● Introduction
In Ethernet design, engineers often encounter two terms: LAN Transformer and LAN Filter. They are sometimes used interchangeably, but in reality, they serve distinct purposes. Both are critical components of Ethernet magnetics, especially in RJ45 magnetic connectors, where they are frequently integrated into a single module. Understanding the differences between them helps engineers design more reliable and compliant Ethernet systems.
● What Is a LAN Transformer?
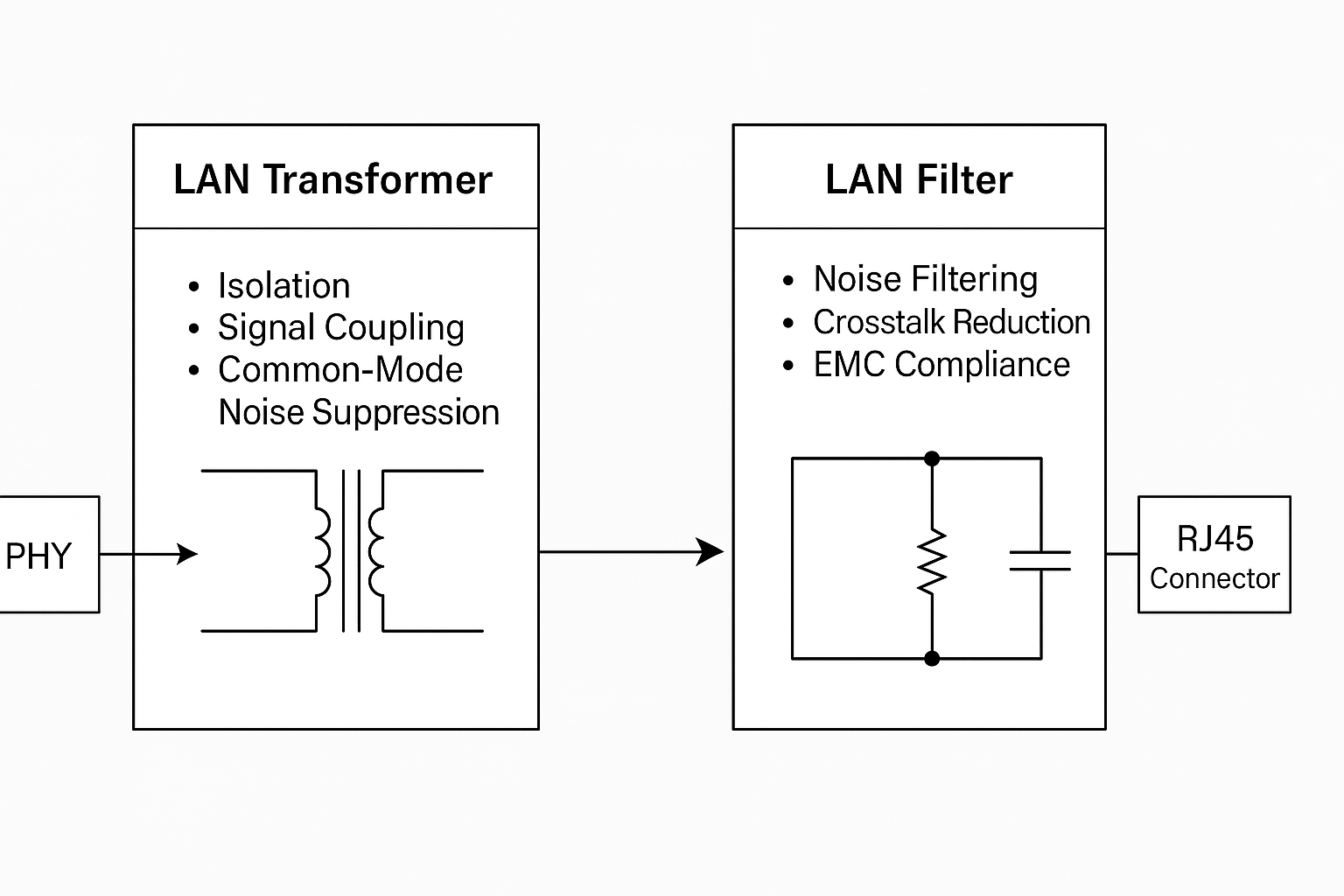
A LAN Transformer, sometimes called an Ethernet Transformer, is a magnetic isolation device placed between the Ethernet PHY (Physical Layer IC) and the twisted-pair cable.
Key Functions of LAN Transformers:
Galvanic isolation: Provides high-voltage isolation (commonly 1500 Vrms or higher) to protect equipment and users.
Signal coupling: Transfers differential Ethernet signals across the isolation barrier.
Common-mode noise suppression: Reduces interference by rejecting noise present equally on both signal lines.
Standards compliance: Essential for meeting IEEE 802.3 Ethernet specifications.
In short, LAN Transformers are responsible for isolation, safety, and signal transfer.
● What Is a LAN Filter?
A LAN Filter is a passive filter circuit—typically composed of inductors and capacitors—integrated into Ethernet magnetics to improve signal quality.
Key Functions of LAN Filters:
Noise filtering: Suppresses high-frequency noise (EMI/RFI).
Signal integrity improvement: Reduces jitter and crosstalk in high-speed Ethernet signals.
EMC compliance: Helps devices meet regulatory standards such as FCC, CE, and IEC.
Power delivery stability: In PoE/PoE+ applications, filters reduce conducted noise on power lines.
While a LAN Transformer handles isolation and coupling, the LAN Filter ensures clean, reliable signal transmission.
● LAN Transformer vs LAN Filter: A Comparison
Feature | LAN Filter | |
|---|---|---|
Core Purpose | Provides galvanic isolation and couples Ethernet signals | Filters EMI/RFI noise and improves signal quality |
Main Structure | Wound magnetic coils (transformer) | Inductor-capacitor filtering network |
Standards Role | Ensures IEEE 802.3 electrical isolation requirements | Supports EMC/EMI compliance |
Location in Circuit | Between PHY IC and Ethernet cable | Often integrated alongside the transformer in RJ45 modules |
Dependency | Always required for Ethernet | Complementary, enhances performance but not standalone |
👉 Together, they ensure safe, compliant, and stable Ethernet transmission.
● Why Are They Integrated Together?
Modern RJ45 magnetic connectors combine LAN Transformers and LAN Filters into one compact module. This integration:
Saves PCB space
Simplifies Ethernet design
Improves EMC and EMI performance
Provides a plug-and-play solution for OEMs
Such integration is particularly important in Gigabit Ethernet, PoE, industrial networking, and automotive Ethernet, where both signal integrity and reliability are critical.
● LINK-PP LAN Magnetics: Transformer + Filter Solutions

At LINK-PP, we design and manufacture RJ45 magnetic connectors and Ethernet magnetics that combine both LAN Transformers and LAN Filters.
Our solutions are:
Fully compliant with IEEE 802.3 standards
Available for 10/100Mbps, Gigabit, and 10G Ethernet
Optimized for PoE/PoE+ applications
Designed to reduce EMI and ensure long-term network reliability
Trusted by global OEMs, LINK-PP products deliver the isolation, filtering, and signal integrity that Ethernet systems demand.
● Conclusion
While the LAN Transformer and LAN Filter serve different purposes, they complement each other in Ethernet design. The transformer ensures isolation and signal transfer, while the filter enhances signal integrity and EMC compliance. In practice, they are often integrated into a single RJ45 magjack to simplify design and guarantee performance.
For high-quality Ethernet magnetics, LINK-PP offers transformer + filter solutions that enable engineers to build reliable, standards-compliant networks.




