In today's connected world, terms like "bandwidth" and "throughput" are often used interchangeably, but they represent distinct concepts that can make or break your network performance. Whether you're streaming videos, managing a data center, or optimizing business operations, understanding the difference between bandwidth and throughput is crucial for maximizing efficiency. In this comprehensive guide, we'll dive into their definitions, explore how they interact, and highlight why this knowledge matters for your network infrastructure. Plus, we'll introduce how advanced components like optical modules from LINK-PP can enhance both metrics. By the end, you'll have a clear grasp of these concepts and practical tips to improve your setup.
✅ Key Takeaways
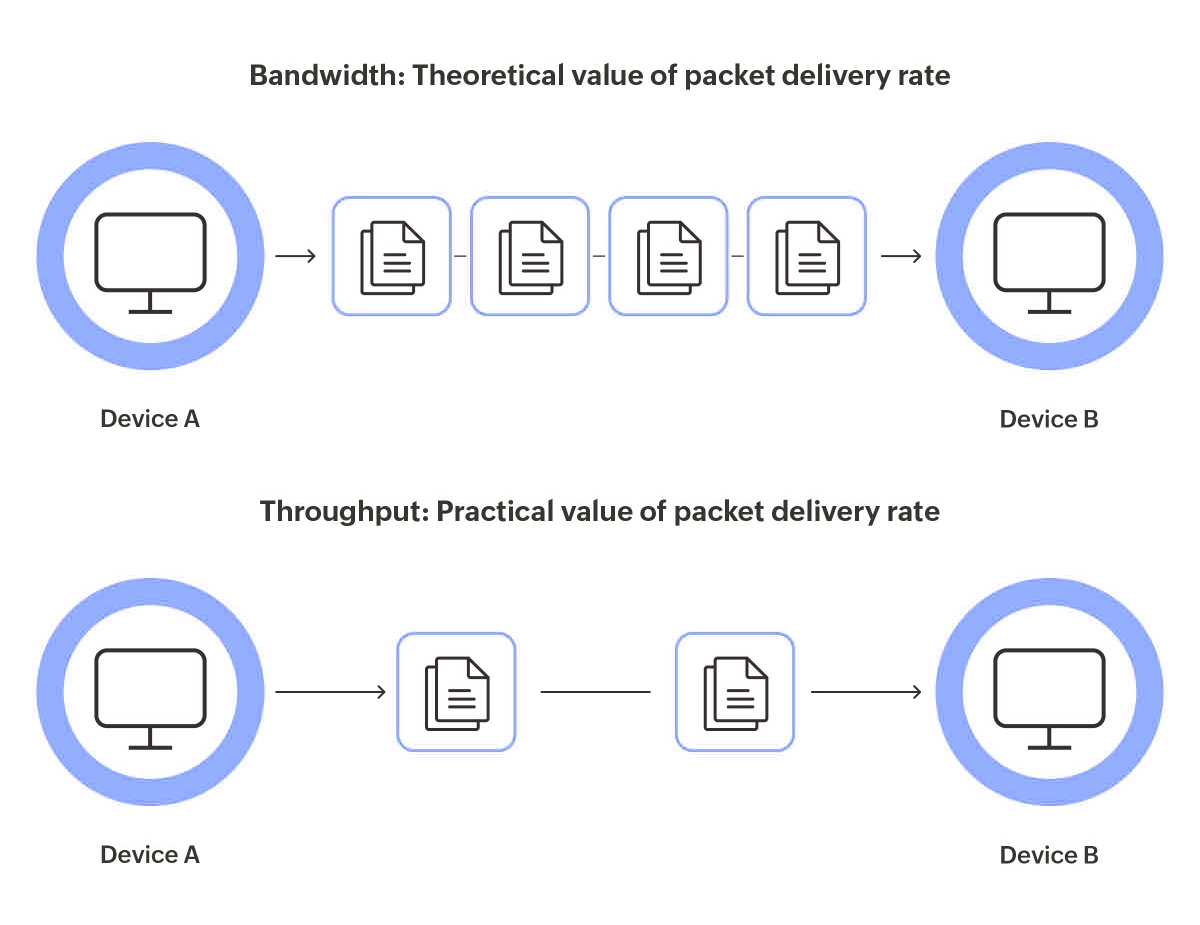
Bandwidth is the most data your network can carry. It is like how wide a highway is. Throughput is the real data that gets sent. It is like how many cars finish a race. High bandwidth does not always mean fast speeds. You should check both bandwidth and throughput for true performance. Problems like traffic jams and old devices can make throughput lower. This can happen even if you have high bandwidth. Use online speed tests to check both bandwidth and throughput. These tests help you find ways to make your network better.
✅ What Is Bandwidth?
