
In the world of networking, simplicity often leads to chaos. Imagine an office where every conversation—from finance and HR to the marketing team—happens in a single, giant room. The noise would be unbearable, and sensitive information would be constantly at risk.
This is exactly how a traditional, flat Local Area Network (LAN) operates. But what if you could build virtual walls within that single room, creating private, secure, and efficient spaces for different groups? That’s the magic of a Virtual LAN (VLAN).
In this comprehensive guide, we'll break down what a VLAN is, how it works, its profound benefits, and how it integrates with modern hardware, including essential components like optical transceivers.
✅ Key Takeaways
A VLAN breaks a network into smaller groups. This helps with security and makes management easier. It keeps important data safe. It also controls which devices can talk to each other.
VLAN tagging puts special IDs on data packets. This makes sure data goes to the right group. It stops data from mixing between different VLANs.
VLANs make networks work better by lowering traffic jams. Each VLAN takes care of its own data. This means faster speeds and less waiting.
VLANs are flexible and let you change device groups easily. You do not need to move cables. You can change your network with simple settings.
There are different VLAN types, like port-based and management VLANs. These help you set up your network the way you want. Pick the type that fits your needs best.
✅ What is a VLAN (Virtual LAN)?
A Virtual LAN (VLAN) is a logical, software-defined subnetwork that partitions a single physical network switch into multiple, isolated broadcast domains. Think of it as creating several independent, virtual switches inside one physical device.
Devices on one VLAN behave as if they are connected to their own dedicated network, even if they are physically plugged into the same switch as devices on other VLANs. This isolation is a fundamental shift from the traditional hardware-based network segmentation.
✅ How Does a VLAN Work? The 802.1Q Tagging Magic
The secret sauce behind VLANs is the IEEE 802.1Q standard, often called "dot1q" tagging. Here's a simplified breakdown:
Frame Tagging: When a device on a VLAN sends data (an Ethernet frame), the network switch adds a special 4-byte "tag" into the frame's header.
The VLAN ID: This tag contains a crucial piece of information: the VLAN ID (a number between 1 and 4094). This ID identifies which VLAN the frame belongs to.
Traffic Steering: As the tagged frame travels through the network, other switches read this VLAN ID. They only forward the frame to ports that are members of the same VLAN.
Tag Removal: When the frame reaches its final destination switch, the 802.1Q tag is stripped away, and the original frame is delivered to the end device.
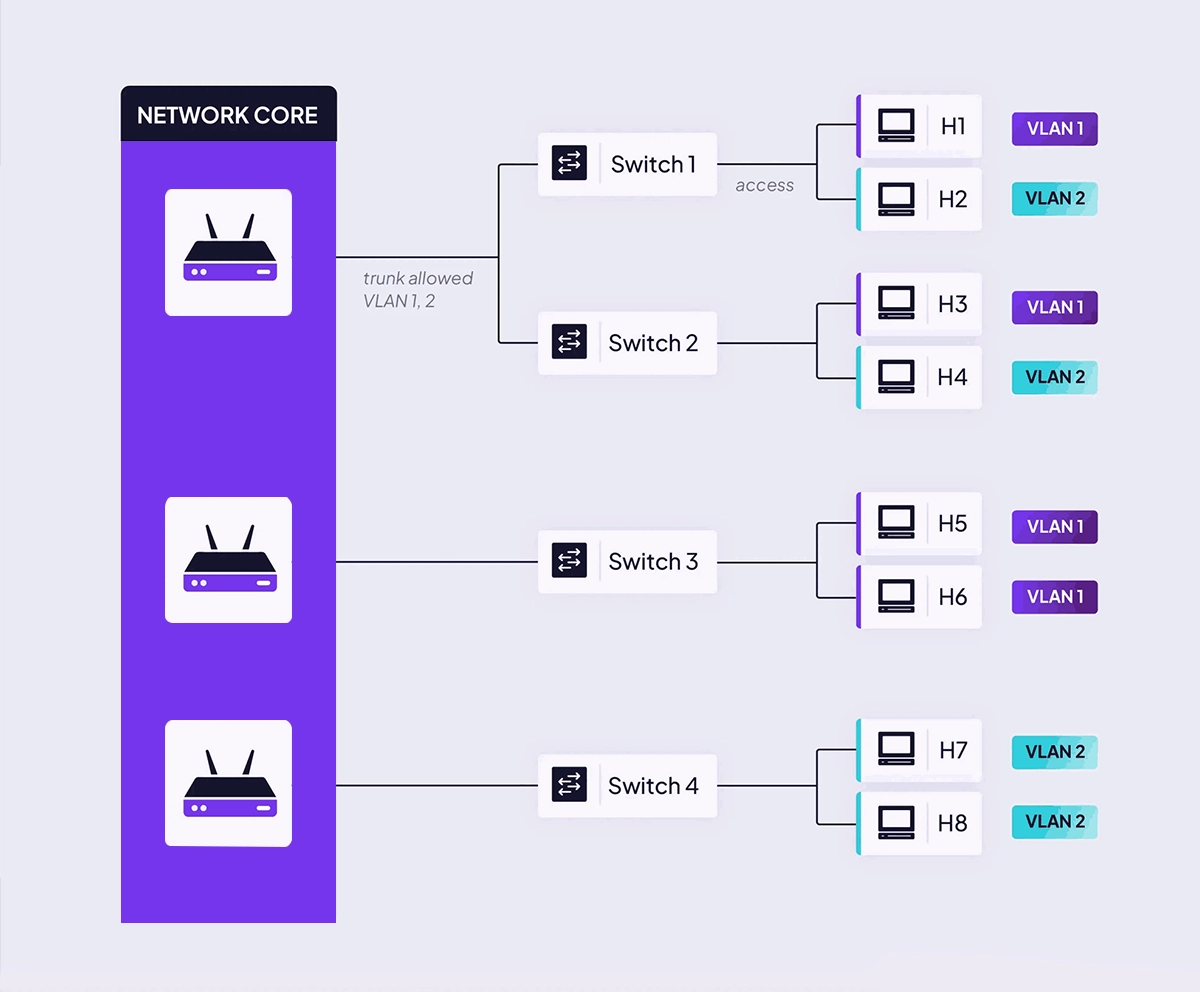
This process allows a single physical network link to carry traffic for multiple VLANs simultaneously, a concept known as a "trunk" link.
