
In our hyper-connected world, we often hear terms like "high-speed internet" and "gigabit networks." But have you ever started a video download expecting lightning speed, only to watch it crawl? The culprit often isn't your bandwidth—it's your throughput.
Understanding throughput is crucial for anyone who relies on a stable and fast network, from IT professionals to everyday users. This guide will demystify network throughput, explain its importance, and show you how to optimize it for a seamless experience.
✅ Key Takeaways
Throughput shows how much data goes from one place to another in a certain time. More throughput means your internet works faster.
You can use online speed tests to see your network throughput. This lets you know how well your connection works.
Put your router in the middle of your home. Use wires instead of Wi-Fi for stronger signals and quicker data.
Check your network often to find problems. Remove devices you do not use to make throughput better.
Learn how throughput, bandwidth, and latency are different. Each one changes how your network works in its own way.
✅ Defining Network Throughput: The Real-World Speed
In simple terms, throughput is the actual rate at which data is successfully delivered over a network connection in a given period. It's the measurable amount of data that reaches its destination. Think of it as the effective data transfer rate you experience.
Measured in: Bits per second (bps), like Mbps or Gbps.
Key Quality: It is always less than or equal to the theoretical maximum speed (bandwidth).
The Analogy: If bandwidth is the total number of lanes on a highway, throughput is the actual number of cars passing a specific point per minute, considering traffic jams, accidents, and slow drivers.
Throughput is the metric that truly impacts your daily activities: how fast a file downloads, how clear your video call is, and how quickly a web page loads.
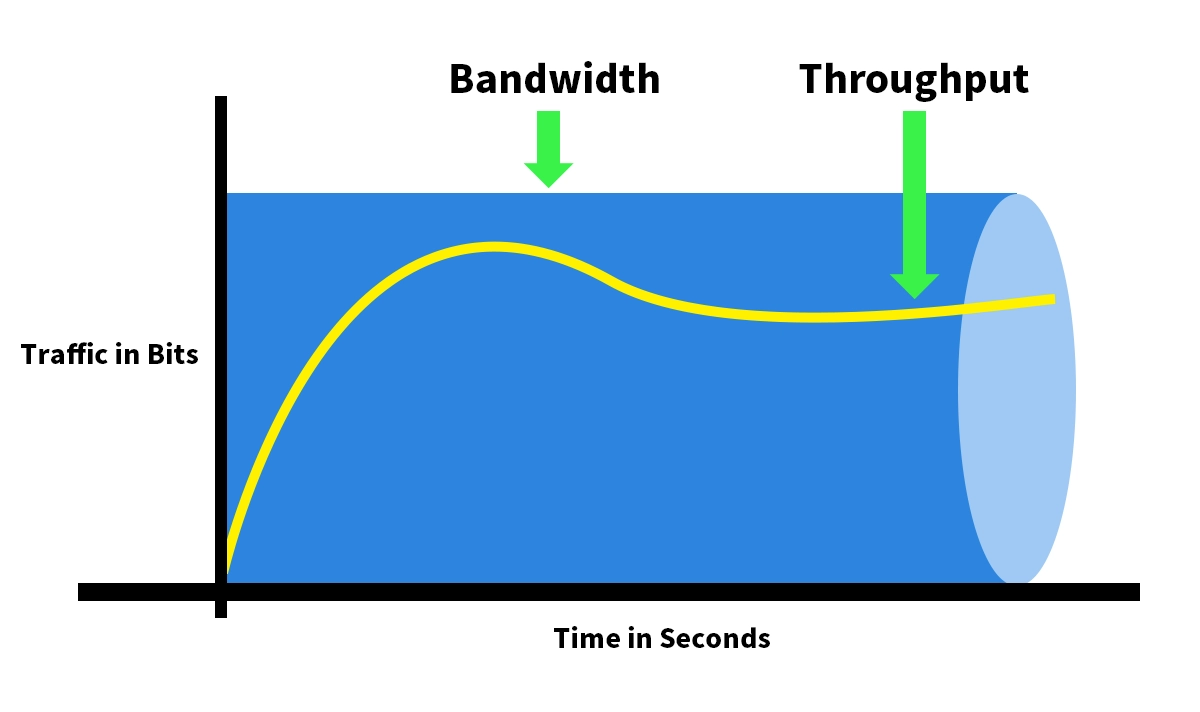
✅ Throughput vs. Bandwidth: What's the Actual Difference?
This is one of the most common confusions in network performance management. While often used interchangeably, bandwidth and throughput are distinct concepts.
