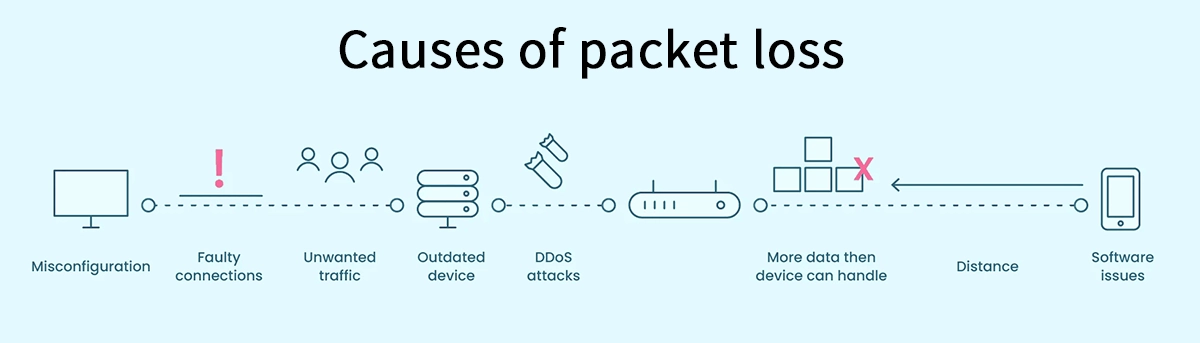
➤ Common Causes of Packet Loss: A Detailed Breakdown
Pinpointing the cause is the first step toward a solution. Packet loss can originate from multiple points in the network chain.
Table: Common Causes of Packet Loss and Their Indicators
Cause Category | Description | Common Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
Network Congestion | The digital equivalent of a traffic jam. When a network link is overloaded with data, routers are forced to drop packets. | Intermittent slowness, especially during peak usage hours. |
Hardware Limitations | Outdated or faulty network equipment (routers, switches, cables) can corrupt or fail to process packets correctly. | Consistent issues, even with a strong signal; affecting all connected devices. |
Software Issues | Bugs, misconfigurations in firmware, or driver conflicts can lead to improper packet handling. | Problems that arise after a software update or on a specific device. |
Wireless Interference | Wi-Fi signals can be disrupted by physical obstructions, other electronic devices, or neighboring networks. | Unstable connection that improves when you move closer to the router or use a wired connection. |
Overwhelmed Devices | The end-user device (your computer, phone) might lack the processing power to handle incoming data, causing it to drop packets. | High CPU usage on your device during network-intensive tasks. |
➤ The Real-World Impact of Packet Loss
The effects of packet loss are not just minor annoyances; they can have significant consequences:
VoIP and Video Conferencing: Causes robotic, choppy audio, frozen video, and call drops, harming professional communication.
Online Gaming and Live Streaming: Results in "lag," rubber-banding (where your character snaps back to a previous position), and disconnections, ruining the experience.
File Transfers and Web Browsing: Leads to significantly slower download/upload speeds and web pages that fail to load completely.
This is why addressing the root causes of high packet loss in real-time applications is a top priority for IT professionals and serious users alike.
➤ How to Diagnose and Test for Packet Loss
Before you can fix it, you need to confirm it. Here are two simple methods:
⒈ The Ping Test: Use your computer's Command Prompt (Windows) or Terminal (Mac).
Type ping -n 20 google.com (Windows) or ping -c 20 google.com (Mac/Linux).
This sends 20 packets to Google. Look for a line that says "Packet loss: X%". Any percentage above 0% indicates loss.
⒉ Traceroute: For a more advanced look, use tracert google.com (Windows) or traceroute google.com (Mac/Linux). This shows the path your packets take and can identify which specific "hop" or network node is causing the loss.
➤ The Hardware Solution: The Role of Optical Modules
While many causes are software or configuration-based, the physical hardware that forms the backbone of your network is often the unsung hero—or the culprit. This is especially true in business and data center environments where fiber optic cables are used for high-speed data transmission.
What is an Optical Module?
An optical module (or transceiver) is a critical component that converts electrical signals from a switch or router into light signals for transmission over fiber optic cables, and vice-versa. Think of it as a sophisticated translator enabling high-bandwidth communication.
How Can an Optical Module Cause Packet Loss?
A failing, low-quality, or incompatible optical module can be a direct source of packet loss.
Signal Degradation: A weak laser can result in a poor signal-to-noise ratio, causing the receiving end to misinterpret data and drop packets.
Physical Damage: Dust, scratches, or misalignment can corrupt the light signal as it passes through.
Overheating: Poorly designed modules can overheat, leading to performance instability and data errors.
Investing in reliable, high-quality optical modules is a fundamental step in building a resilient network infrastructure that minimizes packet loss.
➤ Actionable Steps to Fix and Prevent Packet Loss
Here is a step-by-step guide to troubleshooting and resolving packet loss issues:
Start Simple: Restart your modem and router. This clears temporary glitches and memory leaks.
Check Your Connections: If on Wi-Fi, try a wired Ethernet connection. If the problem disappears, Wi-Fi interference is likely the cause.
Update Everything: Ensure your router's firmware and your device's network drivers are up-to-date.
Scan for Bandwidth Hogs: Identify applications or devices consuming excessive bandwidth and manage their usage.
Upgrade Your Hardware: If your router is old or your cables are damaged, replace them. For enterprise users, auditing and replacing aging network switches and optical modules is critical.
Contact Your ISP: If all else fails, the issue might be with your Internet Service Provider's network. Provide them with your ping and traceroute results.
➤ Conclusion: Build a Faster, More Reliable Network
Packet loss is a complex issue, but it's not an insurmountable one. By understanding its causes—from software bugs and network congestion to the critical role of physical hardware—you are equipped to diagnose and resolve it effectively.
A proactive approach to network health, including investing in quality components from trusted manufacturers, is the best defense. Whether you're a gamer, a remote worker, or a network administrator, eliminating packet loss is key to a superior online experience.
Ready to Build a Zero-Packet-Loss Network? 🚀
Don't let unreliable hardware undermine your network's performance. Explore the full range of certified, high-performance LINK-PP optical transceivers designed to deliver flawless data transmission.
👉 Browse LINK-PP Website [link-pp.com] and find the perfect solution for your network needs today!
➤ FAQ
What is packet loss monitoring?
Packet loss monitoring lets you track lost data packets on your network. You use tools to check how often packet loss happens. This helps you spot problems early and keep your internet connection strong.
What causes packet loss in home networks?
You may see packet loss from network congestion, signal interference, or faulty hardware. Packet loss monitoring helps you find the exact cause. You can fix issues faster when you know what is wrong.
What tools can you use for packet loss monitoring?
You can use speed test websites, ping tests, and special software for packet loss monitoring. These tools show you packet loss rates and help you understand your network’s health.
What should you do if packet loss monitoring shows high packet loss?
You should restart your devices, check cables, and switch to a wired connection. Packet loss monitoring helps you decide if you need to contact your internet provider for more help.
What benefits do you get from regular packet loss monitoring?
Regular packet loss monitoring helps you keep your internet fast and reliable. You can catch problems early, reduce downtime, and enjoy smoother streaming, gaming, and browsing.