✅ Key Types of VLANs
Not all VLANs are created equal. Understanding the different types is crucial for effective VLAN configuration and management. The most common classifications are:
VLAN Type | Primary Function | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|
Data VLAN | Carries user-generated, regular traffic. | Separating departments (e.g., Engineering vs. Guest Wi-Fi). |
Voice VLAN | Prioritizes voice over IP (VoIP) traffic. | Dedicated to IP phones to ensure call quality and minimize latency. |
Management VLAN | Carries administrative traffic for managing network devices. | Isolating SSH/HTTPS access to switches and routers for enhanced security. |
Default VLAN | The pre-configured VLAN all switch ports belong to initially (usually VLAN 1). | It is a security best practice to reassign ports and not use the default VLAN. |
✅ The Compelling Benefits of Using VLANs
Why should you consider implementing VLANs? The advantages are transformative for both security and performance.
Enhanced Security: Isolate sensitive data. For example, a VLAN can ensure the Point-of-Sale system in a retail store cannot be accessed by devices on the public guest network.
Improved Performance: By containing broadcast traffic to smaller logical groups, VLANs reduce unnecessary network-wide traffic, freeing up bandwidth and improving overall performance for all applications.
Simplified Network Management: Grouping devices logically (by function, not physical location) makes it easier to apply policies, troubleshoot issues, and reconfigure networks without physically moving equipment.
Cost-Effectiveness: VLANs achieve network segmentation without requiring separate physical switches and cabling for each group, leading to significant cost savings.
✅ VLAN in Action: Access Ports vs. Trunk Ports
To successfully deploy VLANs, you must understand two critical port types:
Access Port: Connects to an end device (like a computer or IP phone). It belongs to one, and only one, data VLAN. It handles untagged frames.
Trunk Port: Connects between network devices (e.g., switch-to-switch or switch-to-router). It carries traffic for multiple VLANs and uses 802.1Q tags to keep them separate.
💡 Pro Tip: When planning your network segmentation strategy, considering high-quality hardware from providers like LINK-PP can ensure reliable trunk connections and seamless VLAN routing across your infrastructure.
✅ Connecting VLANs: The Role of Layer 3 Switches and Routers
By default, devices in one VLAN cannot communicate with devices in another. This is a core security feature. But what if you need controlled communication? You need a device that can route traffic between these virtual networks.
This is where Layer 3 Switches or Routers come in. They perform "Inter-VLAN Routing," acting as a gateway between VLANs. You can then apply advanced security policies (ACLs) at this routing point to control what traffic is allowed to cross between VLANs.
✅ Expanding Your Network: Where Do Optical Transceivers Fit In?
As networks grow, connecting switches across different floors or buildings becomes necessary. This is often done using fiber optic cables for their high bandwidth, long distance, and immunity to electrical interference. But switches can't send light signals on their own—they need a optical transceiver module.
A transceiver, like an SFP+ (Enhanced Small Form-Factor Pluggable), is a compact, hot-pluggable device that converts electrical signals from the switch into optical signals for fiber cables. When establishing a trunk link over fiber to extend your VLANs between two wiring closets, you would install a compatible transceiver in each connected switch.
For instance, to create a high-speed 10GbE fiber trunk for carrying multiple VLANs, you could use a reliable LINK-PP SFP-10G-SR transceiver. This specific model is designed for short-range connections over multi-mode fiber, making it a perfect and cost-effective solution for intra-building links, ensuring your VLAN architecture remains consistent and performant across your entire network infrastructure.
📌 Ready to build a robust, scalable network? Explore LINK-PP's full range of compatible SFP+, QSFP28, and other optical transceivers to find the perfect solution for your high-speed trunking needs.
✅ Conclusion
VLANs are a non-negotiable technology for modern, professional networks. They provide the foundational pillars of security, performance, and manageability without a massive investment in new hardware. By logically segmenting your network, you gain granular control over your data flow, protect critical assets, and build a scalable infrastructure ready for future growth.
Mastering VLAN configuration and security best practices is a fundamental step for any network administrator looking to optimize their environment.
✅ FAQ
What is the main purpose of a VLAN?
You use a VLAN to split your network into smaller groups. This helps you control traffic and improve network management. Each group stays separate, so you keep your data safe and organized.
What does VLAN tagging do in network management?
VLAN tagging marks each data packet with a unique ID. This tag tells switches which group the packet belongs to. You use VLAN tagging to keep network management simple and make sure data goes to the right place.
What role does a VLAN play in network management?
A VLAN lets you organize devices by function or department. You use this to make network management easier. You can track traffic, control access, and spot problems faster with clear groups.
What are the benefits of using VLANs for network management?
You get better security, faster speeds, and more control. VLANs help you keep devices in the right group. You use VLANs to make network management flexible and easy to change as your needs grow.
What should you check before adding VLANs to your network?
You need to check if your switches and devices support VLAN features. This step helps you avoid problems with network management. Make sure your equipment can handle VLAN tagging and group separation.


