
1️⃣ Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has rapidly evolved from an academic research field into a core enabler of industrial infrastructure, spanning healthcare, networking, telecommunications, and optics. For engineers, technical buyers, and enterprise decision-makers, understanding what AI is, how it works, its classifications, and where it is heading in 2025 is essential for making sound architectural, product, and procurement decisions.
2️⃣ What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Definition
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to machine-based systems that perform tasks requiring human-like intelligence, such as learning from data, reasoning, perception, planning, and language understanding.
ISO/IEC: AI systems are designed to perform tasks normally requiring human intelligence, enabled by algorithms, data, and computational resources.
NASA: AI includes systems that adapt to unpredictable circumstances and learn from experience.
NIST: AI is “a machine-based system that, for given objectives, makes predictions, recommendations, or decisions influencing real or virtual environments.”
Key Technical Foundations
Data & Algorithms – Patterns are extracted from large datasets using algorithms for prediction and decision-making.
Machine Learning (ML) – Systems improve performance through experience (supervised, unsupervised, reinforcement learning).
Deep Learning – Neural networks with multiple layers, effective for vision, speech, and language tasks.
Narrow, General, Super Intelligence – Current AI is primarily “narrow AI,” specialized for specific tasks; AGI and superintelligence remain theoretical.
3️⃣ How AI Works
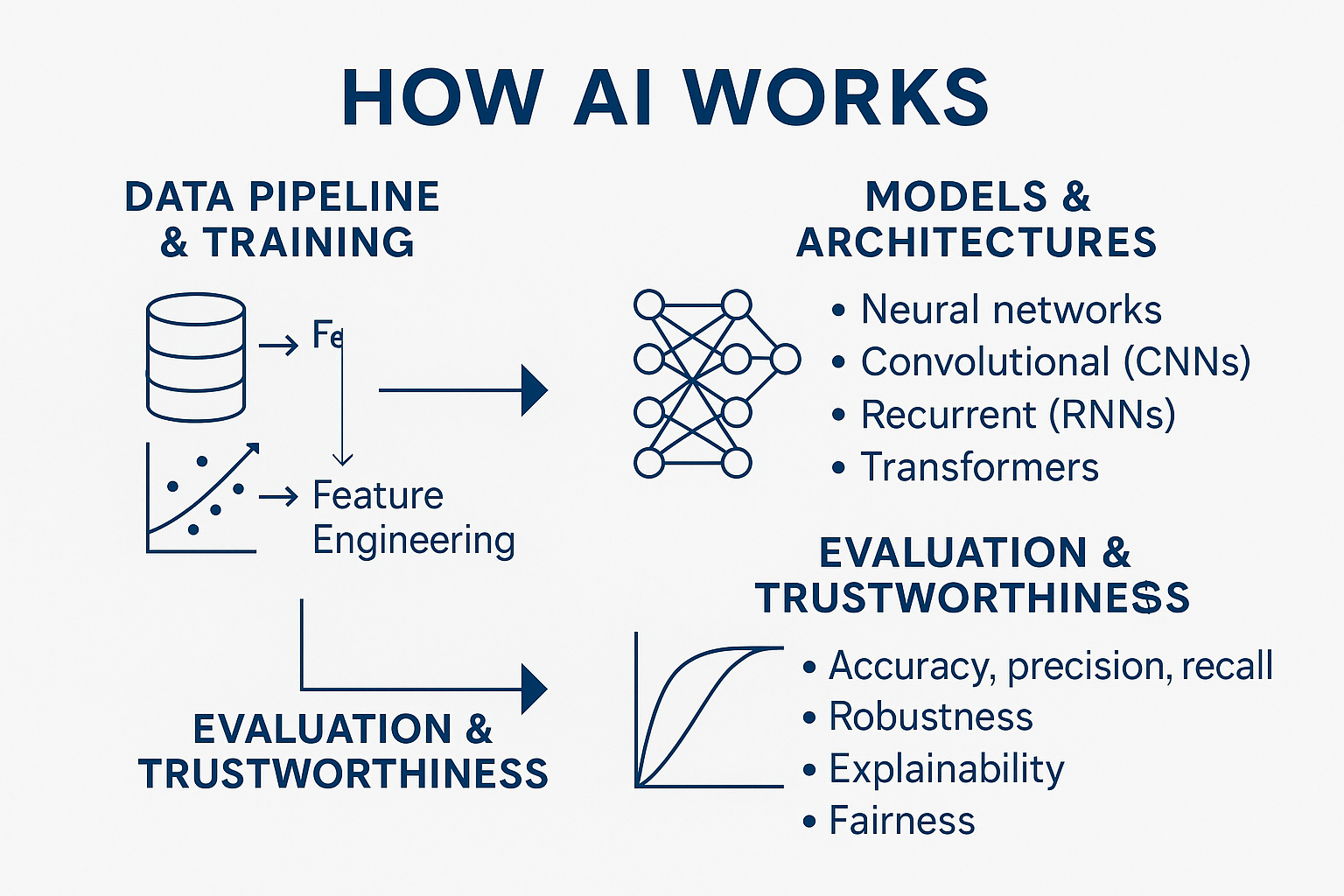
Data Pipeline & Training
Data Collection & Preprocessing
Feature Engineering
Training – Supervised, unsupervised, reinforcement learning
Models & Architectures
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)
Transformers
Evaluation & Trustworthiness
