
In today’s digital landscape, transferring files is a fundamental operation for businesses and individuals alike. While the classic File Transfer Protocol (FTP) has been a workhorse for decades, its lack of inherent security poses significant risks. This is where FTP over SSL (FTPS) comes into play. FTPS is a powerful extension that wraps the standard FTP protocol in a layer of Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) or its successor, Transport Layer Security (TLS), encryption. For IT professionals and businesses seeking a secure file transfer protocol that builds on familiar FTP foundations, understanding FTPS is crucial.
This guide will explain how FTPS works, its key benefits, and why pairing it with robust hardware, like high-performance optical transceivers, is essential for modern, secure data infrastructure.
📑 Key Takeaways
FTPS, also called FTP over SSL, keeps your files safe when you send them. It uses encryption to stop hackers from stealing your data.
You should always look for a real server certificate before you send files. This helps you make sure you are using a trusted server.
Update your FTPS software often. This helps fix security problems and makes it work better.
Pick strong passwords and change them often. This stops people who should not see your files from getting in.
FTPS works well for sharing private information in places like hospitals and banks. These places need to keep data safe.
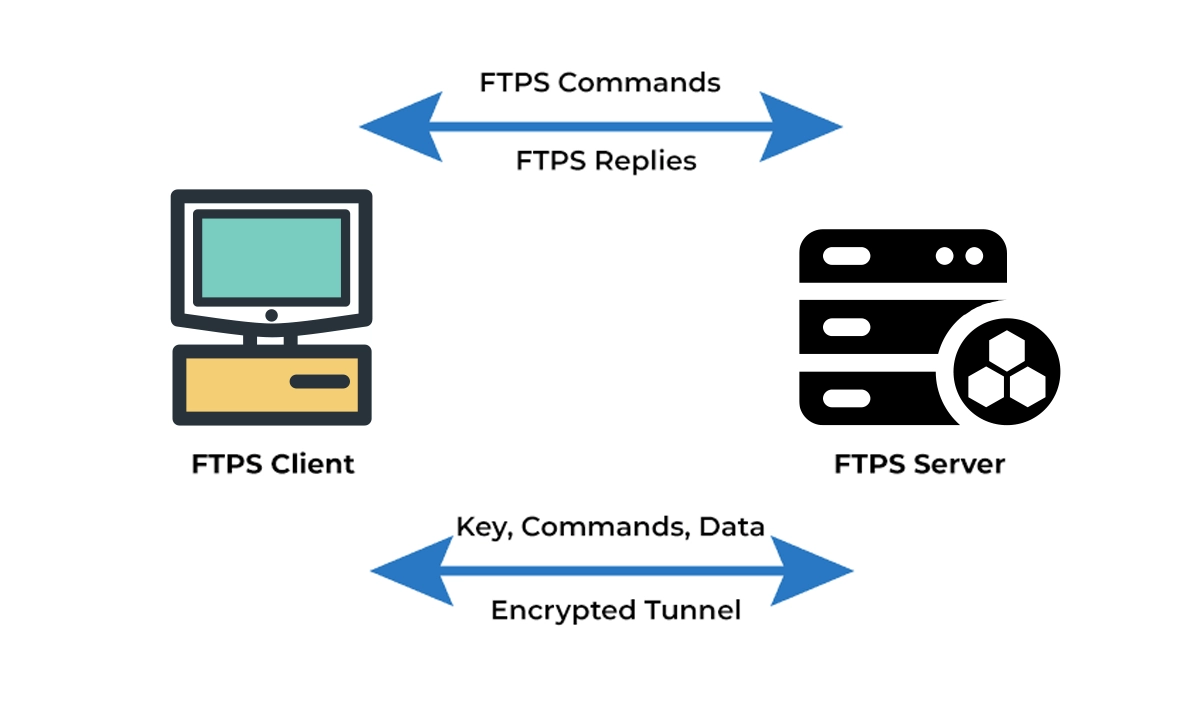
📑 How Does FTPS Work? The Two Modes Explained
FTPS secures the connection in two distinct ways, often referred to as FTPS implicit SSL and FTPS explicit SSL. This dual-mode operation provides flexibility for different security requirements.
1. Implicit SSL/TLS (A Legacy Approach)
In this strict mode, security is mandatory from the very first connection. The client is expected to establish an SSL/TLS connection immediately upon contacting the server’s dedicated port (typically port 990). If the SSL handshake fails, the connection is terminated. While highly secure, this mode is less common today due to its inflexibility.
2. Explicit SSL/TLS (The Modern Standard)
This is the more prevalent and flexible mode. The connection starts as a plain FTP session over the standard command port (port 21). The client then explicitly requests security by issuing an AUTH TLS or AUTH SSL command. The server and client then negotiate and upgrade the connection to an encrypted state. This allows for backward compatibility with systems that may not support encryption.
Key Takeaway: Explicit FTPS is generally preferred as it allows administrators to offer both secure and (if absolutely necessary) insecure connections from the same port, simplifying configuration and management.
