1️⃣ Introduction: What is a Resistor?
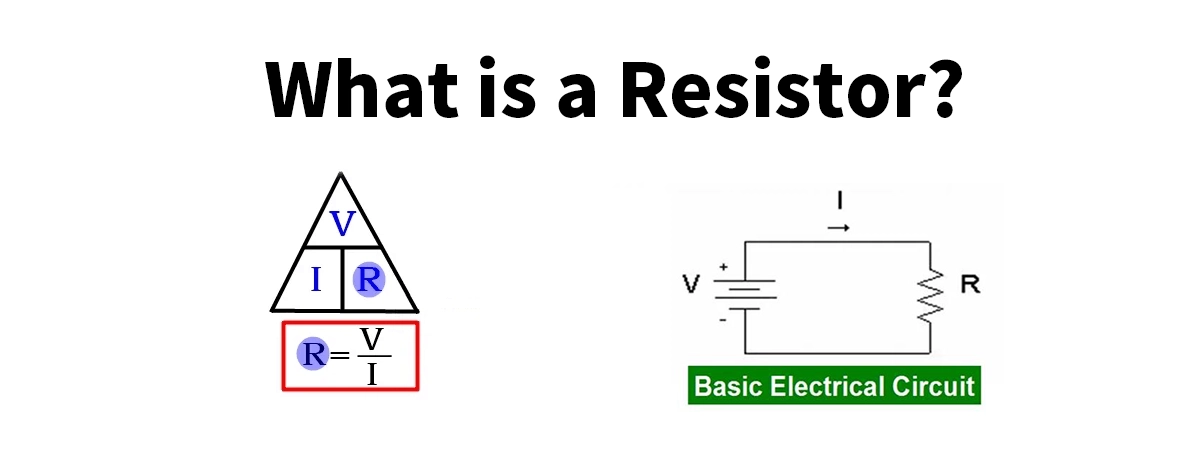
A resistor is one of the most fundamental components in electronic circuits. Its primary function is to limit current, divide voltage, and protect sensitive devices. Measured in ohms (Ω), resistors play a critical role in ensuring circuit stability, energy efficiency, and safety.
Engineers, designers, and procurement specialists rely on resistors for applications ranging from consumer electronics to industrial automation, networking equipment, and automotive systems.
2️⃣ How Do Resistors Work?
Resistors operate on Ohm’s Law (V = I × R), which describes the relationship between voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R). By introducing resistance into a circuit, resistors:
Control current flow to prevent component damage.
Adjust signal levels in analog and digital devices.
Enable biasing in active components like transistors.
Dissipate power in the form of heat.
3️⃣ Types of Resistors
♦ Fixed Resistors
Carbon Film Resistors: Cost-effective, general-purpose use.
Metal Film Resistors: High stability and low noise.
Wire-Wound Resistors: High power handling, used in industrial systems.
♦ Variable Resistors
Potentiometers: Adjustable voltage dividers.
Rheostats: Used for current control in motors and lighting.
♦ Surface Mount Resistors (SMD)
Compact, reliable, and widely used in modern PCBs.
Suitable for networking equipment, telecom systems, and compact electronics.
♦ Specialized Resistors
Precision Resistors: Tolerance as low as ±0.01%, ideal for measurement systems.
Power Resistors: Designed to handle high-energy loads.
Thermistors: Temperature-dependent resistance for sensing and protection.
4️⃣ Key Specifications When Choosing Resistors
When sourcing resistors, engineers and buyers must evaluate:
Resistance Value (Ω) – Defines how much current is limited.
Tolerance (%) – Accuracy of resistance (e.g., ±1%, ±5%).
Power Rating (W) – Maximum heat a resistor can safely dissipate.
Temperature Coefficient (ppm/°C) – Stability across temperature changes.
Package Type (Through-Hole, SMD) – Determines assembly compatibility.
Reliability & Certification – Especially important in automotive, networking, and telecom industries.
5️⃣ Applications of Resistors
Resistors are used in virtually all electronic systems. Common applications include:
Signal Conditioning – Adjusting voltages in communication devices.
Load Regulation – Stabilizing circuits in power supplies.
Networking Equipment – Essential in switches, routers, and PoE devices.
Automotive Electronics – Supporting sensors, ECUs, and LED systems.
Industrial Control Systems – Ensuring safe operation of motors and automation equipment.


