➡️ ROADM: Reconfigurable Optical Add-Drop Multiplexer Explained
What is ROADM?
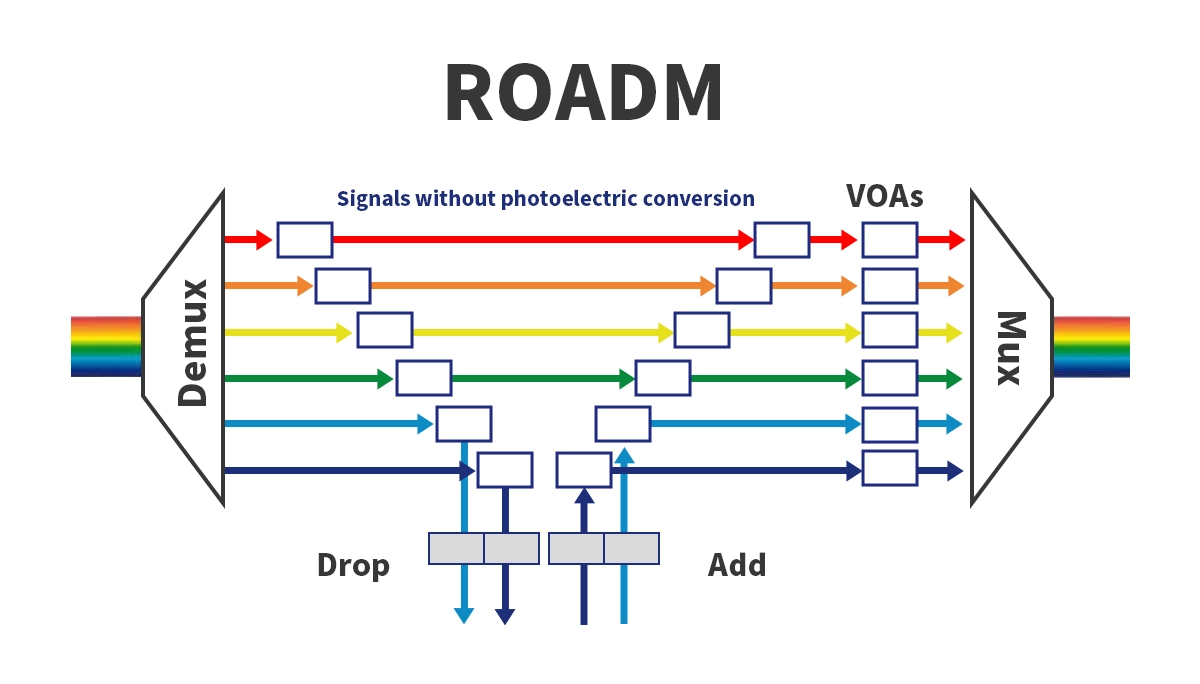
ROADM (Reconfigurable Optical Add-Drop Multiplexer) is a key component of optical transport networks (OTN / DWDM systems).
It enables adding (Add), dropping (Drop), or passing (Pass) optical channels remotely and flexibly without converting optical signals to electrical signals. Unlike fixed OADMs, ROADMs allow network operators to dynamically adjust wavelength paths via software or network control systems, improving network agility and reducing manual intervention.
Core Functions
Reconfigurable: Dynamically adjusts optical paths under software or network control.
Optical Add-Drop: Adds or removes specific wavelengths from a fiber link.
Multiplexer: Combines multiple wavelengths onto a single fiber for transmission.
This technology is central to DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) networks, widely deployed in Metro Networks (MAN), backbone optical networks, and 5G front-haul/backhaul optical transport.
➡️ How ROADM Works
The main component of a ROADM is the Wavelength Selective Switch (WSS). WSS allows specific wavelengths to be directed to Add, Drop, or Pass ports without converting optical signals to electrical form.
Add: Inject a local wavelength into the fiber.
Drop: Extract a wavelength from the fiber for local use.
Pass: Allow other wavelengths to continue on their path.
Remote control via SDN or network management systems allows operators to reconfigure optical paths dynamically, improving operational efficiency and reducing downtime.
➡️ Types of ROADMs
1. Fixed OADM vs Reconfigurable ROADM
Fixed OADM: Static wavelength assignment, suitable for simple or cost-sensitive networks.
Reconfigurable ROADM: Dynamic, software-controlled routing via WSS, ideal for modern DWDM/OTN networks.
2. 1-Degree and Multi-Degree ROADMs
1-Degree: Single-direction routing for simpler point-to-point scenarios.
Multi-Degree: Supports multiple directions in mesh or ring topologies, enabling complex network routing.
3. Advanced CDC-F ROADMs
Colorless: Any wavelength can be added/dropped at any port.
Directionless: Signals can route to any fiber direction.
Contentionless: Multiple channels of the same wavelength can be added/dropped simultaneously.
Flex-grid: Supports variable channel spacing for high-capacity modulation formats.
➡️ ROADM Applications
Metro and Backbone Networks: Flexible wavelength routing and capacity optimization.
OTN/DWDM Systems: Dynamic wavelength provisioning for fast deployment.
5G and Data Center Interconnects (DCI): Scalable and automated optical transport.
Disaster Recovery & Redundancy: Rapid rerouting for high network reliability.
➡️ ROADM vs Related Technologies
ROADM vs OADM: ROADM supports remote, dynamic reconfiguration; OADM is static.
ROADM vs DWDM Mux/Demux: Mux/Demux passively combines/separates channels; ROADM actively routes wavelengths.
ROADM vs Optical Cross-Connect (OXC): OXC switches circuits at the optical layer; ROADM focuses on wavelength-level routing.
ROADM and WSS: WSS enables selective wavelength switching, the functional core of a ROADM.
➡️ Advantages and Limitations
▷ Advantages:
High flexibility for software-defined wavelength routing.
Remote and automated management for simplified operation.
Eliminates OEO conversion, reducing latency and power consumption.
▷ Limitations:
Higher initial cost than fixed OADM.
Complex configuration requiring careful optical power and link planning.
Potential insertion loss requiring amplification and OSNR optimization.
➡️ Product and Market Overview
Leading vendors include Ciena, Cisco, Huawei, Infinera, ADVA, and Nokia, offering CDC-F and Flex-grid ROADMs.
LINK-PP provides DWDM-compatible optical transceivers designed to integrate seamlessly with ROADM systems.
Explore LINK-PP SFP/SFP+ DWDM Optical Modules for:
1000BASE-DWDM and 10GBASE-DWDM support
Up to 80 km transmission distance
ITU-T G.694.1 wavelength grid compliance
Compatibility with major ROADM-enabled network equipment
➡️ Key Takeaways
ROADM enables dynamic, remote wavelength management in DWDM networks.
Uses WSS-based selective switching for Add, Drop, and Pass functionality.
CDC-F ROADMs are ideal for flexible, high-capacity networks.
LINK-PP DWDM transceivers ensure plug-and-play compatibility with ROADM-based systems.