📑 FTPS vs. Other Protocols: A Quick Comparison
Choosing the right secure file transfer protocol depends on your specific needs. Here’s how FTPS stacks up against two other common solutions:
Feature | FTPS | HTTPS/WebDAV | |
|---|---|---|---|
Basis | Extension of traditional FTP | Part of the SSH protocol suite | Uses HTTP/HTTPS web protocols |
Security | SSL/TLS encryption | SSH encryption | SSL/TLS encryption |
Port | 21 (Explicit), 990 (Implicit) | Port 22 | Port 443 (HTTPS) |
Firewall Friendliness | Can be challenging due to dynamic data ports | Very friendly; uses a single port | Excellent; uses standard web port |
Authentication | Certificates & Username/Password | SSH Keys & Username/Password | Certificates & Username/Password |
Best For | Environments with existing FTP infrastructure | Secure automation & Unix/Linux environments | User-friendly web-based uploads/downloads |
For organizations with established FTP server infrastructure looking to enhance security without a complete overhaul, FTPS presents an optimal path forward. It's a critical component for achieving compliant data transfer in regulated industries.
📑 The Critical Role of Hardware: Why Your FTPS Server Needs a Reliable Optical Module
While FTPS provides the software-level encryption for secure data in transit, the physical hardware carrying this data is equally vital. This is especially true for data centers, cloud providers, and enterprises handling high-volume, sensitive transfers. A secure and fast FTPS server depends on a stable and high-bandwidth network backbone.
Optical transceiver modules (or SFP modules) are the unsung heroes here. They convert electrical signals from your server into optical light for transmission over fiber optic cables, enabling high-speed, long-distance, and low-latency connections. A faulty or low-quality module can become a single point of failure, leading to:
Connection Drops: Interrupting critical file transfers.
Data Corruption: Compromising the integrity of encrypted files.
Bandwidth Bottlenecks: Slowing down transfer speeds, negating efficiency gains.
When deploying a high-availability FTPS server for business-critical operations, investing in industrial-grade, compatible optical modules is non-negotiable. For instance, ensuring your data center switches are equipped with reliable, high-performance modules guarantees that the encrypted data pipeline remains robust from end-to-end.
LINK-PP Transceivers: Engineered for Demanding Data Pipelines
For infrastructure that demands reliability, LINK-PP offers a range of high-quality, MSA-compliant optical transceivers. A model like the LINK-PP SFP-10G-SR is designed for high-performance 10 Gigabit Ethernet connections within data centers, providing the stable, high-bandwidth link that a busy FTPS server relies upon. Using trusted components like LINK-PP SFP+ modules helps ensure that your secure file transfer ecosystem is built on a foundation of hardware excellence, preventing physical layer issues from undermining your protocol-level security.
📑 Implementing FTPS: Best Practices
Use Explicit TLS (AUTH TLS): Favor this mode over Implicit SSL for better compatibility and flexibility.
Enforce Strong Encryption: Disable weak ciphers (like SSLv2, SSLv3) and obsolete algorithms. Mandate TLS 1.2 or higher.
Utilize Certificate-Based Authentication: Move beyond passwords. Use SSL/TLS certificates to authenticate servers and, optionally, clients for stronger secure data exchange.
Manage Firewall Rules Carefully: For explicit FTPS, you may need to configure firewalls to allow the FTPS data channel, which can use a range of ports. Consider using passive mode (PASV) extensively to simplify client-side firewall configuration.
Monitor and Audit Logs: Keep detailed logs of all FTPS connections and file transfer activities. This is essential for secure FTP server auditing and compliance.
📑 Conclusion
FTPS effectively bridges the gap between the ubiquitous FTP protocol and modern security necessities. By encrypting both commands and data, it provides a secure method for file transfer that is ideal for organizations needing to modernize existing FTP setups without starting from scratch.
Remember, a truly resilient system considers both software and hardware. Pairing a properly configured FTPS solution with reliable network hardware, such as LINK-PP optical transceivers, creates a comprehensive strategy for secure and fast file transfer. Whether you are evaluating how to set up FTPS or looking to optimize your current setup, focusing on both protocol security and physical infrastructure will ensure your data remains protected throughout its entire journey.
Ready to upgrade your file transfer security? Start by auditing your current FTP servers and exploring the FTPS options in your server software, and don’t forget to assess the health and capability of your underlying network hardware.
📑 FAQ
What is the main purpose of FTPS?
FTPS helps you send files safely over the internet. You use it to protect your data from hackers and keep your information private.
What do you need to use FTPS?
You need an FTPS server and an FTPS client. You also need a valid certificate for secure connections. Most programs set this up for you.
What makes FTPS different from regular FTP?
FTPS uses encryption to hide your files during transfer. Regular FTP does not protect your data, so anyone can see your files.
What types of files can you send with FTPS?
You can send any type of file with FTPS. You use it for documents, images, videos, or backups. FTPS keeps all your files safe.
What should you check before sending files with FTPS?
Always check for a valid certificate. Make sure your software is updated. Use strong passwords to keep your files secure.


