
In today's hyper-connected world, network reliability isn't just a luxury; it's the very backbone of business operations, entertainment, and communication. For service providers leveraging Passive Optical Networks (PON), a single fiber cut or equipment failure can lead to significant revenue loss and customer dissatisfaction.
This is where robust protection switching mechanisms come into play. While there are several types, Type B Protection stands out as a highly effective and popular solution for ensuring service continuity. In this article, we'll demystify PON protection, starting with the basic single-homing architecture, then zooming in on the advanced dual-homing redundancy of Type B, and explore how the right components, like LINK-PP's optical modules, are critical to a resilient network.
📑 Why PON Protection is Non-Negotiable
A standard PON architecture is a point-to-multipoint network. A single Optical Line Terminal (OLT) port at the central office serves multiple Optical Network Units (ONUs) at customer premises through a passive optical splitter. This efficiency, however, introduces a single point of failure: the feeder fiber connecting the OLT to the splitter.
A break in this fiber can disrupt service for dozens or even hundreds of end-users. PON protection schemes are designed to eliminate these single points of failure, creating a redundant path for data to travel.
📑 Unpacking the Protection Schemes: Type A, B, and C
The ITU-T G.983.1 and G.984.1 recommendations define several protection models. Here’s a quick comparison:
Protection Scheme | Redundancy Focus | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
Type A (1+1) | Feeder Fiber | Dedicated backup fiber running parallel to the working fiber. The OLT has a backup port. | Protecting against feeder fiber cuts. A cost-effective step up from no protection. |
🛡️ Type B (1:1) | Full OLT & Feeder Fiber | A standby OLT and a completely separate, redundant fiber path. | High-availability scenarios requiring protection against both OLT failure and fiber cuts. |
Type C (1:1) | Full Duplex Path | Redundancy for every element, including the splitter and distribution fibers. | Mission-critical applications where any downtime is unacceptable (e.g., financial, military). |
As the table shows, Type B protection offers a balanced and robust solution, often considered the sweet spot for many service providers seeking comprehensive PON redundancy without the extreme cost of Type C.
📑 From Single-Homing to Dual-Homing: The Core of Type B Protection
To truly appreciate Type B, we must first understand the standard it improves upon: Single-Homing.
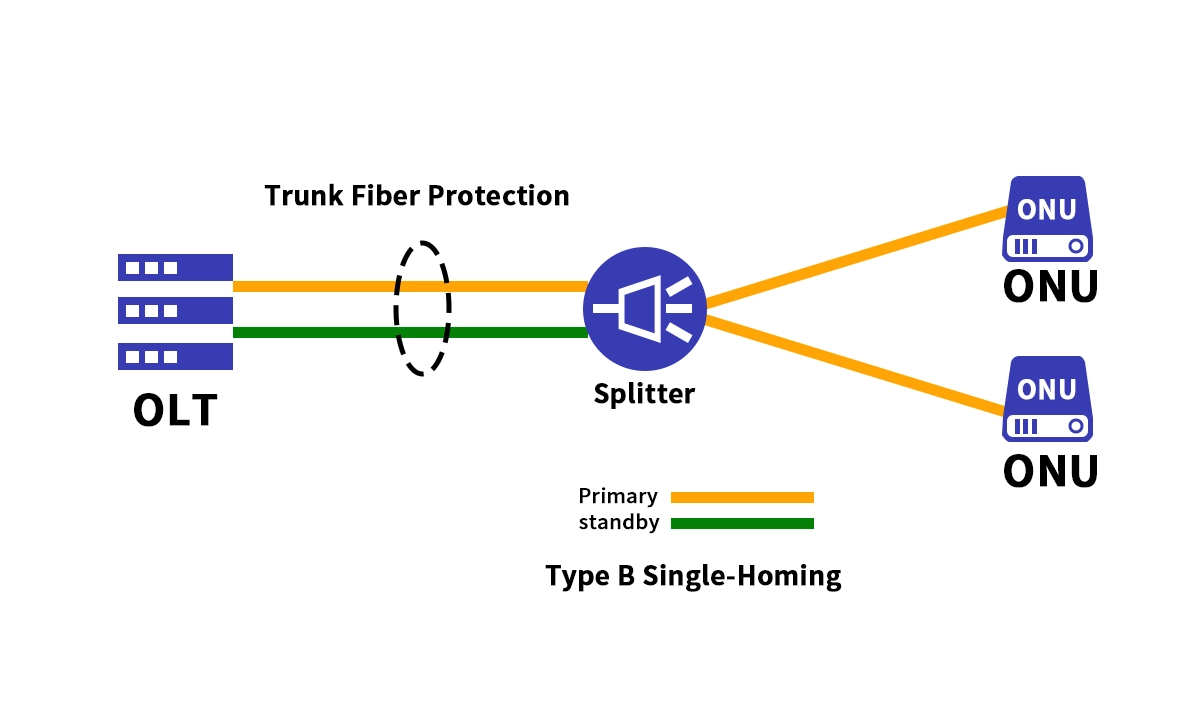
Single-Homing PON Architecture: This is the basic, non-redundant setup. Each ONU is connected to a single OLT port via a single feeder fiber and splitter. It's simple and cost-effective but poses a significant risk. Any failure in the OLT port, the core transceiver, or the feeder fiber leads to an immediate and complete service outage for all connected ONUs.
