
Welcome to the backbone of modern communication—the dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) network. Here, dozens, even hundreds, of individual light signals, each on a unique wavelength, travel together down a single fiber. Managing this "rainbow of light" requires precision, and that's where the unsung hero, the Optical Channel Monitor (OCM), comes into play.
This guide will demystify the OCM, explore its critical role, and show you how it integrates with key components like optical transceivers to create a robust, high-performance network. Whether you're a network engineer, a procurement manager, or a tech enthusiast, understanding OCMs is crucial for optimizing your infrastructure.
🚀 Key Takeaways
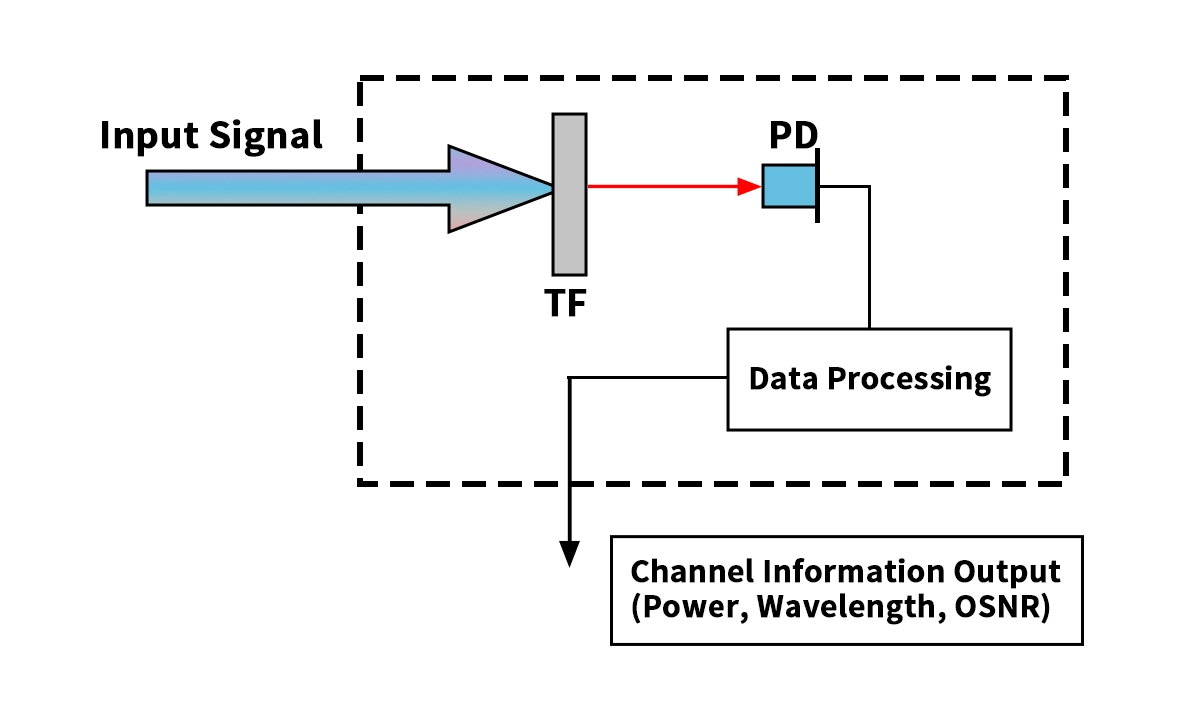
An Optical Channel Monitor (OCM) checks fiber optic networks. It measures signal power and wavelength.
Using an OCM lets you watch the network in real time. This helps find and fix problems fast. It stops issues from getting worse.
There are two types of OCMs. Passive OCMs are cheap and easy to use. Active OCMs have more features and give real-time data.
Some OCMs are high-resolution and small. These work well for networks with many channels or little space. They help monitor things accurately.
Adding an OCM makes the network work better. It helps the network be more reliable and efficient. This gives better service and less downtime.
🚀 What Exactly is an Optical Channel Monitor (OCM)?
An Optical Channel Monitor is a sophisticated device used in optical communication systems to measure and monitor the physical parameters of individual wavelength channels in a DWDM system. Think of it as the network's diagnostic dashboard, providing real-time insights into the health of every single data-carrying light beam.
In essence, an OCM performs a continuous, non-intrusive health check on your optical spectrum, ensuring that each channel is performing within its specified parameters.
Core Parameters an OCM Tracks:
Channel Wavelength: Ensures each signal is on its assigned frequency to avoid crosstalk.
Optical Power: Monitors the signal strength for each channel, detecting degradation or failures.
Optical Signal-to-Noise Ratio (OSNR): A critical measure of signal quality, indicating how much the signal stands out from the background noise.
Without an OCM, network operators would be "flying blind," unable to proactively detect issues like wavelength drift or power attenuation before they lead to costly service outages.
🚀 Why Your Network Can't Live Without an OCM: Key Features & Benefits
Integrating an OCM into your network isn't a luxury; it's a necessity for reliability and efficiency. Let's break down its core advantages.
