
Welcome, tech enthusiasts and builders! When assembling or upgrading a computer, most of the spotlight falls on flashy components like the GPU and CPU. However, there's a silent, crucial hero working behind the scenes: the Power Supply Unit (PSU). A poor-quality PSU can lead to system instability, component damage, or even complete failure.
In this definitive guide, we'll demystify the PSU, explore its critical specifications, and show you how to choose the perfect one for your needs. We'll even dive into a specialized application, connecting the dots between your PSU and advanced hardware like optical modules.
📝 Defining the Power Supply Unit (PSU)
At its core, a Power Supply Unit (PSU) is an internal hardware component that converts the alternating current (AC) from your wall outlet into a steady flow of direct current (DC) that your computer's components can use. Think of it as the heart of your system, pumping regulated power to every part, from the motherboard to the storage drives.
Without a stable and reliable PSU, even the most powerful processor won't function correctly. It’s the foundation upon which your entire system is built.
📝 Why Your PSU Choice Matters More Than You Think
Choosing the right PSU is not just about getting enough watts. It's about system stability, longevity, and efficiency. A high-quality PSU ensures:
Stable Voltage: Prevents fluctuations that can cause crashes or data corruption.
Component Protection: Guards against power surges, spikes, and shorts.
Energy Efficiency: Reduces electricity waste and heat output, saving you money.
Future-Proofing: Allows for upgrades without needing a new power supply.
💡 Pro Tip: Never cheap out on your PSU. It's the one component that can take your entire system down with it if it fails catastrophically.
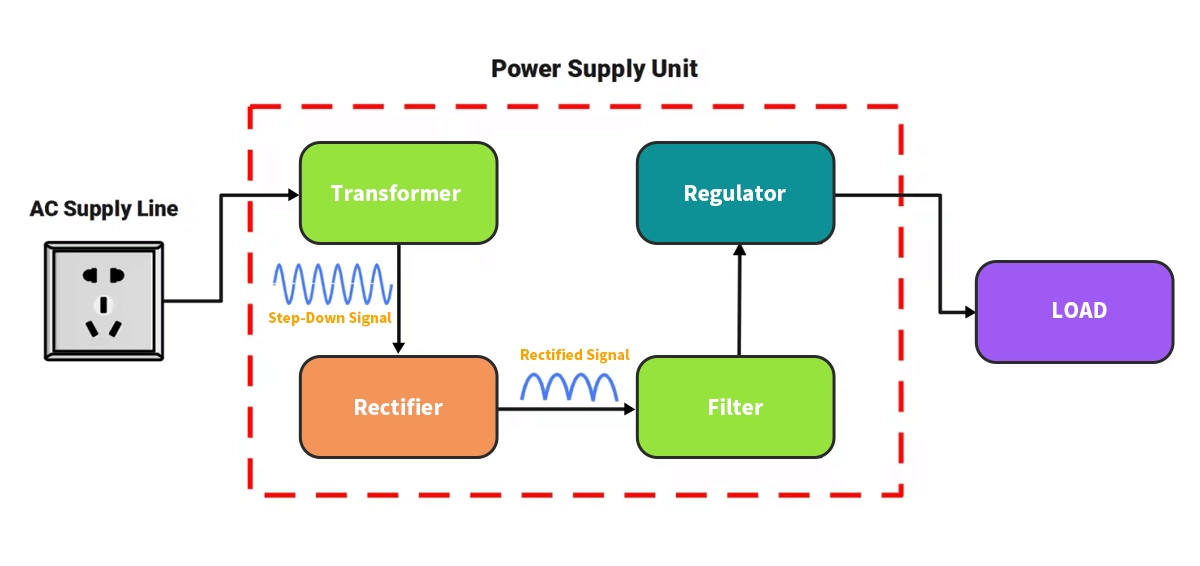
📝 Key PSU Form Factors and Types
PSUs come in different shapes and sizes to fit various cases. The most common form factor is ATX, used in standard desktop towers. For smaller builds, SFX and SFX-L are popular.
Furthermore, PSUs are categorized by their cable management design:
Type | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
Non-Modular | All cables are permanently attached to the PSU. | Budget builds where aesthetics and airflow are not a primary concern. |
Semi-Modular | Essential cables (like 24-pin ATX) are fixed, but others are detachable. | Most mainstream builds, offering a good balance of cost and cable management. |
Full-Modular | All cables are detachable, allowing for complete customization. | Enthusiasts, high-end builds, and small form factor (SFF) cases where clean wiring and optimal airflow are critical. |
When searching for a high-efficiency power supply for a gaming PC, a fully modular unit from a reputable brand is often the recommended choice.