Metrics: accuracy, precision, recall, F1, ROC-AUC
Key considerations: robustness, explainability, fairness
4️⃣ Types of AI & Use Cases
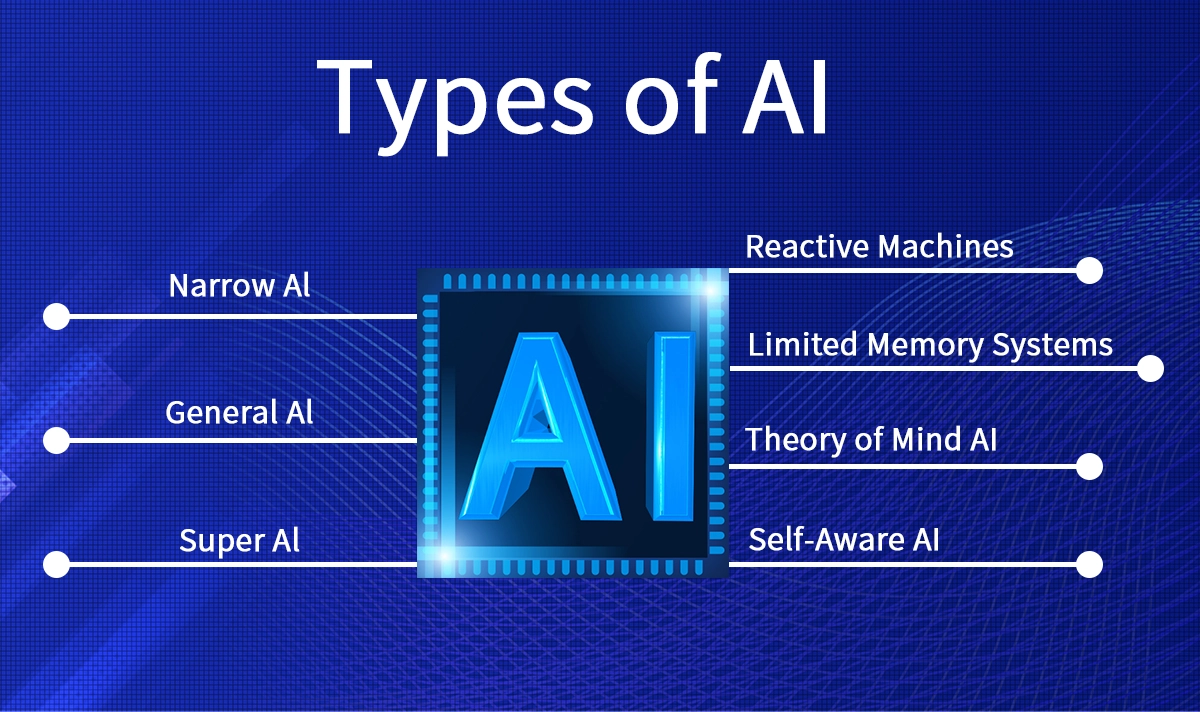
By Capability
Reactive Machines
Limited Memory Systems
Theory of Mind AI (research stage)
Self-Aware AI (hypothetical)
Industrial Applications
Natural Language Processing – Chatbots, translation
Computer Vision – Object detection, video analytics
Speech Technologies – Recognition and synthesis
Predictive Analytics – Demand forecasting, financial modeling
Autonomous Systems – Robotics, autonomous vehicles
AI in Networking & Optics
Traffic Prediction & Optimization
Hardware Anomaly Detection
Optical Network QoS Monitoring
5️⃣ Trends for 2025 and Beyond
Generative AI and Agentic Systems
Next-generation AI agents that can plan, decide, and act with partial autonomy.
Responsible AI
Ethics, fairness, governance, transparency
Auditing for bias
Increasing regulation across regions
AI in Hardware & Efficiency
Lower inference costs
Edge AI deployment
AI-accelerated chipsets
Embedded & Industrial AI
Real-time decision-making in IoT and manufacturing
AI-driven predictive maintenance in networking
6️⃣ AI in Optical Networking: Practical Considerations
For professionals in optical networking and transceiver hardware:
AI can predict hardware failures (e.g., SFP module anomalies).
AI enhances network performance monitoring.
Telemetry data from transceivers can feed AI-driven optimization systems.
7️⃣ Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence is no longer abstract—it is embedded in technical infrastructure. For decision-makers, the key is not only choosing the right AI models but also ensuring integration with existing hardware and operations.
👉 If you are evaluating optical networking gear such as SFP modules, consider whether your network hardware can generate telemetry data suitable for AI-driven analytics. This capability determines the extent to which your infrastructure can benefit from AI-based monitoring and optimization.


