
✅ Introduction
I/O modules (Input/Output modules) serve as the foundational interface between a control system and the outside world. Whether in industrial automation, embedded platforms, or modern network equipment, I/O modules manage how physical devices exchange signals, data, and control instructions with a central processor.
As networks transition to higher speeds and industrial systems adopt smarter, more distributed architectures, the performance and reliability of I/O modules directly influence system stability, latency, and data integrity. This article provides a complete technical overview suitable for engineers, integrators, and system designers.
✅ Definition: What Are I/O Modules?
An I/O module is a hardware component that enables a controller—such as a PLC, industrial PC, embedded SoC, or network processor—to communicate with external equipment. It handles:
Input (I): Receiving data or electrical signals from sensors or external devices
Output (O): Sending commands or electrical signals to actuators or network interfaces
Signal Conversion: Mapping between electrical/optical/logic levels
Protocol Handling: Supporting specific communication standards
In essence, I/O modules form the physical and logical bridge between a system’s internal computing resources and the operating environment.

✅ Why I/O Modules Are Critical
1. Signal Conditioning & Conversion
I/O modules often convert between:
Analog ↔ Digital
Low-voltage logic ↔ Industrial-level currents
Electrical ↔ Optical signals (e.g., in SFP/SFP+ modules)
This ensures accurate data acquisition and safe control output.
2. Electrical Isolation & Protection
Isolation barriers (magnetic, optical, or capacitive) protect the system from:
Isolation is crucial in industrial sites and high-speed network hardware.
3. Interface Expansion
I/O modules allow systems to scale by adding:
Ethernet ports
Serial channels
Sensor inputs
High-speed optical links
This modularity keeps systems flexible and future-proof.
4. Real-Time Operation Support
In automation and networking, latency-sensitive applications rely heavily on I/O responsiveness—particularly for:
Motion control
Factory automation
Data center switching
Telecom transmission
✅ Types of I/O Modules
▷ Digital I/O Modules
Used for switches, relays, discrete sensors.
Typical signals: 0/24 VDC, TTL, or dry contacts.
▷ Analog I/O Modules
Handle variable electrical signals.
Examples:
4–20 mA loops
0–10 V
Temperature probes (RTD/thermocouple)
▷ Communication I/O Modules
Expand interface protocols such as:
RS-232/485
CAN
Modbus
EtherCAT
PROFINET
▷ Network Interface I/O Modules
Used in switches, routers, servers, and telecom hardware. They include:
This category is key to modern networking infrastructure.
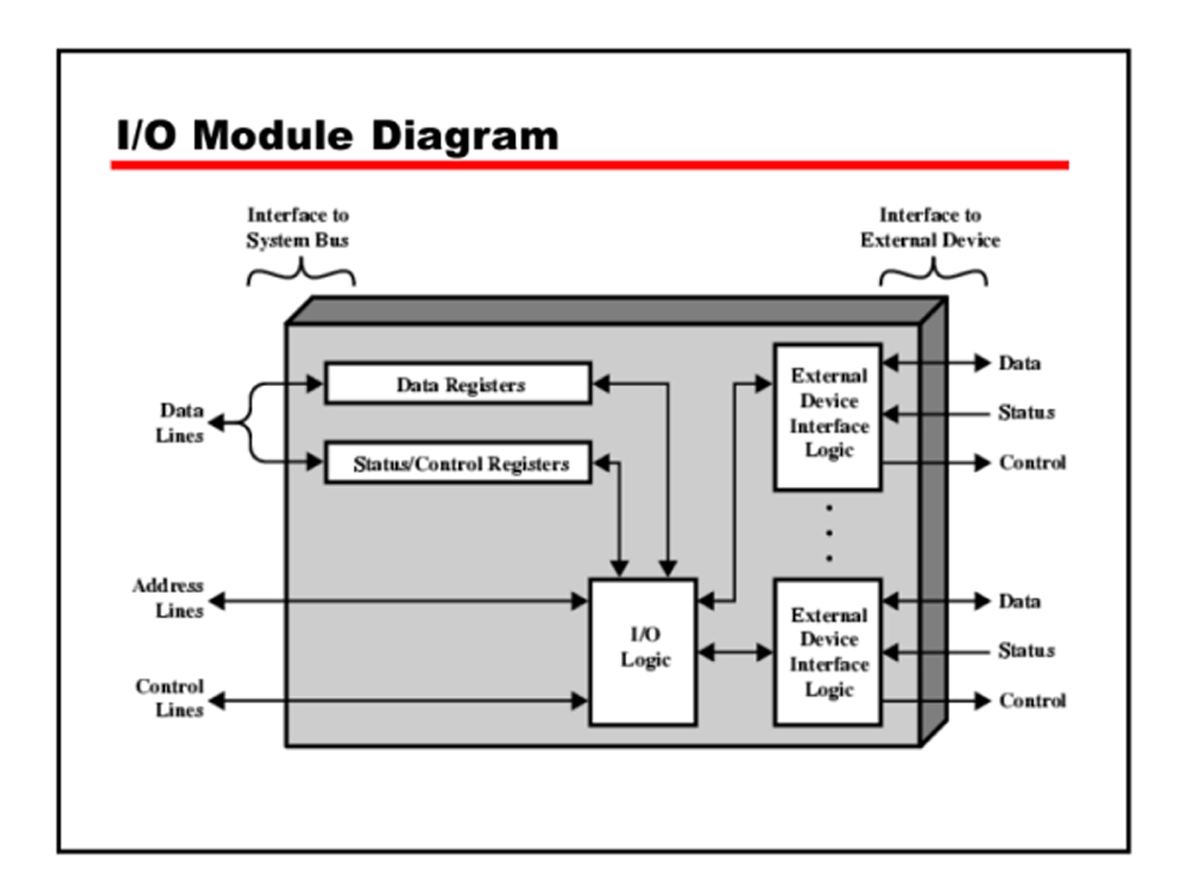
✅ I/O Modules in Networking Devices