Bandwidth refers to the maximum capacity of a network channel to transmit data over a given period, typically measured in bits per second (bps). Think of it as the width of a highway—the more lanes (higher bandwidth), the more cars (data) can theoretically travel at once. For example, a 1Gbps Ethernet connection has a higher bandwidth than a 100Mbps one, allowing for faster potential data transfers. However, bandwidth alone doesn't guarantee speed; it's just the upper limit. Factors like network type (e.g., fiber-optic vs. copper) and hardware capabilities influence bandwidth. In networking, optimizing bandwidth is a key step toward handling large data loads, such as in cloud computing or video conferencing.
✅ What Is Throughput?
Throughput, on the other hand, is the actual amount of data successfully transmitted over a network in a specific time frame, also measured in bps. It's the real-world performance metric—like the number of cars actually moving on that highway, considering traffic jams, accidents, or road conditions. Throughput is affected by latency, packet loss, network congestion, and protocol overheads. For instance, even with high bandwidth, throughput might drop due to interference or inefficient routing. Measuring throughput helps diagnose network issues and ensures reliable data delivery, making it vital for applications like online gaming or VoIP services where consistency matters.
✅ Bandwidth vs Throughput: A Detailed Comparison
To clarify the differences, let's break it down with a table. This comparison highlights why both metrics are essential but not the same.
Aspect | Bandwidth | Throughput |
|---|---|---|
Definition | Maximum data capacity of a channel | Actual data transferred successfully |
Measurement | Bits per second (e.g., Mbps, Gbps) | Bits per second over time (e.g., average Mbps) |
Key Influencers | Hardware, medium (e.g., fiber), signal strength | Latency, congestion, errors, protocol efficiency |
Analogy | Highway width | Cars actually reaching their destination |
Focus | Potential speed | Real-world performance |
As shown, bandwidth sets the stage, while throughput delivers the results. For example, a network with 10Gbps bandwidth might only achieve 7Gbps throughput due to delays—this gap is why monitoring both is critical. Understanding this distinction can help you troubleshoot slow networks and make informed upgrades, such as investing in high-performance optical transceivers to reduce bottlenecks.
✅ How Bandwidth and Throughput Relate in Real-World Scenarios
In practice, bandwidth and throughput work together to define network efficiency. A high-bandwidth connection can support greater throughput, but only if other factors like low latency and minimal packet loss are in place. For instance, in data centers, increasing bandwidth without addressing congestion might not boost throughput. This is where tools like LINK-PP's network solutions come into play, offering optimized hardware that balances both metrics.
✅ The Role of Optical Modules in Bandwidth and Throughput
Optical modules are critical components in modern networking, converting electrical signals to light for high-speed data transmission over fiber-optic cables. They directly impact both bandwidth and throughput by enabling faster data rates and reducing signal degradation. For example, a high-quality optical transceiver can maximize available bandwidth and sustain higher throughput by minimizing latency and errors.
In this context, LINK-PP offers reliable optical modules designed for peak performance. A standout model is the LINK-PP LQ-LW100-LR4C, which supports up to 100Gbps bandwidth over long distances (up to 10km). This module integrates advanced forward error correction (FEC) and low-power design, helping to maintain high throughput even in congested environments. By choosing LINK-PP components, you can enhance network reliability and scalability, making them ideal for data centers, ISPs, and enterprises focused on "optimizing network throughput with fiber optics."
Tips to Optimize Bandwidth and Throughput
Monitor Regularly: Use network analytics tools to track bandwidth usage and throughput metrics. This helps identify bottlenecks early.
Upgrade Hardware: Invest in modern equipment, such as LINK-PP optical modules, to increase bandwidth capacity and improve throughput efficiency.
Reduce Congestion: Implement Quality of Service (QoS) settings to prioritize critical traffic and minimize packet loss.
Check for Errors: Regularly inspect cables and connections for faults that could degrade throughput.
✅ Conclusion
Bandwidth and throughput are two sides of the same coin, each playing a vital role in network performance. While bandwidth defines the potential, throughput reveals the reality—and bridging that gap requires smart infrastructure choices. By incorporating high-quality products like the LINK-PP QSFP28 100G LR4 optical module, you can boost both metrics for smoother, faster data transfers. We hope this guide has clarified these concepts and empowered you to take action. For more insights on networking solutions, explore LINK-PP's innovative portfolio and stay ahead in the digital race!
✅ FAQ
What is the main difference between bandwidth and throughput?
Bandwidth shows the maximum data your network can handle. Throughput tells you the actual data you receive. You need both numbers to understand your network’s true speed.
Can throughput ever be higher than bandwidth?
No, throughput cannot be higher than bandwidth. Bandwidth sets the upper limit. Throughput always stays equal to or below that limit.
Why does my throughput drop even with high bandwidth?
Network congestion, interference, or old equipment can slow your throughput. You may have high bandwidth, but these issues block data and lower your actual speed.
How do I check both bandwidth and throughput?
You can use online speed tests to measure both. Your internet plan shows bandwidth. Speed tests show throughput. Compare the results to spot problems.