Feature | Throughput | |
|---|---|---|
Definition | The actual, successful data transfer rate. | The theoretical maximum data-carrying capacity of a link. |
What it Measures | Real-world performance and efficiency. | Potential capacity; the "size" of the pipe. |
Primary Influence | Network conditions (latency, packet loss, congestion). | Physical hardware and infrastructure. |
Analogy | The amount of water actually flowing from a tap. | The diameter of the water pipe. |
Why does this matter? You could pay for a 1Gbps (bandwidth) internet plan, but if network congestion and high latency are severe, your actual data throughput might only be 600Mbps. Focusing on throughput gives you a realistic picture of your network's health.
✅ Key Factors That Affect Your Network Throughput
Several elements can create bottlenecks, limiting your throughput and affecting overall network communication efficiency. Understanding these factors affecting data throughput is the first step toward optimization.
Latency (Delay): The time it takes for a data packet to travel from source to destination. High latency (lag) can drastically reduce throughput, especially for real-time applications like gaming and VoIP.
Packet Loss: When data packets fail to reach their destination, they must be re-sent. This retransmission consumes available capacity, lowering effective throughput.
Network Congestion: When too many devices or users are trying to use the same network path simultaneously, it creates a traffic jam, slowing data down for everyone.
Hardware Limitations: Outdated routers, switches, or network interface cards (NICs) may not be able to process data at high speeds, creating a bottleneck.
Protocol Overhead: Communication protocols like TCP/IP add headers and control information to data packets. This overhead isn't "user data," so it consumes some of the available bandwidth, reducing the throughput available for your actual files and streams.
✅ How to Measure and Optimize Throughput
To improve your network, you must first measure it. Tools like iPerf3, Speedtest.net, and built-in network monitors can provide accurate throughput measurements.
Effective throughput optimization techniques include:
Upgrading Hardware: Ensure your routers, switches, and cables can handle your required speeds. For instance, using a managed switch can provide better traffic control than an unmanaged one.
Quality of Service (QoS): Configure your router's QoS settings to prioritize critical traffic (e.g., video calls over file downloads).
Using Wired Connections: Where possible, use Ethernet cables instead of Wi-Fi to reduce interference and packet loss.
Monitoring for Bottlenecks: Use network monitoring software to identify which devices or applications are consuming disproportionate resources.
✅ The Role of Optical Modules in Maximizing Throughput
As network demands soar, especially in data centers and enterprise backbones, fiber optic cables have become the standard for high-speed data transmission. This is where optical modules, or transceivers, play a pivotal role.
An optical module is a small device that plugs into a switch, router, or server. Its job is to convert electrical signals from the device into optical light signals for transmission over fiber optic cables, and vice-versa.
How does this relate to throughput?
The quality and capability of the optical module directly determine the speed and integrity of the data passing through it. A low-quality or mismatched module can become a severe bottleneck, introducing errors and limiting the throughput of an otherwise high-bandwidth link.
For high-throughput, low-latency applications like financial trading or high-performance computing clusters, choosing a reliable, high-performance transceiver is non-negotiable. This is a critical step in any network throughput optimization strategy.
When selecting an optical module for your high-speed network infrastructure, it's essential to choose a reputable brand that guarantees performance and compatibility. For example, the LINK-PP SFP-10G-SR optical module is an excellent choice for achieving 10 Gigabit Ethernet throughput over multimode fiber. It's designed for reliability and low power consumption, ensuring that your network's physical layer does not become the weak link that limits your overall data throughput. Integrating proven components like those from LINK-PP helps future-proof your network and maintain consistent performance.
✅ Conclusion: Mastering Throughput for a Faster Network
Throughput is more than just a technical term; it's the definitive measure of your network's real-world performance. By understanding the difference between bandwidth and throughput, recognizing the factors that degrade it, and taking proactive steps to measure and optimize, you can ensure your network operates at its full potential.
Remember, investing in robust infrastructure, including high-quality components from trusted manufacturers like LINK-PP, is a cornerstone of building a high-throughput, low-latency network ready for the demands of tomorrow. Stop focusing solely on bandwidth and start paying attention to the throughput that powers your digital life.
✅ FAQ
What is the main purpose of network throughput?
Network throughput tells you how much data moves in a certain time. It helps you know how well your network works. You use it for things like streaming, gaming, or downloading files.
What tools can you use to check your network throughput?
You can use online speed tests to check throughput. Network monitoring software also helps you see data movement. Some routers have built-in tools for this job.
What causes low throughput on your network?
Low throughput can happen if you have old hardware. Too many people using the network can slow it down. Bad settings or broken cables can also cause problems.
What is the difference between throughput and bandwidth?
Throughput is the amount of data you get each second. Bandwidth is the most data your network can carry. Throughput shows what you really get, bandwidth shows the highest limit.