Type B protection in PON system eliminates this vulnerability by implementing a dual-homing PON architecture.
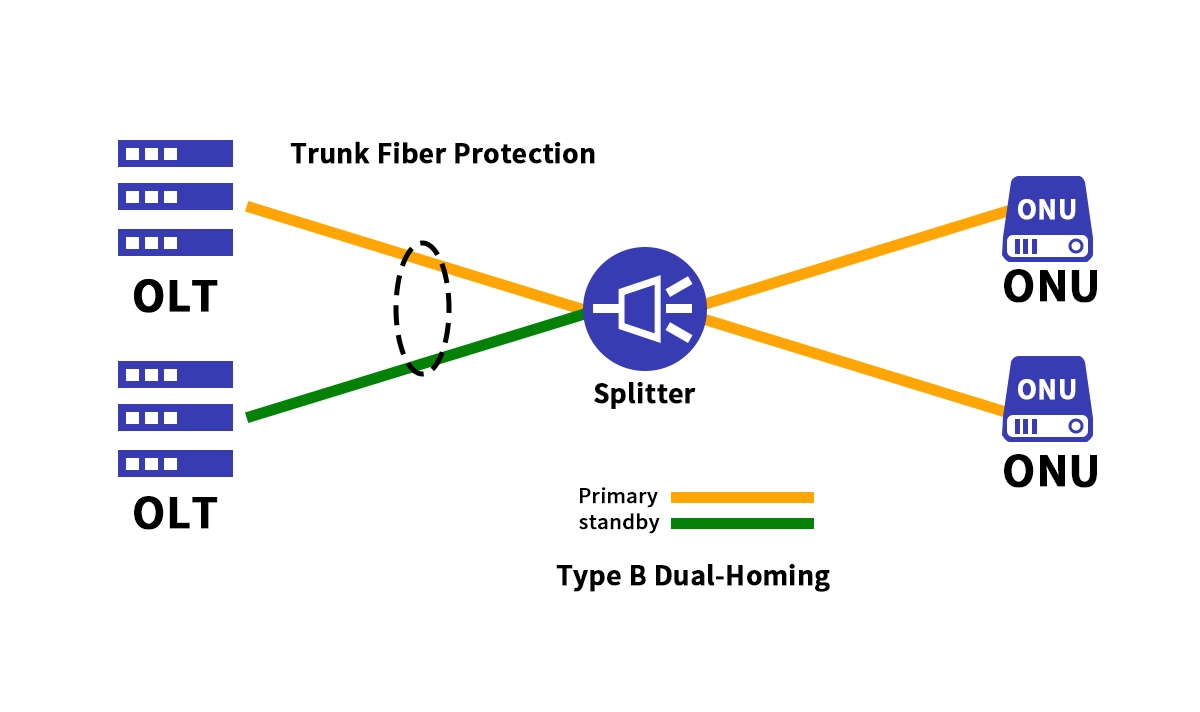
In a Type B setup, each ONU is connected to two completely separate OLTs:
A Working OLT (active)
A Standby OLT (backup)
These OLTs are connected via two independent feeder fibers to a 2:N splitter. The following table summarizes the key differences:
Feature | Single-Homing Architecture | Type B Dual-Homing Architecture |
|---|---|---|
OLT Path | Single OLT | Working + Standby OLT |
Feeder Fiber | Single Path | Two Physically Separate Paths |
Cost | Lower | Higher (CapEx) |
Availability | Standard | Carrier-Grade, High Availability |
Risk Profile | Single point of failure at OLT & feeder | Protected against OLT and feeder failure |
The "Switchover" Magic:
Under normal conditions, all traffic flows through the Working OLT. The moment a failure is detected—be it a feeder fiber cut or a critical fault in the working OLT—the automated protection switching mechanism kicks in. Traffic is seamlessly rerouted through the Standby OLT and the backup feeder fiber within milliseconds. For end-users, this switchover is often completely unnoticeable, ensuring uninterrupted gigabit broadband and VoIP services.