In network equipment, I/O modules perform both physical-layer and data-link-layer functions. A typical network I/O subsystem includes:
Ethernet PHYs (signal conditioning, auto-negotiation, PCS/PMA)
SerDes lanes for high-speed serial transmission
Magnetics/RJ45 Magjack modules for copper interfaces
Optical transceiver modules (SFP/SFP+/QSFP+) for fiber connectivity
Why They Matter:
Stable clock recovery ensures low jitter
Accurate optical/electrical conversion supports long-distance links
High-speed interfaces reduce packet loss and latency
Hot-swapping enables flexible upgrades in data centers
✅ I/O Modules in Industrial Automation
Industrial systems rely heavily on reliable I/O to interact with physical processes. I/O modules connect PLCs or controllers to:
Sensors (pressure, temperature, vibration)
Actuators (motors, valves, relays)
Industrial networks (EtherNet/IP, Modbus TCP, PROFINET)
Key Requirements:
High isolation voltage
Deterministic timing
Support for hazardous-area standards
These characteristics ensure plant uptime and safety.
✅ Example Application: 10G SFP+ Modules as High-Speed Network I/O
In modern enterprise and telecom networks, 10G SFP+ modules are among the most widely used network I/O components. They function as removable, hot-swappable interfaces that convert high-speed electrical signals from the system’s SerDes into optical signals suitable for fiber transmission.
Common Applications
Ethernet switches
Data center servers
Storage systems
Wireless backhaul
Industrial IP networks
Why LINK-PP 10G SFP+ I/O Modules Fit These Scenarios

LINK-PP’s 10G SFP+ transceivers offer:
Reliable signal integrity with low jitter and low BER
Compatibility with mainstream switch ASICs
Industrial-grade temperature options for harsh environments
Flexible distances (from 300 m SR to 10 km/40 km LR/ER)
Stable optical performance + robust EMI design
These modules serve as a key part of a network’s I/O subsystem, enabling fast, stable, and long-distance fiber connectivity.
✅ Benefits of Using High-Quality I/O Modules
Improved system reliability
Higher data throughput
Reduced noise interference
Extended communication distance
Increased design flexibility
Lower maintenance and replacement costs
Whether in factory automation or cloud infrastructure, well-designed I/O modules help ensure consistent system performance.
✅ Conclusion
I/O modules are fundamental building blocks for any system that needs to interact with the physical world or external networks. From digital and analog modules in industrial equipment to high-speed SFP+/RJ45 network interfaces in modern Ethernet hardware, I/O modules determine how accurately, safely, and efficiently data travels between systems.
As networks scale to multi-gigabit speeds and industrial systems adopt smarter architectures, selecting reliable I/O solutions—such as properly engineered 10G SFP+ modules—becomes essential for long-term stability and performance.


