📞 Definition & Technical Overview
● What is VoIP?
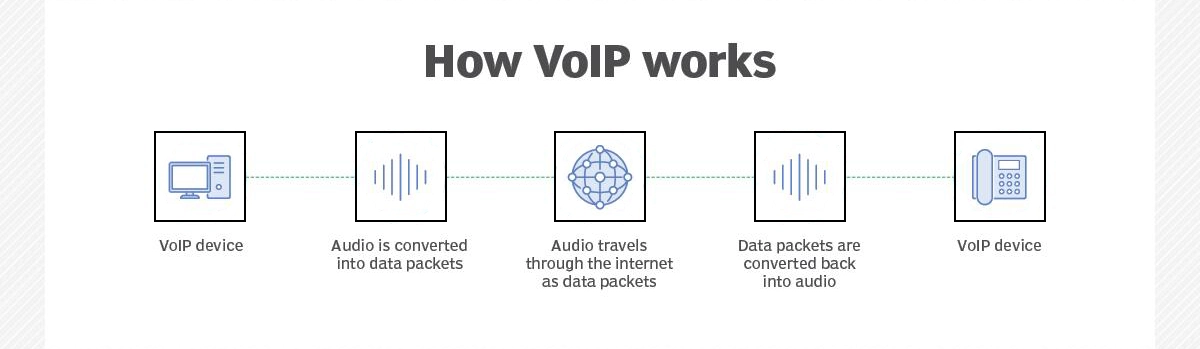
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) is a technology that enables voice and multimedia communications over IP networks instead of traditional telephone circuits. Analog audio is digitized, packetized, and transmitted over Ethernet or WAN links, then reconstructed at the receiving end. This shift allows voice to operate on the same network infrastructure as data, reducing costs and increasing flexibility.
● Why VoIP matters for modern networks
VoIP transforms traditional telephony by converging voice and data onto a single network. Enterprise and data center networks benefit from simplified cabling, cost reduction, and integration of advanced features. High-quality RJ45 connectors and LAN transformers are critical to ensuring signal integrity, minimizing latency, and maintaining reliable voice communication.
📞 Technical Architecture & Protocol Stack
1. Signaling and Media Layers
Key VoIP protocols include:
SIP (Session Initiation Protocol): Handles call setup, modification, and termination.
RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol): Carries voice and video streams.
UDP Transport: Minimizes latency and avoids retransmission delays that would disrupt real-time communication.
2. Network Interface and Hardware Considerations
VoIP depends on high-performance Ethernet interfaces. LINK‑PP RJ45 connectors with integrated magnetics ensure low insertion loss, robust EMI/EMC performance, and stable signal transmission. LAN transformers provide isolation and improve signal integrity, critical for maintaining voice quality over IP networks.
3. Media Conversion and Gateways
Gateways enable VoIP to interface with PSTN or legacy telephony networks, converting both signaling protocols and media streams. Hardware designers must ensure RJ45 connectors and transformers support these conversions without degrading performance.
📞 Core Performance Metrics & Quality of Service (QoS)
Latency, Jitter & Packet Loss
To maintain natural voice communication:
One-way latency: ≤100 ms (ideally), rarely >150 ms
Jitter: ≤30–40 ms
Packet loss: ≤1–3 %
MOS & QoE Metrics
Mean Opinion Score (MOS) rates perceived voice quality from 1.0 to 5.0. Voice codecs like G.711 typically achieve MOS ~4.5 under optimal network conditions. Maintaining low latency, jitter, and packet loss ensures high QoE for VoIP systems.
Hardware & Network Implications
VoIP performance depends on:
VLAN and QoS tagging for voice prioritization
Low-latency switches with minimal buffering
High-quality RJ45 connectors and magnetics
Real-time monitoring for latency, jitter, and packet loss
📞 Applications & Use-Cases
▷ Enterprise IP-Phones & Unified Communications
VoIP powers IP phones, soft clients, and unified communication systems. PoE-enabled RJ45 connectors allow voice and power over a single cable, simplifying deployment.
▷ Contact Centers & Data Centers
High-density VoIP deployment in data centers requires robust hardware and network design, including high-speed RJ45 interfaces, magnetics, and switches that maintain QoS metrics.
▷ Converged Voice/Video in 5G & Edge Networks
VoIP is evolving into VoLTE and voice/video over 5G NR, relying on reliable Ethernet interfaces. LINK‑PP’s high-speed RJ45 connectors and LAN transformers support these converged networks.
📞 Advantages, Challenges & Hardware Design Considerations
1. Key Advantages
Lower costs compared to traditional phone lines
Converged voice, video, and data infrastructure
Easy scalability for enterprise and remote sites
2. Technical Challenges
Ensuring QoS for real-time voice traffic
Security against eavesdropping, DoS attacks, and fraud
Interoperability with legacy PSTN systems
High-quality RJ45 and LAN transformer design to meet latency and signal requirements
3. Design Implications for LINK‑PP Components
Minimize insertion loss, skew, and crosstalk
Ensure isolation and PoE support in LAN transformers
Maintain latency budgets for voice-grade performance
Future-proof interfaces for Gigabit and multi-Gig Ethernet

📞 Summary & Outlook
VoIP transforms voice communications by leveraging IP networks, providing cost efficiency, flexibility, and convergence with data services. Engineers and integrators must carefully design network infrastructure and select high-performance hardware to maintain voice quality. LINK‑PP RJ45 connectors and LAN transformers play a critical role in delivering reliable, low-latency, and high-quality VoIP solutions for modern enterprise, data center, and converged communication networks.
As 5G, edge computing, and unified communications continue to evolve, the demand for robust Ethernet interfaces and magnetics will grow, making LINK‑PP components essential for next-generation VoIP deployments.
📞 FAQ – Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
1. What devices require VoIP-compatible RJ45 connectors?
VoIP endpoints such as IP phones, soft clients, gateways, routers, and network switches rely on high-quality RJ45 connectors with integrated magnetics. These ensure signal integrity, minimal latency, and reliable voice/data transmission over Ethernet.
2. How does a LAN transformer improve VoIP call quality?
LAN transformers (network magnetics) provide electrical isolation, reduce EMI/EMC interference, and preserve signal integrity. This minimizes latency, jitter, and packet loss, which are critical for clear, stable VoIP communication.
3. What are the most important network metrics for VoIP performance?
Key performance metrics include:
Latency: ≤100 ms one-way is ideal
Jitter: ≤30–40 ms
Packet loss: ≤1–3 %
Maintaining these metrics ensures high MOS (Mean Opinion Score) and excellent voice quality.
4. Can VoIP work with Power over Ethernet (PoE)?
Yes. PoE-enabled RJ45 connectors allow VoIP devices to receive both power and data over a single Ethernet cable. This simplifies deployment and is common in enterprise IP phones and IP-based gateways.
5. How does LINK‑PP hardware support enterprise and data center VoIP deployment?
LINK‑PP RJ45 connectors and LAN transformers are designed for low insertion loss, minimal crosstalk, and high EMI immunity. They maintain QoS requirements for voice traffic, support PoE, and are compatible with Gigabit and multi-Gigabit Ethernet—ensuring stable and high-quality VoIP in large-scale networks.