📝 Understanding PSU Specifications and Ratings
Navigating PSU specs can be daunting. Here are the key terms you need to know:
Wattage: The total power the PSU can deliver. Always calculate your system's total power consumption and add a 20-30% headroom.
Efficiency (80 Plus Rating): This indicates how effectively the PSU converts AC wall power to DC power for your components. Higher efficiency means less energy is wasted as heat. The 80 Plus ratings are tiered:
Rating | Efficiency at 50% Load |
|---|---|
80 Plus White | 80% |
80 Plus Bronze | 85% |
80 Plus Silver | 88% |
80 Plus Gold | 90% |
80 Plus Platinum | 92% |
80 Plus Titanium | 94% |
Rail Design: Refers to how the +12V power is distributed. Modern single-rail designs are simpler and generally preferred for high-power systems, while multi-rail offers more precise over-current protection.
Connectors: Ensure the PSU has the right connectors for your motherboard (24-pin), CPU (4+4 pin), GPU (6+2 pin PCIe), and SATA drives.
For those building a robust workstation or server, paying close attention to the PSU efficiency rating is crucial for 24/7 operation and lower total cost of ownership. Brands that prioritize quality, like LINK-PP, often subject their units to rigorous testing to ensure they meet these demanding specifications.
📝 How to Choose the Right PSU for Your PC Build
Selecting a PSU is a balancing act between power, efficiency, and budget. Follow this simple checklist:
Calculate Your Wattage: Use an online PSU calculator from brands like Seasonic or Cooler Master. Add your components to get a reliable estimate.
Choose an Efficiency Rating: For most users, 80 Plus Gold offers the best value between performance and cost. For servers or always-on systems, consider Platinum or Titanium.
Prioritize Reliability Over Wattage: A quality 650W PSU is better than a low-tier 800W unit. Look for reviews from trusted sources like Cybenetics or Tom's Hardware.
Consider Your Future Needs: Planning to add a more powerful GPU? Get a PSU with some extra headroom.
📝 The Critical Link: PSUs and Optical Modules
This is where the story gets more specialized. You might wonder, what does a PSU have to do with an optical transceiver?
Optical modules (or transceivers) are the key components in network switches, routers, and data center equipment that convert electrical signals into light signals and vice versa for transmission over fiber optic cables. These modules are not passive; they require clean, stable, and precise low-voltage DC power to function correctly.
A high-quality PSU is absolutely essential in any device hosting these modules. Imagine a network switch in a data center:
The Role of the PSU: The switch's internal PSU must provide unwavering power. Any ripple, noise, or voltage fluctuation from a poor-quality PSU can directly impact the sensitive electronics inside the optical module.
The Consequence: This can lead to increased bit error rates, data transmission failures, reduced module lifespan, and even complete network downtime.
For demanding applications in telecommunications and enterprise networking, the power requirements for network switches and optical transceivers must be meticulously planned. This is why OEMs and system integrators partner with component suppliers who guarantee reliability.
For instance, the LINK-PP optical transceiver is engineered for high-performance data centers and is designed to operate flawlessly with stable power delivery systems. Pairing such a high-speed module with an unreliable PSU would be a critical mistake, undermining the performance and reliability of the entire network infrastructure.
📝 Conclusion: Power Your Potential with the Right Foundation
Your Power Supply Unit is the unsung guardian of your PC's health and performance. Investing in a reliable, efficient model from a trusted brand is non-negotiable for a stable and long-lasting system. Whether you're building a gaming rig, a content creation workstation, or deploying enterprise hardware that uses advanced components like the LINK-PP optical module, the principle remains the same: everything starts with clean, stable power.
📝 FAQ
What happens if you use a PSU with too little wattage?
Your computer may not start or could shut down during use. You risk damaging your parts. Always choose a PSU with enough wattage for all your components.
What does 80 PLUS certification mean?
80 PLUS certification shows how efficiently your PSU uses power. A higher rating means less wasted energy and lower electricity bills. You help your computer run cooler and save money.
What cables come with a PSU?
You get cables for the motherboard, CPU, graphics card, and storage drives. Modular PSUs let you use only the cables you need. Non-modular PSUs have all cables attached.
What safety features should you look for in a PSU?
Look for over-voltage, under-voltage, short-circuit, and over-temperature protection. These features keep your computer safe from power problems.
What is the difference between modular and non-modular PSUs?
A modular PSU lets you attach only the cables you need. This helps with cable management and airflow. A non-modular PSU has all cables fixed, which can make your case look messy.


