🔄 Introduction
In industrial automation, IIoT systems, and high-availability networks, reliability metrics determine how well equipment performs under continuous operation. Among the most important indicators are MTTR (Mean Time to Repair) and MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures).
Both metrics evaluate different aspects of system reliability—MTBF measures how long equipment runs before failure, while MTTR measures how quickly it can be restored. Understanding both is essential for improving network uptime and optimizing maintenance strategies.
🔄 What Is MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures)?
MTBF represents the average time a system or component operates without failure. It reflects hardware reliability and is commonly used for industrial switches, PLCs, edge gateways, transceivers, and network interfaces.
Formula:

Why MTBF Matters
Predicts service life and replacement intervals
Reduces unplanned downtime
Supports long-term reliability planning
Essential for designing high-availability industrial networks
A higher MTBF means more durable components and fewer operational interruptions.
🔄 What Is MTTR (Mean Time to Repair)?
MTTR measures the average time required to diagnose, repair, and fully restore a system after a failure. It reflects maintainability rather than reliability.
Formula:
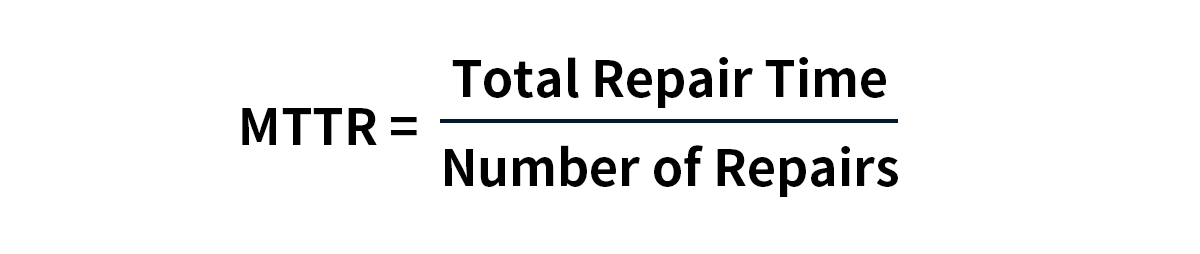
Why MTTR Matters
Determines how fast a system can return to service
Reduces downtime costs
Helps evaluate maintenance efficiency
Critical for SLA and uptime planning
Lower MTTR directly improves network availability and operational continuity.
🔄 MTTR vs MTBF: What’s the Difference?
Metric | Focus | Meaning | Impact on Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
Reliability | Time between failures | Higher MTBF = fewer disruptions | |
Maintainability | Time to restore service | Lower MTTR = shorter downtime | |
Together | Availability | MTBF / (MTBF + MTTR) | Determines actual uptime |
Both metrics are complementary. High MTBF reduces the frequency of failures, while low MTTR minimizes recovery time—both are essential for achieving stable, resilient industrial networks.
🔄 System Availability: How MTTR and MTBF Work Together
System availability is a key performance indicator in industrial networking.
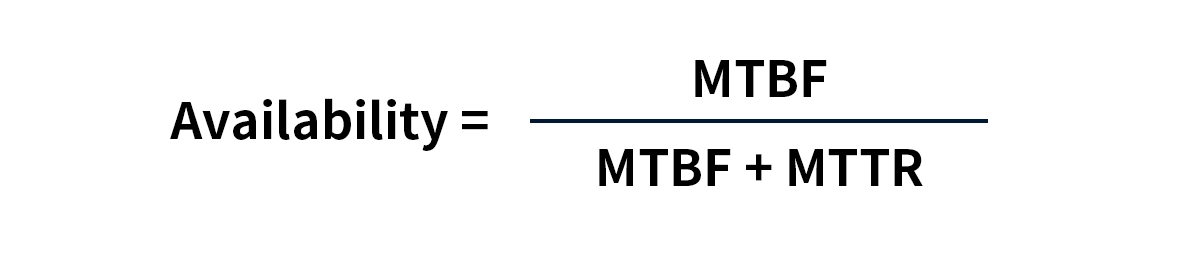
Example
MTBF = 5,000 hours
MTTR = 1 hour
Availability ≈ 99.98%
To maximize availability, engineers work to increase MTBF and decrease MTTR, often through better component selection and maintenance strategies.
🔄 How LINK-PP Products Improve Both MTBF and MTTR

High-quality hardware plays a crucial role in reliability metrics. LINK-PP industrial networking components are engineered to enhance durability, stability, and serviceability.
1. Improving MTBF with LINK-PP Products
▷ Industrial-Grade SFP / SFP+ Optical Transceivers
LINK-PP SFP/SFP+ Modules are designed for harsh environments and extended temperature ranges, minimizing optical link failures and increasing MTBF.
▷ High-Reliability RJ45 & Integrated Ethernet Connectors
Reinforced housings, premium magnetics, and EMI suppression ensure stable Ethernet performance and reduce failure frequency, increasing MTBF of industrial switches and controllers.
▷ Robust LAN Magnetics
Stable LAN magnetic components reduce electrical stress on PHY devices, extending equipment lifespan and preventing premature failures.
2. Reducing MTTR with LINK-PP Products
▷ Hot-Swappable SFP/SFP+ Modules
Field technicians can replace optical modules within seconds, drastically reducing MTTR and minimizing downtime.
▷ Standardized Mechanical Footprints
Consistent pin layouts and compliance with IEEE and MSA standards simplify field service and replacement procedures.
▷ Reliable Electrical Performance
Predictable, standards-driven performance reduces troubleshooting time, allowing systems to return to operation faster.
🔄 Best Practices to Optimize MTTR and MTBF Together
Use industrial-grade components designed for harsh conditions
Implement predictive maintenance based on operational data
Standardize hardware across deployments
Keep spare SFP/SFP+ modules and connectors for quick replacement
Monitor environmental factors (EMI, temperature, vibration)
Document consistent repair and testing procedures
Combining strong hardware reliability with efficient service strategies ensures optimal uptime.
🔄 Conclusion
MTTR and MTBF are fundamental metrics for evaluating and improving system reliability in industrial networks and IIoT environments. MTBF focuses on how long systems operate without failure, while MTTR measures how quickly they can be restored.
By integrating high-quality, industrial-grade components—such as LINK-PP SFP/SFP+ optical transceivers, Ethernet connectors, and LAN magnetics—engineers can significantly increase MTBF, reduce MTTR, and build networks with exceptional availability and long-term stability.
These improvements directly translate into reduced downtime, lower maintenance costs, and more resilient industrial systems.