Feature | Benefit to Your Network |
|---|---|
Real-time Performance Monitoring | Enables proactive maintenance. Detect issues like power degradation or wavelength drift before they impact service, dramatically reducing downtime. |
Enhanced Network Reliability | Provides the data needed for automated power balancing and fault localization, creating a self-healing and more resilient network infrastructure. |
Simplified Network Management | Offers a centralized view of all DWDM channels, simplifying operations and reducing the workload for network engineers. This is vital for effective DWDM network performance optimization. |
Cost Efficiency | Prevents over-provisioning and allows for optimal use of existing fiber capacity. By catching problems early, it avoids expensive emergency repairs and service level agreement (SLA) penalties. |
For businesses relying on high-speed data transmission, these benefits translate directly into improved customer satisfaction and a stronger bottom line. When searching for a comprehensive optical channel monitoring solution, ensuring it offers these features is paramount.
🚀 Applications: Where is an OCM Used?
OCMs are versatile and find applications across the entire optical networking landscape:
Telecom & Long-Haul Networks: The primary domain. OCMs are essential for managing the complex DWDM links that form the internet's backbone.
Data Center Interconnects (DCI): As data centers exchange massive amounts of data, OCMs ensure the interconnecting links are stable and high-performing.
Cable TV (CATV) Networks: Monitor the integrity of multiple broadcast channels carried over fiber.
Research & Development Labs: Used for testing and validating the performance of new optical components and systems.
🚀 The Critical Link: Optical Channel Monitors and Optical Transceivers
An OCM doesn't operate in a vacuum. Its performance is intrinsically linked to the quality of the optical modules (transceivers) within the network. An OCM can detect a problem, but a high-quality optical module is what prevents many problems from occurring in the first place.
How do they work together?
The Source: An optical transceiver (e.g., a QSFP28 or CFP2 module) generates the precise wavelength of light that carries the data.
The Journey: This light, combined with other wavelengths, travels through the DWDM system.
The Watchdog: The OCM continuously samples the combined light, measuring the power, wavelength, and OSNR of the signal from each transceiver.
The Feedback Loop: If the OCM detects that the wavelength from a specific transceiver is drifting or its power is fading, it alerts the network management system. This could indicate an aging or failing transceiver that needs replacement.
This synergy is why pairing a high-performance OCM with reliable optical modules is a best practice. Inferior transceivers can have unstable wavelengths or poor signal quality, forcing the OCM to work overtime and still potentially leading to network impairments.
This is where the quality of components becomes non-negotiable. For instance, the 400G QSFP-DD ZR coherent transceiver is engineered for exceptional wavelength stability and low noise, making it an ideal partner for advanced OCM systems. Its high performance ensures clean signals from the source, simplifying the monitoring task and enhancing overall network stability. Similarly, for 100G applications, the LINK-PP 100G CFP2 coherent module offers the precision and reliability that network architects trust for mission-critical long-haul and metro links.
🚀 How to Choose the Right Optical Channel Monitor: A Quick Guide
Not all OCMs are created equal. When evaluating an Optical Channel Monitor, consider the following criteria. The table below can serve as a starting point for your selection process.
Selection Criteria | What to Look For |
|---|---|
Monitoring Accuracy | High wavelength accuracy (± pm) and high power measurement resolution (dB). |
Channel Count & Spacing | Must support the number of channels in your network and the standard grid spacing (e.g., 50GHz, 100GHz). |
Measurement Speed | Fast sweep times for real-time feedback, crucial for dynamic networks. |
Integration Capabilities | Easy integration with your existing Network Management System (NMS) for centralized control. |
Form Factor | Can it be deployed as a standalone unit, a plug-in card for your platform, or integrated within an amplifier? |
When you are looking for a best optical channel monitor for DWDM systems, partnering with a vendor that understands the entire ecosystem, from transceivers to monitors, provides a significant advantage. LINK-PP's expertise in both high-precision optical modules and monitoring solutions ensures seamless compatibility and optimal performance for your network.
🚀 Conclusion: See Your Network in a New Light
In an era where data demand is insatiable, the Optical Channel Monitor has evolved from a niche tool to a foundational element of any robust optical network. It provides the critical visibility needed to ensure reliability, maximize performance, and reduce operational costs.
By investing in advanced OCM technology and pairing it with high-quality, stable components like LINK-PP's extensive range of optical transceivers, you are not just building a network—you are building a resilient, future-proof asset.
Ready to gain unparalleled visibility into your optical network?
Don't let signal degradation or wavelength drift catch you by surprise. Contact the experts at LINK-PP today to discuss your specific needs. We can help you select the perfect optical channel monitoring solution and compatible LINK-PP optical modules to build a faster, more reliable, and intelligent network.
➡️ Visit our website [link-pp.com] or get in touch for a personalized consultation!
🚀 FAQ
What does an Optical Channel Monitor measure?
An Optical Channel Monitor checks channel power, wavelength, and OSNR. These checks help you see if each channel works right in your fiber network.
What makes an OCM important in DWDM systems?
You need an OCM in DWDM systems to watch many channels together. It helps you spot weak signals or wrong wavelengths fast. This keeps your network strong and working well.
What types of networks use Optical Channel Monitors?
OCMs are used in telecom networks, data centers, and metro networks. These networks need real-time checks to keep data moving fast and safe.
What is the difference between passive and active OCMs?
Passive OCMs are for simple, low-cost checks. Active OCMs give you real-time data and let you control them from far away. You pick the type that fits your network best.


