🛑 What Is an MCU (Microcontroller Unit)?
An MCU (Microcontroller Unit) is a compact computing system on a single chip that integrates a CPU, non-volatile program memory (Flash), volatile memory (RAM), and a wide range of peripherals, including GPIO, ADC, timers, PWM, UART, I²C, and SPI.
MCUs are optimized for deterministic, low-power control tasks and serve as the “brains” of millions of embedded devices.
From smart wearables to industrial controllers, MCUs enable real-time signal processing, sensor interfacing, and deterministic decision-making with minimal power and cost.
🛑 MCU Architecture — Core Components
CPU Core & Instruction Pipeline
Modern MCUs typically use highly efficient, low-power cores such as ARM Cortex-M, RISC-V, or proprietary 8- or 16-bit cores. These cores deliver deterministic instruction execution, ideal for real-time embedded tasks.
Memory System
An MCU integrates all key memory elements on-chip:
Flash/ROM — stores firmware
SRAM — holds runtime variables, stacks, buffers
Optional EEPROM — retains configuration data
Integrated Peripherals & Interfaces
MCUs bundle essential interfaces to directly control hardware:
Peripheral | Function |
|---|---|
GPIO | Switches, LEDs, sensors, interrupt inputs |
ADC | Convert analog sensor signals to digital values |
Timers / PWM | Timing control, motor drivers, and lighting |
UART / SPI / I²C | Communication with modules & sensors |
DMA | Offloads data movement from the CPU |
Watchdog | Reliability and safe recovery mechanism |
🛑 Why Engineers Choose MCUs
Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
Low power | Sleep modes, fast wake-up, battery-friendly |
Low cost | Single-chip architecture reduces BOM |
Real-time control | Deterministic interrupt response for precise timing |
Small footprint | Ideal for compact product designs |
Rich ecosystem | Mature toolchains, libraries, RTOS support |
MCUs excel in low-power, cost-sensitive, reliably timed applications.
🛑 MCU vs MPU vs SoC
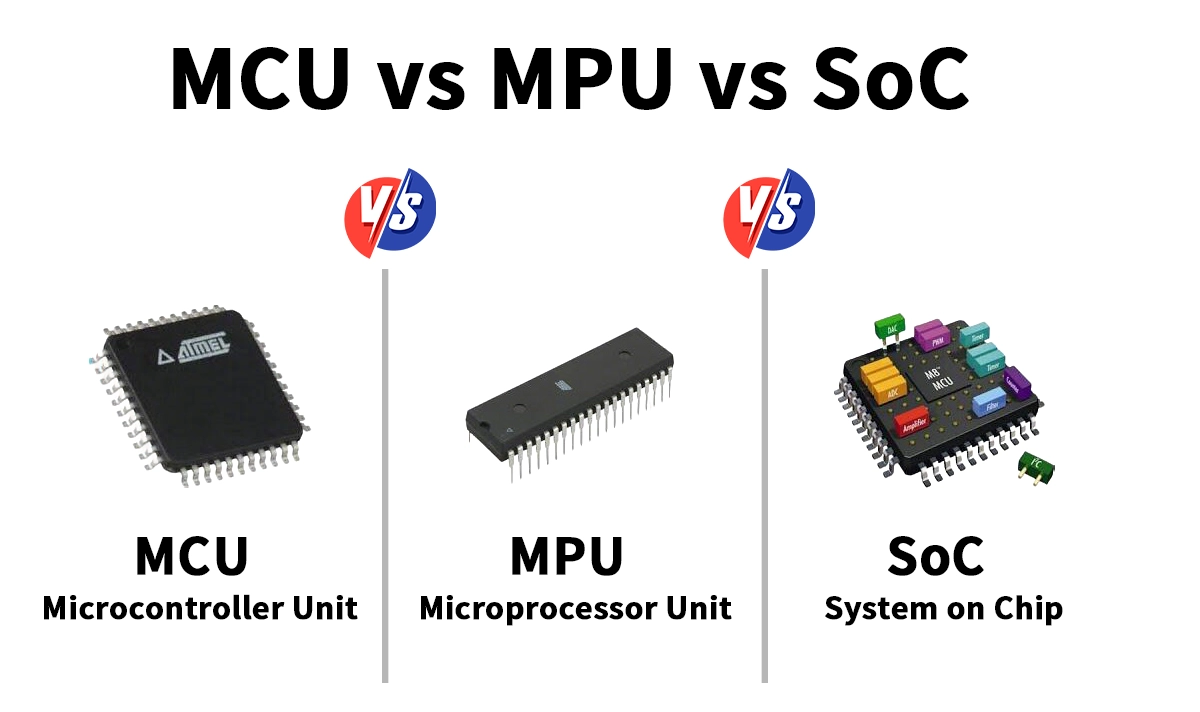
Feature | MCU | MPU | SoC |
|---|---|---|---|
Primary use | Real-time control | High-performance OS | Converged functions |
Memory | On-chip | External DRAM required | Mixed-core + complex IP |
OS | Bare-metal / RTOS | Linux / Android | May run Linux |
Use cases | IoT, control, industrial | UI, networking, smart gateways | Mobile, edge, automotive compute |
Simplified rule:
Choose MCU for real-time & low-power control; choose MPU/SoC for rich OS & heavy compute.
🛑 Common MCU Applications
Consumer & IoT
Smart plugs, home appliances
Wearables & health devices
Low-power wireless sensors
Automotive & Mobility
Body control modules
Sensor fusion nodes
EV battery controllers
Industrial & Edge Control
PLC-like control functions
Automation sensors & actuators
Energy meters & IIoT gateways
Networking & Connectivity Devices
Many MCU-based devices integrate Ethernet, PoE, and serial networking, often paired with MagJacks for reliable PHY-to-RJ45 signaling.
🛑 Design Considerations for MCU-Based Ethernet Devices
Peripheral & Interface Planning
Select MCUs with hardware peripherals supporting:
Ethernet MAC
DMA for efficient packet handling
External PHY interfacing
PHY + Magnetics Requirement
MCU Ethernet designs require:
MAC (MCU integrated)
External PHY
LAN Magnetics (transformer & EMI choke)
RJ45 connector
Why Integrated RJ45 Connectors Help
RJ45 Magetics connectors simplify:
Ethernet magnetics integration
EMI/EMC compliance
Board routing & footprint
PoE implementation
🛑 MCU Selection Checklist
Core performance (MIPS, clock, pipeline depth)
Flash & RAM capacity
ADC resolution & channel count
UART / SPI / I²C availability
Power modes & wake-up latency
Security features (secure boot, crypto engines)
RTOS compatibility & ecosystem maturity
Popular MCU families include STM32, NXP LPC, PIC / AVR, TI MSP430, and Espressif ESP32 / ESP32-C3.
🛑 Development Workflow Best Practices
Write firmware in C or C++ with static analysis and MISRA-style checks
Use SWD/JTAG debugging and real-time trace
Implement watchdog timers & brown-out detection
Plan secure firmware update / OTA where needed
Validate EMC compliance early in design
🛑 Conclusion
MCUs are the foundation of modern embedded control — compact, efficient, and versatile.
In networked systems, pairing an MCU with a PHY and integrated RJ45 MagJack enhances signal integrity, reduces BOM complexity, and accelerates product certification.
For robust Ethernet hardware in embedded devices, explore LINK-PP’s industrial-grade MagJack portfolio.