📑 The Unsung Hero: Your Optical Transceivers
A high-availability system is only as strong as its weakest link. This is where the critical role of optical modules comes into focus. In a Type B protected system, both the Working and Standby OLTs must be equipped with high-performance, reliable SFP or SFP+ transceivers.
Any inconsistency or failure in these modules can cause the entire protection scheme to fail. Therefore, choosing vendor-quality, compatible, and durable optical modules is paramount.
LINK-PP, a trusted name in optical networking solutions, offers a range of high-stability transceivers designed for demanding PON environments. For instance, the LINK-PP GPON module is an excellent choice for OLTs in a protected setup.
Why this module fits perfectly in a Type B system:
Proven Reliability: Built to withstand 24/7 operational demands, reducing the risk of module-induced switchovers.
Consistent Performance: Ensures that both the working and standby paths have identical optical characteristics, crucial for a smooth and stable switchover.
Full Compatibility: Designed to work seamlessly with major OLT vendors, eliminating interoperability concerns that can plague a PON protection switch.
Integrating LINK-PP's optical modules into your network design not only enhances performance but also future-proofs your infrastructure against component-level failures.
📑 Type B vs. The Rest: Making the Right Choice
Why would an ISP choose Type B over the others?
vs. Single-Homing: Type B is a direct upgrade for any service provider for whom minimizing network downtime is a key business objective, moving from a fragile single-point architecture to a resilient dual-homed one.
vs. Type A: Type A only protects the fiber. If the OLT itself fails, you're still offline. Type B protects against both fiber and OLT failure, offering a significantly higher level of service availability.
vs. Type C: Type C offers the highest level of protection but at a substantially higher cost. For most business and residential services, Type B provides the optimal balance of cost-efficiency and network resilience.
If your goal is to implement a reliable PON solution that maximizes uptime without the capital expenditure of a full Type C deployment, Type B is undoubtedly the most strategic choice.
📑 Conclusion: Build a Network Your Customers Can Trust
Implementing Type B protection in PON system is a clear declaration that your network is built for reliability. It transforms your infrastructure from a basic single-homing utility into a resilient, dual-homed service, capable of weathering common failures without impacting the end-user experience. By combining this robust architecture with high-quality components from specialists like LINK-PP, you lay a foundation for customer satisfaction and long-term operational success.
🚀 Ready to Fortify Your PON Infrastructure?
Don't leave your network's reliability to chance. Our experts at LINK-PP are here to help you design and implement the perfect protection strategy for your needs.
📞 [Contact us today] for a personalized consultation and discover how our optical modules and solutions can empower your resilient network journey.
📑 FAQ
What is type B protection in a fiber optic network?
You use type B protection to keep your network running if one fiber line fails. It gives you backup and helps prevent service loss.
What makes type B RCDs different from standard RCDs?
Type b rcds detect all types of leakage currents. You get better safety, especially in places where you risk electric shock from direct or high-frequency currents.
What should you check before choosing type B protection?
You should check your system needs and equipment. Pick the right device to avoid shock and keep your network or electrical system safe.




