
In modern industrial automation, real-time data exchange is essential for achieving fast, synchronized, and highly reliable control. EtherCAT—one of the leading Industrial Ethernet technologies—achieves its exceptional performance through several architectural innovations. Among these, the FMMU (Fieldbus Memory Management Unit) plays a central role.
This article provides a clear, technically accurate explanation of what the FMMU is, why it matters, and how it enables EtherCAT to deliver microsecond-level real-time communication. We also introduce how LINK-PP’s SFP fiber transceiver modules seamlessly support high-speed EtherCAT networks.
1. What Is the FMMU in EtherCAT?
FMMU (Fieldbus Memory Management Unit) is a hardware mechanism inside each EtherCAT slave device that maps logical process data addresses from the EtherCAT Master to the physical memory addresses of individual slave nodes.
In simple terms:
The FMMU allows the EtherCAT Master to access scattered data across multiple slave devices as if it were one continuous block of memory.
This mechanism is critical for EtherCAT’s high-speed “on-the-fly” data processing, enabling deterministic, low-latency fieldbus communication.
2. Why Does EtherCAT Need an FMMU?
Traditional fieldbus systems often require the master to communicate with each node separately, resulting in:
Higher latency
Increased communication overhead
Lower update rates
EtherCAT solves this with a different approach:
✔ The EtherCAT frame passes through all slaves in sequence.
Each slave reads and writes only the data that belongs to it.
✔ FMMU ensures the data is placed at the correct logical position.
The result is extremely efficient cyclic data exchange.
Key benefits enabled by FMMU:
Continuous logical address space for the Master
Precise byte-level mapping
Zero-copy, on-the-fly processing
Ultra-low cycle times (sub-100 μs)
High bandwidth utilization (close to 100%)
This is one of the main reasons EtherCAT is suitable for:
Motion control
Robotics
High-speed servo drives
Precision automation
3. How FMMU Works: Logical vs. Physical Address Mapping
EtherCAT communication uses two types of memory addressing:
Logical Address (Master view)

A virtual, continuous address space defined by the Master for process data.
Physical Address (Slave view)
Actual register or data buffer addresses inside a slave device.
The FMMU maps logical memory → physical memory, enabling:
Bit-level granularity
Read/write control
Efficient synchronization with SyncManagers
Example:
If the Master creates a 60-byte logical PDO region:
Slave | Physical Memory | Mapped Logical Address |
|---|---|---|
Slave A | 0x1100 | 0x0000 – 0x000F |
Slave B | 0x2000 | 0x0010 – 0x0023 |
Slave C | 0x3200 | 0x0024 – 0x003B |
The Master only reads/writes one continuous 60-byte area, but data is automatically routed to each slave via their FMMU hardware.
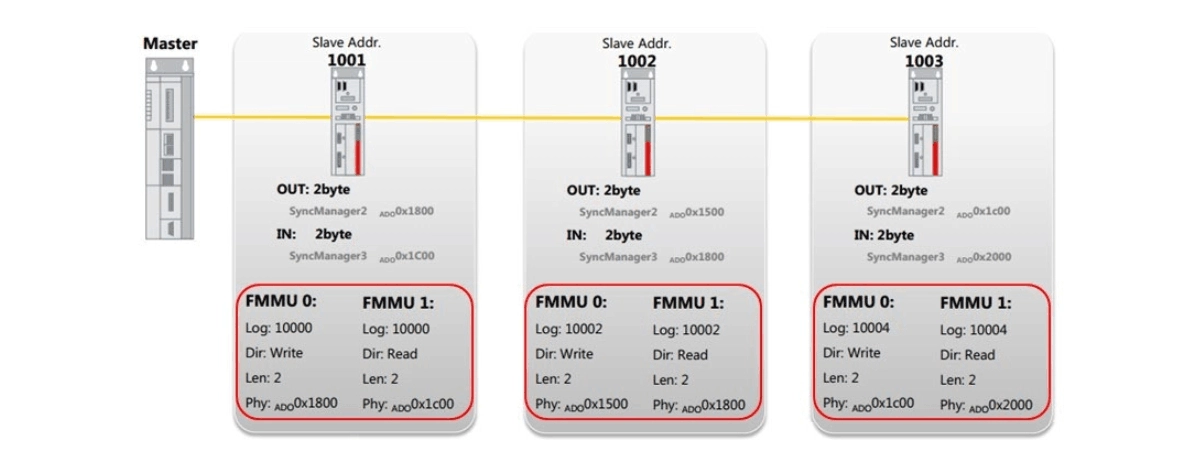
4. FMMU Inside the EtherCAT Slave Controller (ESC)
The FMMU is implemented in the ESC (EtherCAT Slave Controller), which is integrated in EtherCAT slave chips such as:
Beckhoff ET1100
ET1200
Third-party ESC IP cores
Typical ESC includes:
FMMUs (usually 1–3 instances)
SyncManagers (SM)
AL state machine
Mailbox handlers
The FMMU configuration is performed during initialization via mailbox protocols (CoE, FoE, EoE).
5. FMMU and On-the-Fly Processing
One of EtherCAT's hallmark features is that slaves do not copy or buffer the entire Ethernet frame.
Instead:
The Ethernet frame streams through the slave.
The FMMU checks which bytes belong to this slave.
Data is inserted or extracted on the fly.
The frame continues to the next slave with a delay of nanoseconds.
This design enables update rates in the range of:
< 100 μs for 100+ axes servo control
< 10 μs per slave forwarding delay
No other fieldbus architecture achieves this level of determinism with such simple wiring.
6. Applications Where FMMU Is Critical
FMMU contributes directly to EtherCAT’s performance in:
Multi-axis motion controllers
Pick-and-place robots
CNC machines
Packaging and printing equipment
Semiconductor manufacturing
Real-time distributed I/O
Where the control cycle is extremely tight, the FMMU ensures stable and accurate data consistency.
LINK-PP Industrial Fiber Products for EtherCAT Networks

EtherCAT commonly uses Ethernet physical layers such as:
100BASE-TX
100BASE-FX
1000BASE-X
For environments requiring long-distance or EMI-resistant communications, LINK-PP provides a wide range of industrial-grade fiber transceivers and SFP modules:
Benefits for EtherCAT applications:
High EMC immunity
-40°C to +85°C industrial temperature options
Low latency and stable optical performance
Compatibility with PLCs, servo drives, and industrial switches
Long-distance links up to 80 km
These optical modules ensure reliable physical-layer connectivity for EtherCAT networks that rely on FMMU-based deterministic control.
7. Summary
The FMMU (Fieldbus Memory Management Unit) is one of the fundamental innovations that makes EtherCAT one of the fastest and most deterministic industrial networks. By mapping logical process data into slave-specific physical addresses and supporting on-the-fly frame processing, the FMMU enables:
Microsecond-level cycle times
Highly accurate synchronization
Efficient bandwidth use
Scalable distributed control
When paired with robust industrial optical modules, such as LINK-PP’s SFP and fiber transceivers, EtherCAT becomes a powerful and reliable backbone for modern automation systems.


